What is an Optoisolator?
What is an Optoisolator?
Optoisolator Definition
An optoisolator (also known as an optocoupler or optical isolator) is defined as an electronic component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits using light.
Working Principle
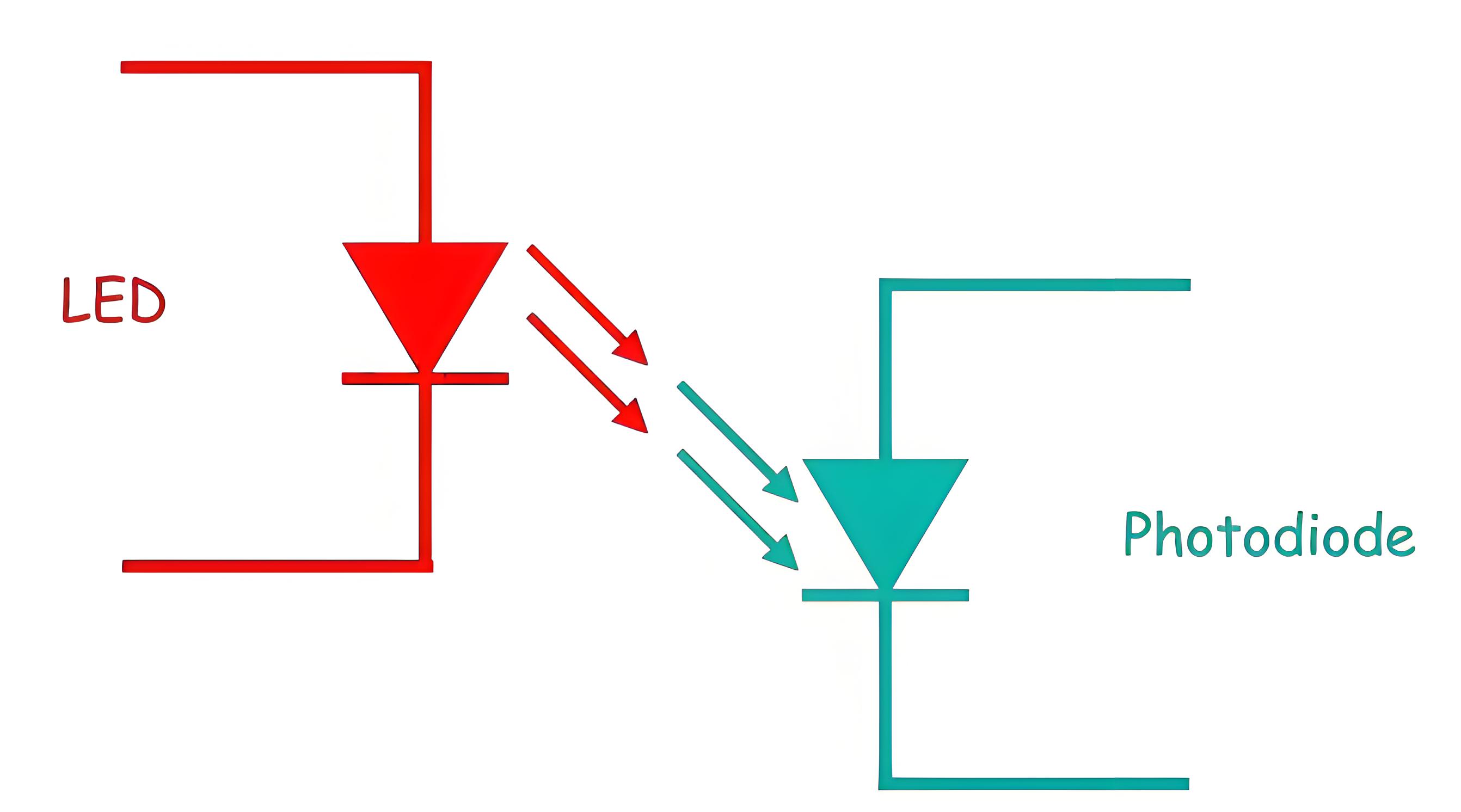
The input circuit consists of a variable voltage source and an LED. The output circuit consists of a phototransistor and a load resistor. The LED and the phototransistor are enclosed in a light-tight package to prevent external interference.
When the input voltage is applied to the LED, it emits infrared light proportional to the input signal. This light crosses the dielectric barrier and hits the reverse-biased phototransistor. The phototransistor converts the light into electric current, which flows through the load resistor, creating an output voltage. This output voltage is inversely proportional to the input voltage.
The input and output circuits are electrically isolated by the dielectric barrier, which can withstand high voltages up to 10 kV and voltage transients with speeds up to 25 kV/μs. This means that any surge or noise in the input circuit will not affect or damage the output circuit.
Electrical Isolation
Optoisolators use a dielectric barrier to provide electrical isolation between input and output circuits, protecting against high voltages and voltage transients.
Optoisolator Parameters and Specifications
Current transfer ratio (CTR)
Isolation voltage
Input-output capacitance
Switching speed
Types of Optoisolators
LED-photodiode
LED-LASCR
lamp-photoresistor pairs
Applications
Power electronics
Communication
Measurement
Safety
Advantages
They provide electrical isolation between input and output circuits.
They prevent high voltages or currents.
They prevent high voltages or currents from damaging or interfering with the low-voltage or low-current circuits.
They enable communication between circuits that have different voltage levels, ground potentials, or noise characteristics.
They can handle high switching speeds and data rates.
Disadvantages
They have limited bandwidth and linearity compared to other isolation methods, such as transformers or capacitors.
They have temperature and aging effects that can degrade their performance over time.
They have variations in the current transfer ratio and input-output capacitance that can affect their accuracy and stability.
Conclusion
Optoisolators are useful devices that can transfer electrical signals between isolated circuits by using light. They have many advantages, such as providing electrical isolation, preventing high voltages, removing electrical noise, and enabling communication between incompatible circuits. They also have some disadvantages, such as limited bandwidth, aging effects, variations in performance, and switching speed. Optoisolators have various parameters and specifications that determine their suitability for different applications. Optoisolators are widely used in power electronics, communication, measurement, safety, and other fields.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













