What is the Torque Equation of DC Motor?
What is the Torque Equation of DC Motor?
Torque Definition
Torque in a DC motor is defined as the force’s tendency to cause or change rotational motion.
When a DC machine is loaded either as a motor or as a generator, the rotor conductors carry current. These conductors lie in the magnetic field of the air gap.
Thus each conductor experiences a force. The conductors lie near the surface of the rotor at a common radius from its center. Hence torque is produced at the circumference of the rotor and rotor starts rotating. The term torque as best explained by Dr.
Huge d Young is the quantitative measure of the tendency of a force to cause a rotational motion, or to bring about a change in rotational motion. It is in fact the moment of a force that produces or changes a rotational motion.
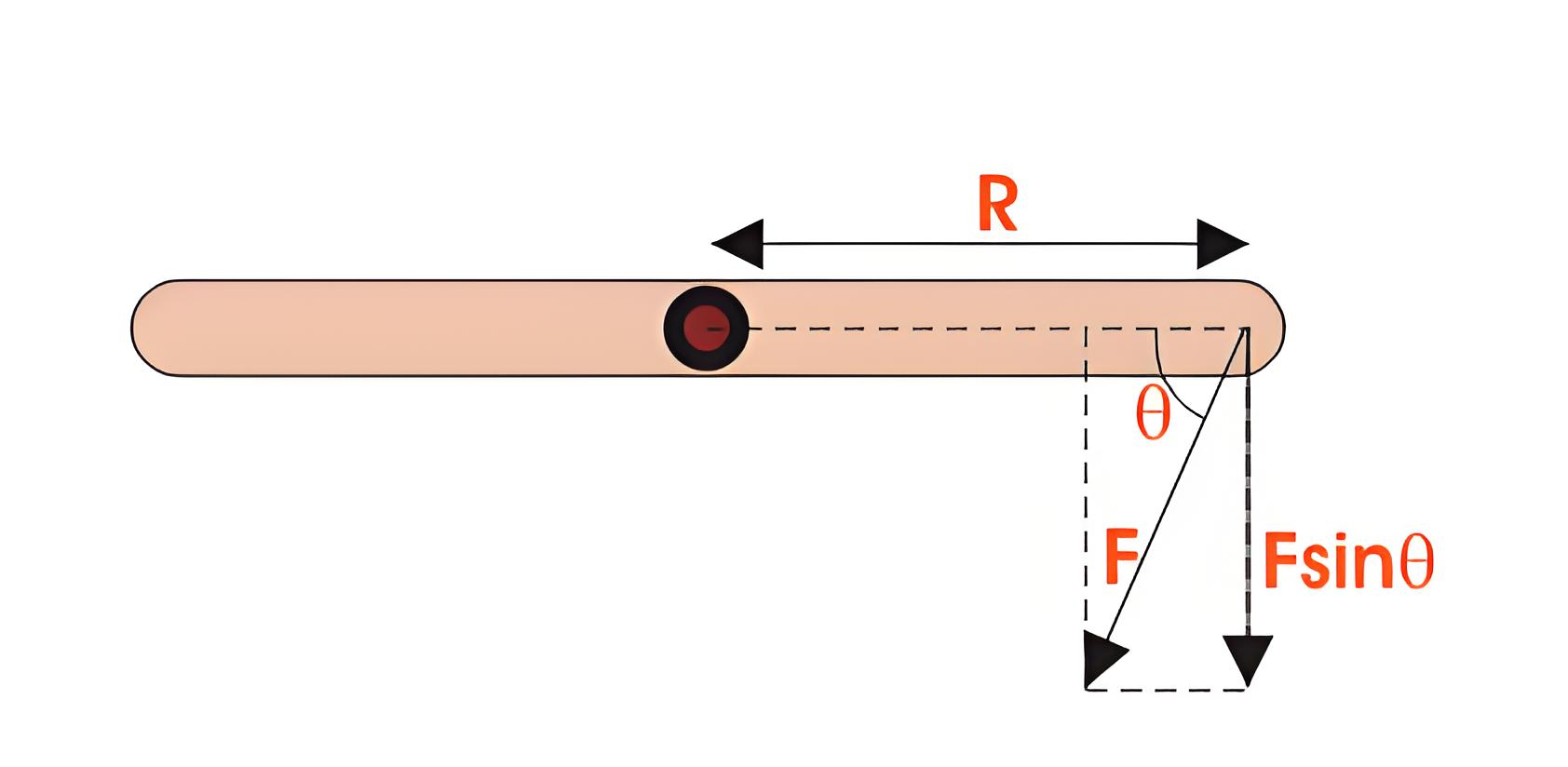
The equation of torque is given by,
Where, F is force in linear direction.
R is radius of the object being rotated,
and θ is the angle, the force F is making with R vector
A DC motor is a rotational machine where torque is a crucial parameter. Understanding the torque equation of a DC motor is essential for determining its operating characteristics.
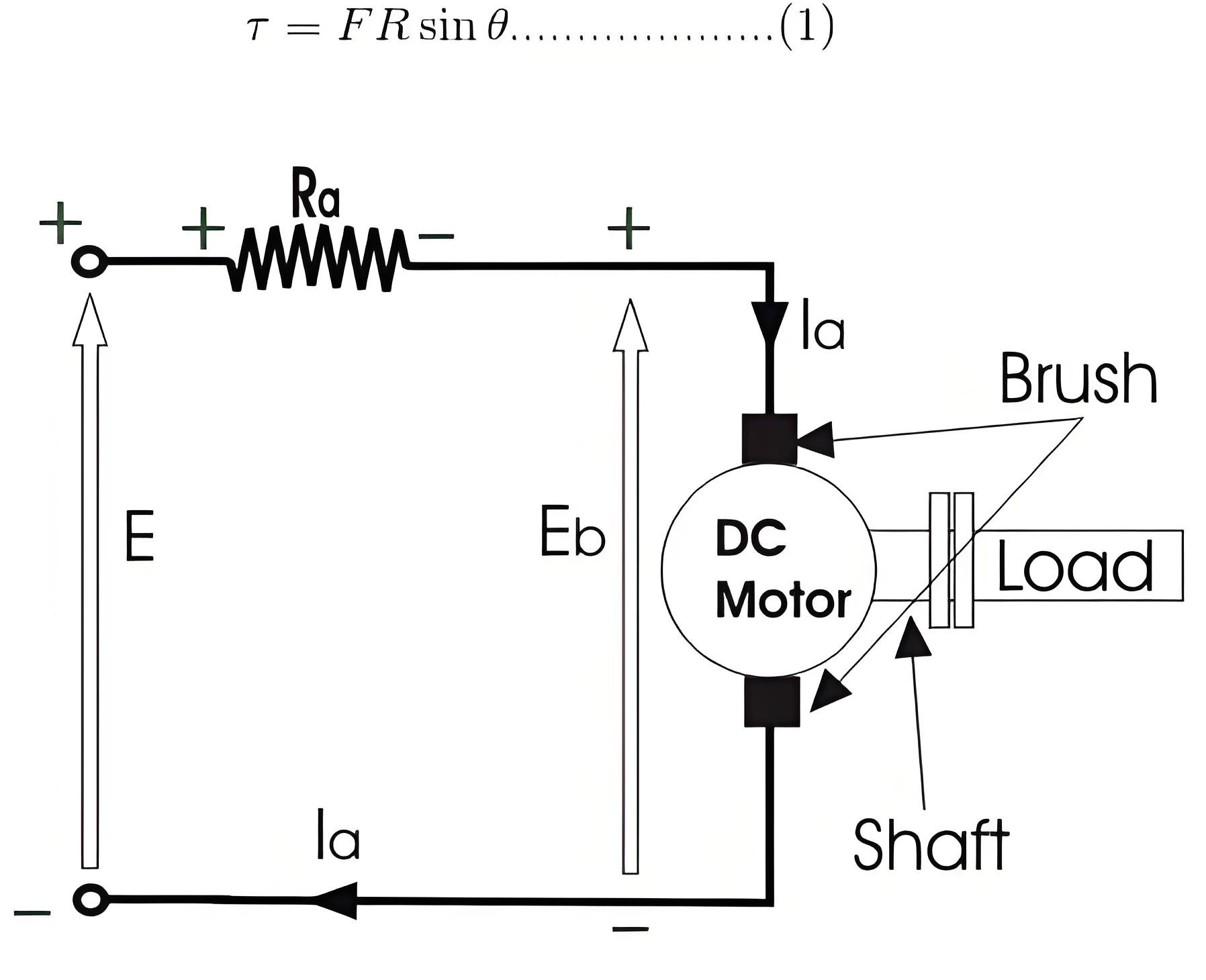
To establish the torque equation, let us first consider the basic circuit diagram of a DC motor and its voltage equation.Referring to the diagram beside, we can see, that if E is the supply voltage, Eb is the back emf produced and Ia, Ra are the armature current and armature resistance respectively then the voltage equation is given by,
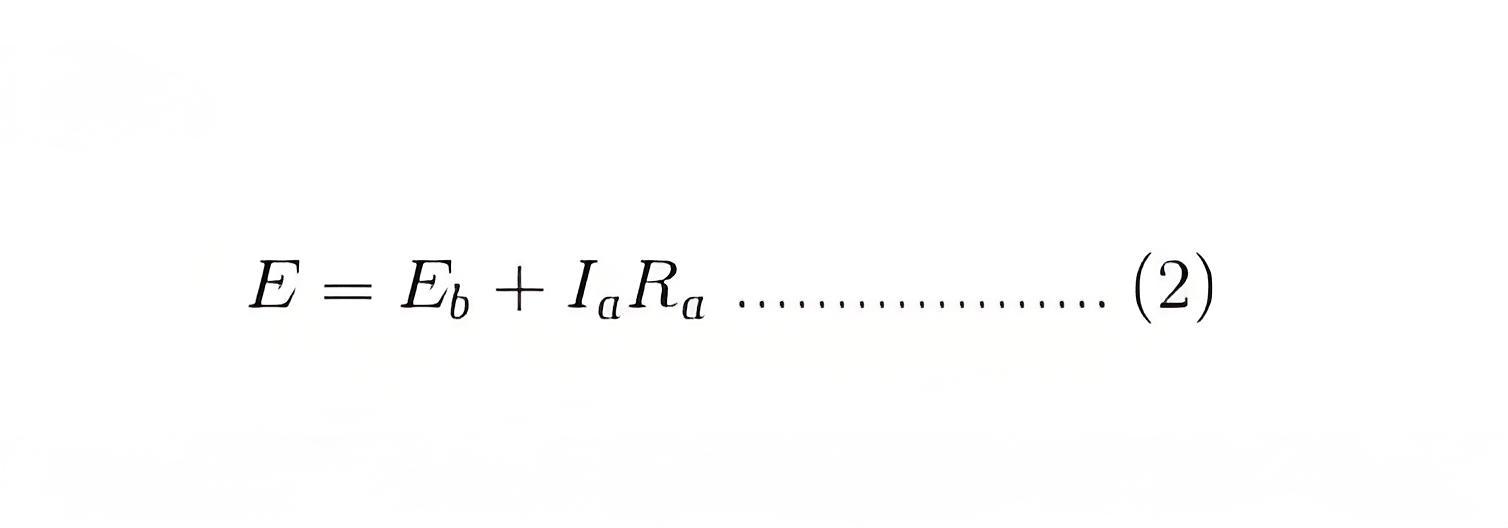
To derive the torque equation of a DC motor, we multiply both sides of the voltage equation by Ia.
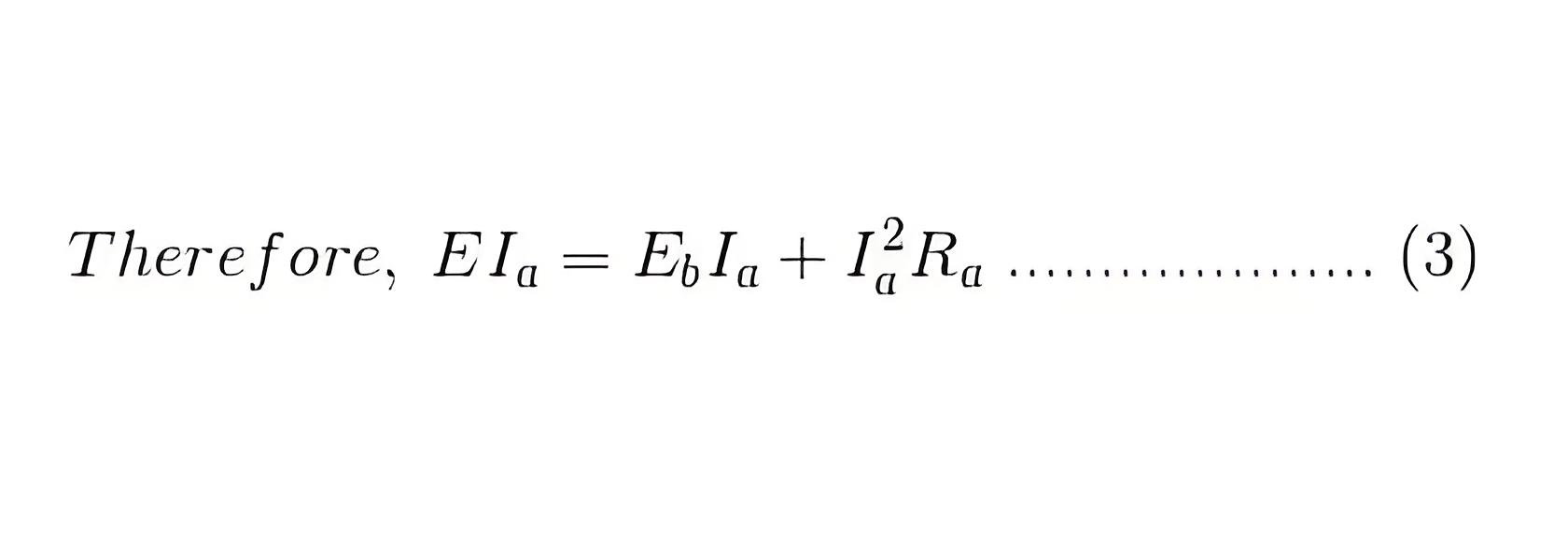
Now Ia2.Ra is the power loss due to heating of the armature coil, and the true effective mechanical power that is required to produce the desired torque of DC machine is given by,
The mechanical power Pm is related to the electromagnetic torque Tg as,
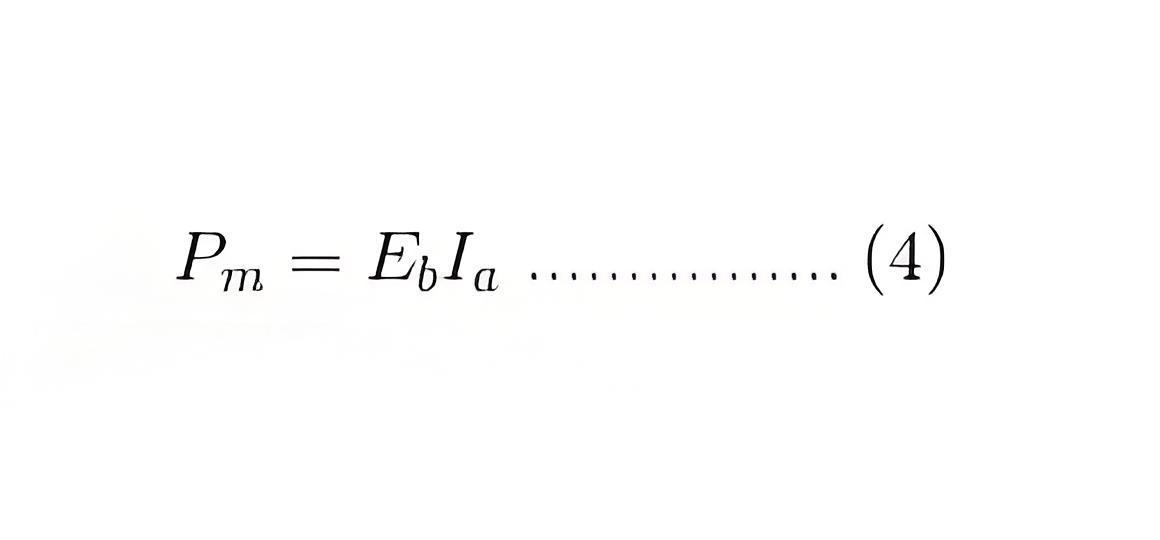
Where, ω is speed in rad/sec.
Now equating equation (4) and (5) we get,
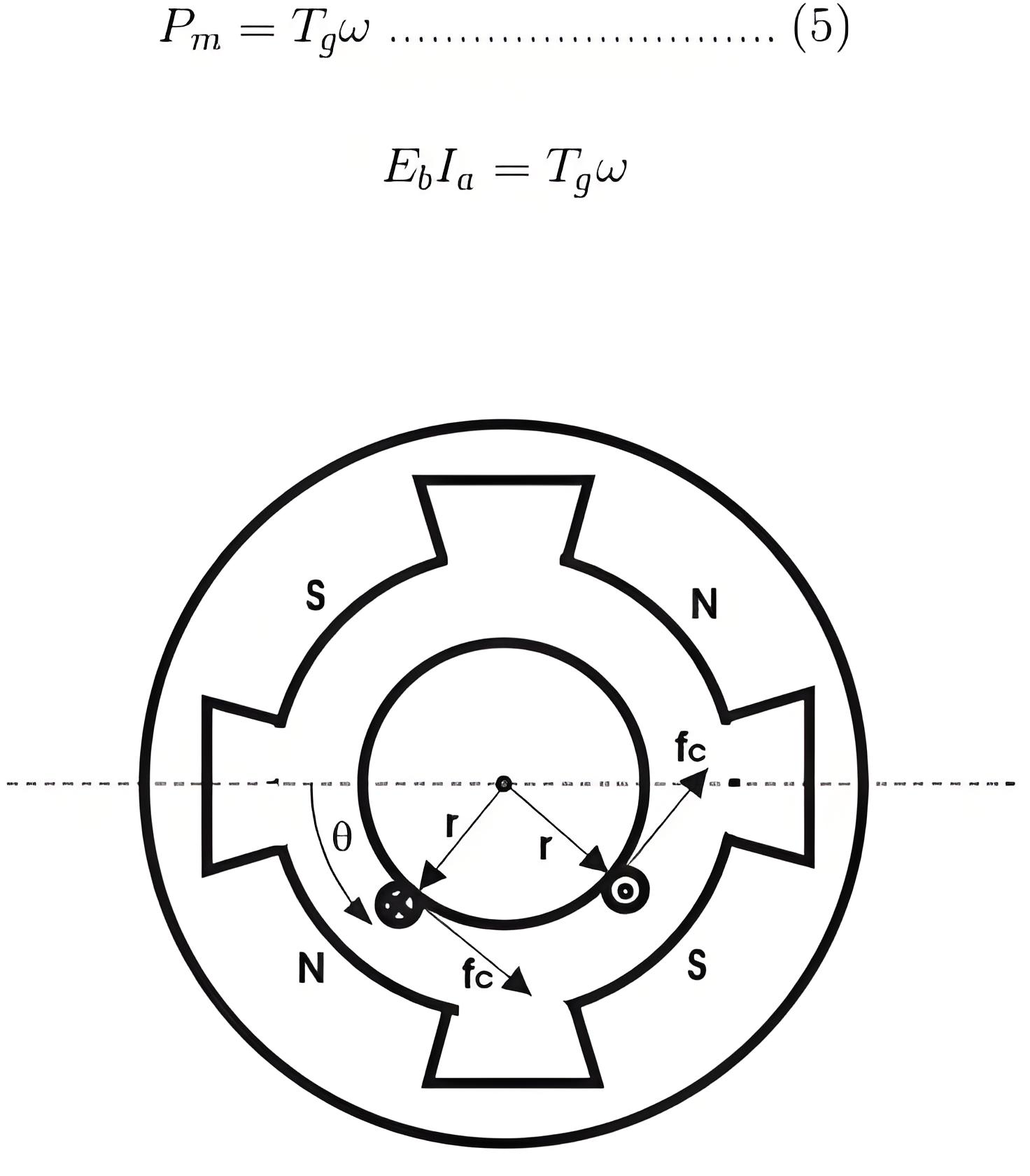
Now for simplifying the torque equation of DC motor we substitute.
Where, P is no of poles,
φ is flux per pole,
Z is no. of conductors,
A is no. of parallel paths,
and N is the speed of the DC motor.
Substituting equation (6) and (7) in equation (4), we get:
The obtained torque is known as the electromagnetic torque of a DC motor. By subtracting mechanical and rotational losses, we get the mechanical torque.
Therefore,
This is the torque equation of DC motor. It can be further simplified as:
Which is constant for a particular machine and therefore the torque of DC motor varies with only flux φ and armature current I a.
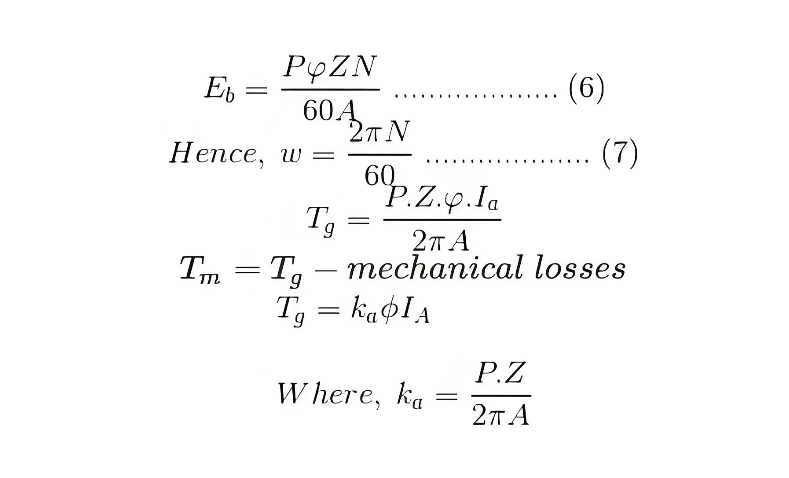
The Torque equation of a DC motor can also be explained considering the figure below
Current/conductor I c = Ia A

Therefore, force per conductor = fc = BLIa/A
Now torque Tc = fc. r = BLIa.r/A
Hence, the total torque developed of a DC machine is,
This torque equation of DC motor can be further simplified as:
Which is constant for a particular machine and therefore the torque of DC motor varies with only flux φ and armature current I a.
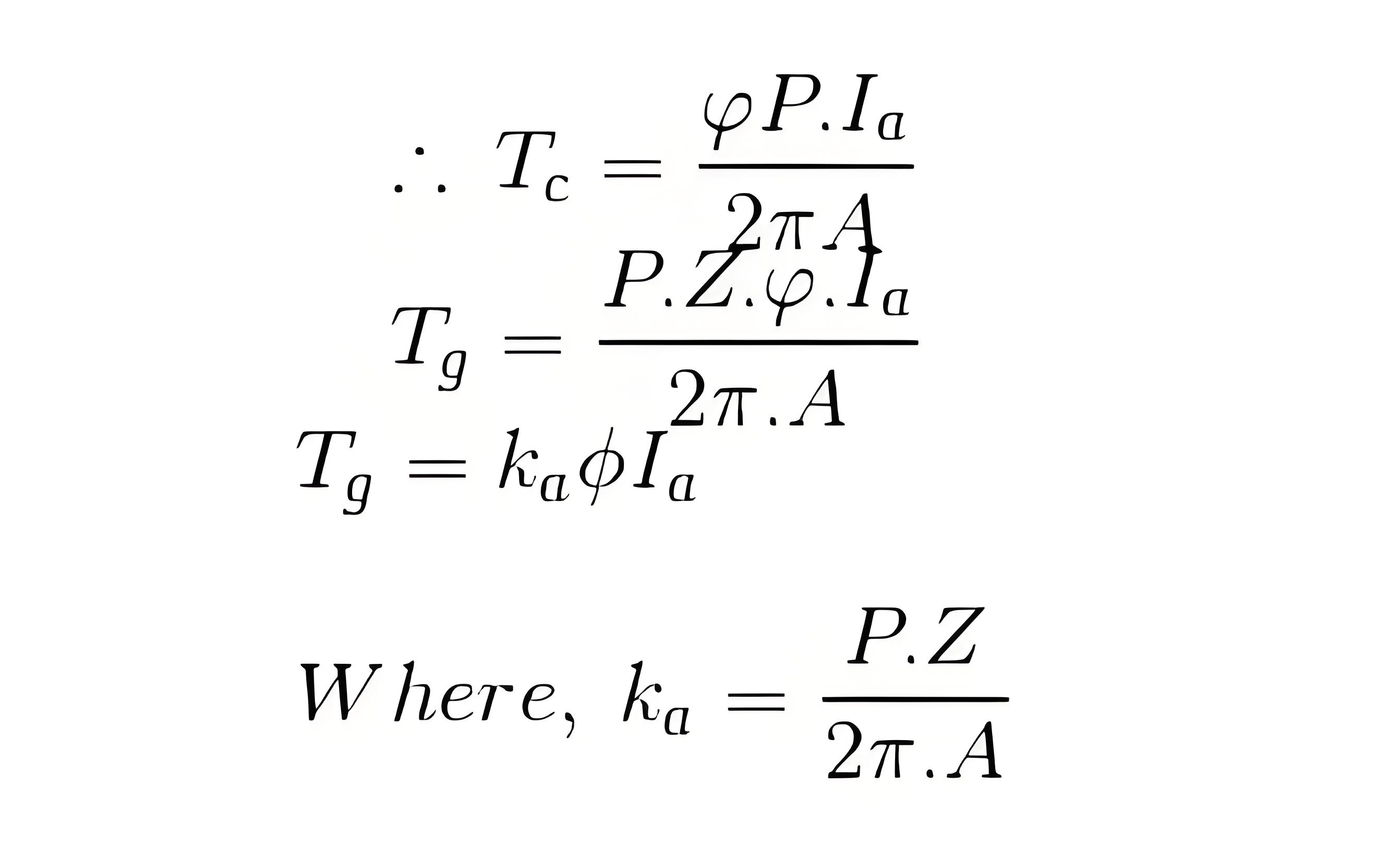
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













