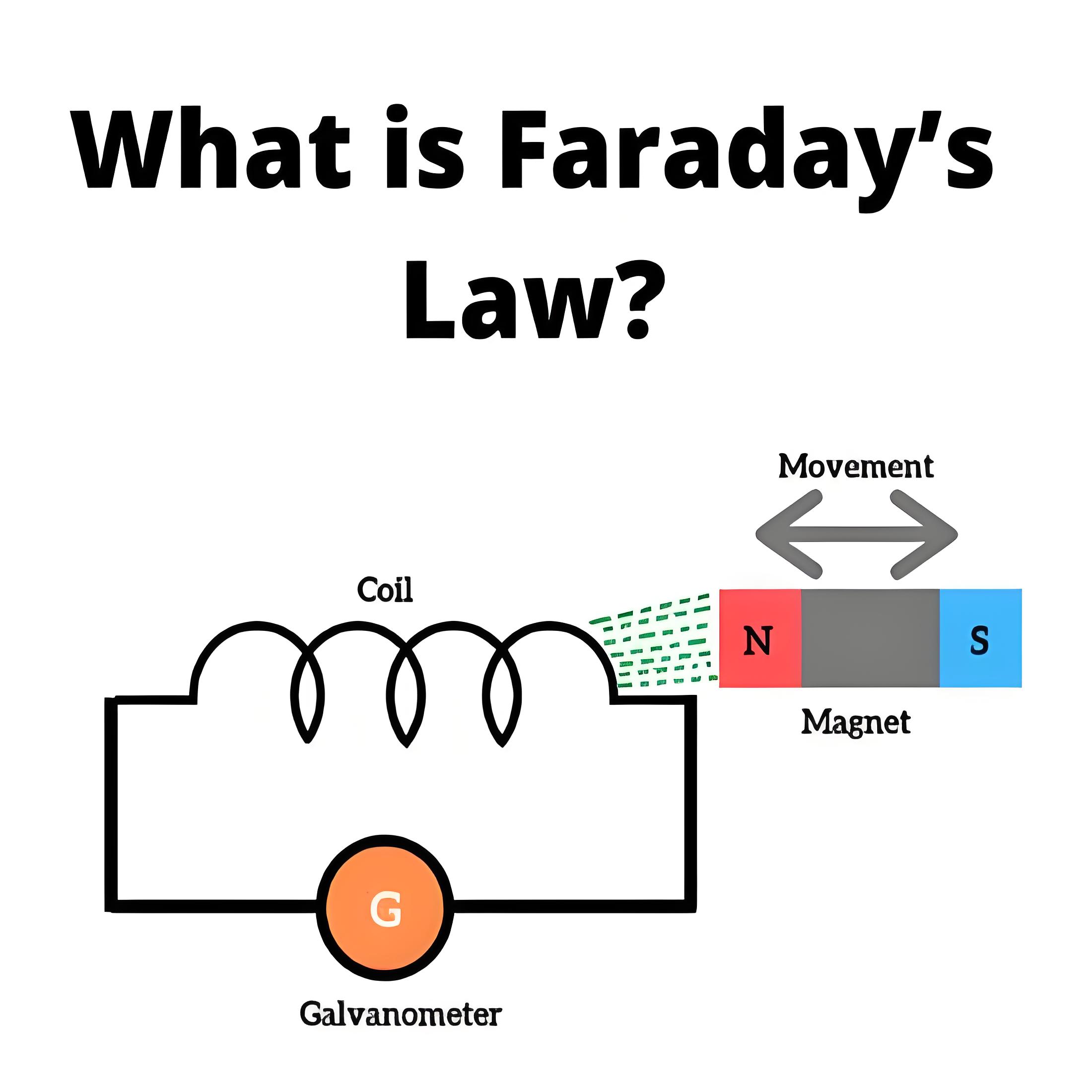
What is are Resistivity Laws?
What is are Resistivity Laws?
Resistivity Definition
Resistivity is defined as a material’s property that opposes the flow of electrical current.
Factors Affecting Resistance
Resistance depends on length, cross-sectional area, material nature, and temperature.
Unit of Resistivity
The unit of resistivity is Ω-m in the MKS system and Ω-cm in the CGS system.
First Law of Resistivity
Resistance increases with the length of the substance.
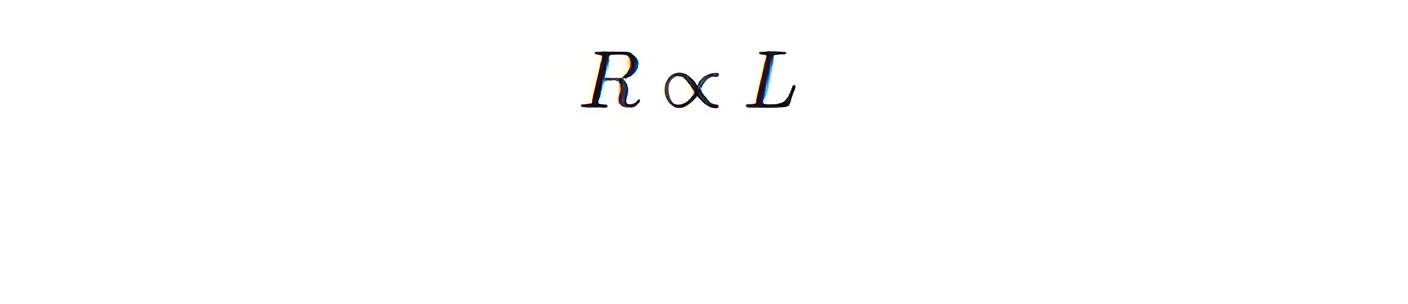
Second Law of Resistivity
Resistance decreases with a larger cross-sectional area.
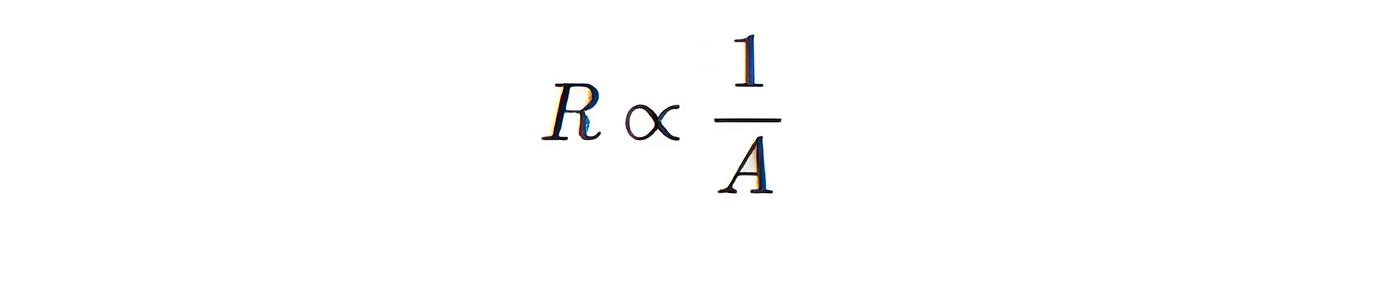
Resistivity
That means resistance of a material of unit length having unit cross – sectional area is equal to its resistivity or specific resistance. Resistivity of a material can alternatively be defined as the electrical resistance between opposite faces of a cube of unit volume of that material.
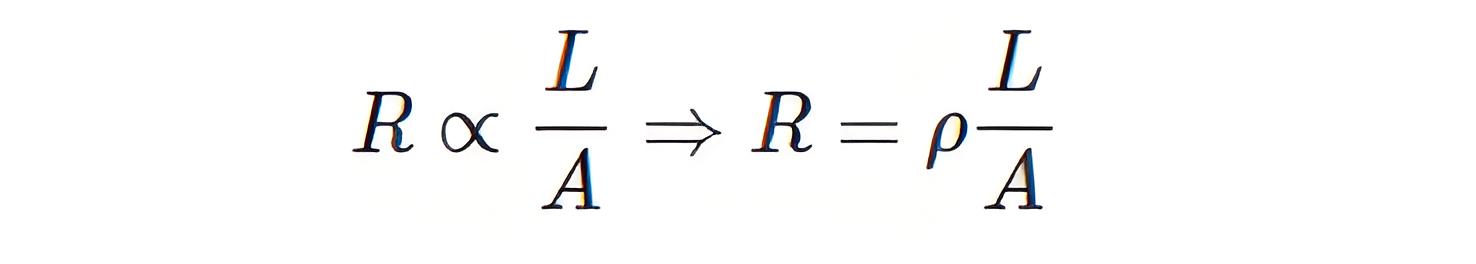
Third Law of Resistivity
The resistance of a substance is directly proportional to the resistivity of the materials by which the substance is made.
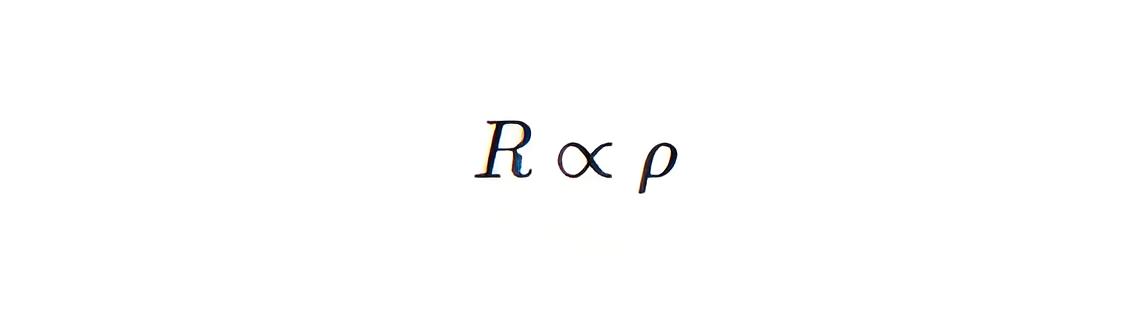
Fourth Law of Resistivity
Temperature affects the resistance of a substance.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.