What is Faraday’s Law?
What is Faraday’s Law?
Faraday’s Law Definition
Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction is defined as the principle that a changing magnetic field within an electric circuit produces an electromotive force.
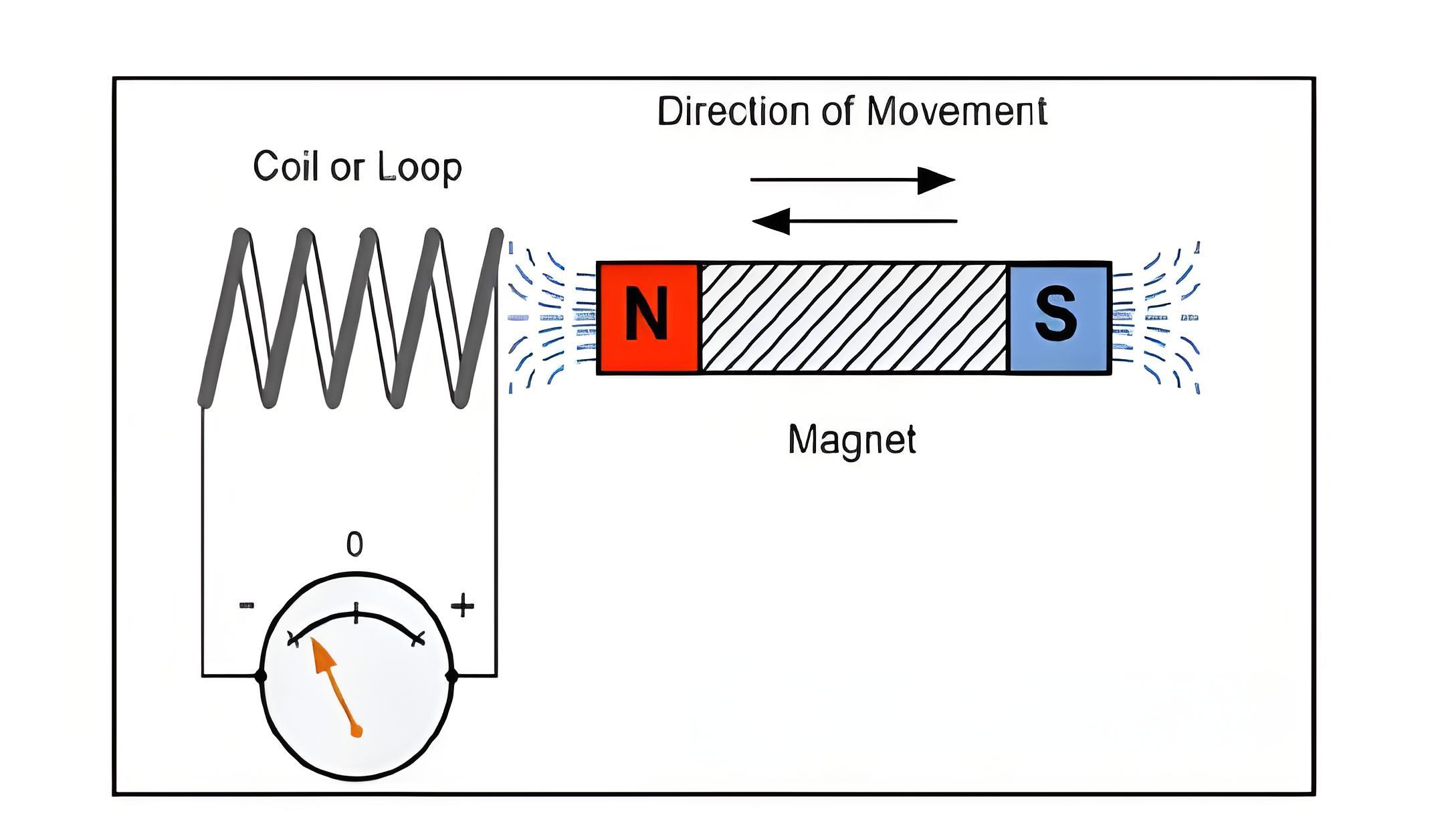
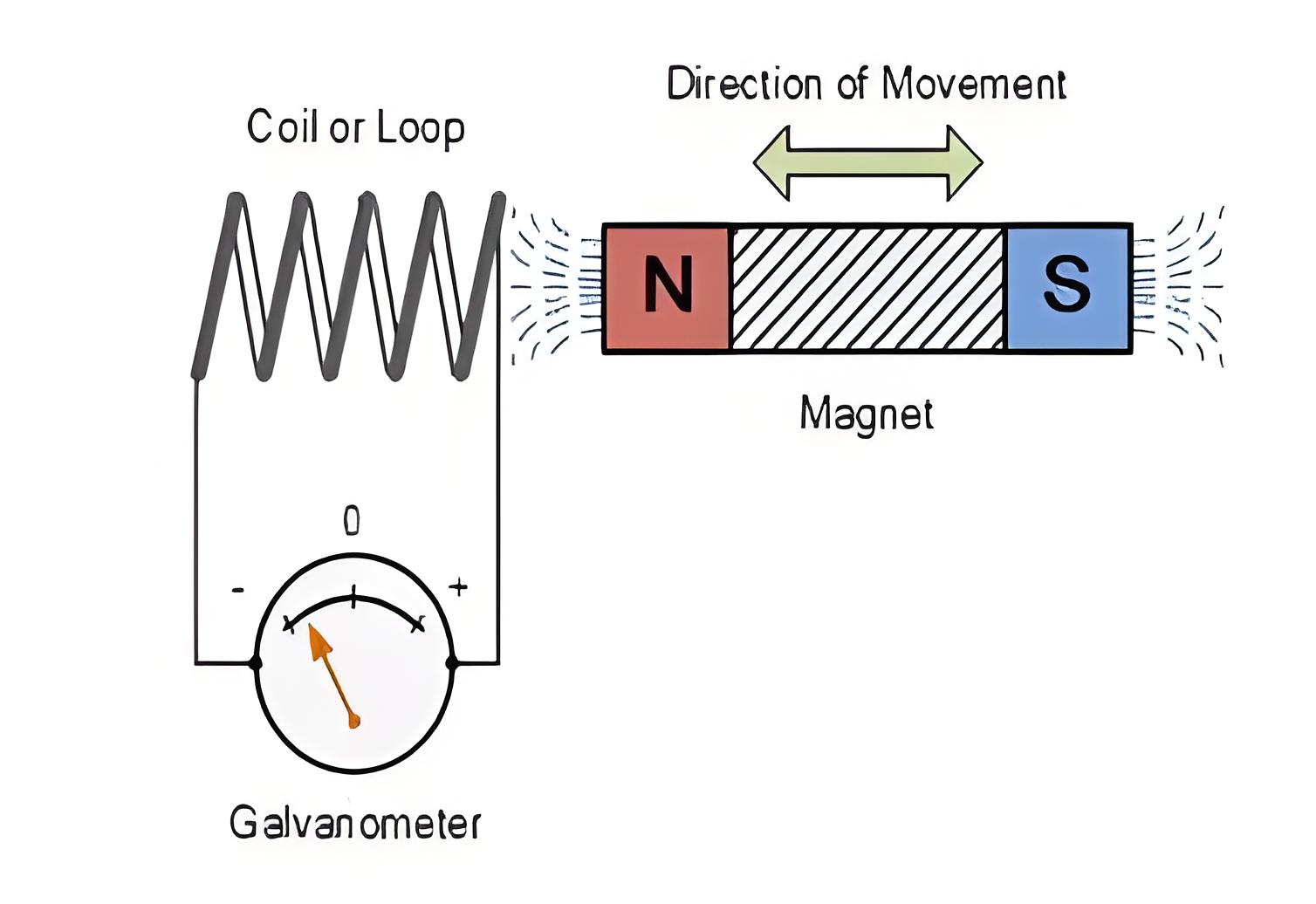
First Law
Faraday’s first law states that any change in the magnetic environment of a coil induces an EMF, known as induced EMF, and, if the circuit is closed, induces current as well.
Method to change the magnetic field:
By moving a magnet towards or away from the coil
By moving the coil into or out of the magnetic field
By changing the area of a coil placed in the magnetic field
By rotating the coil relative to the magnet
Second Law
Faraday’s second law clarifies that the induced EMF’s magnitude equals the rate at which the magnetic flux linkage through the coil changes.
Enhancing EMF
Increasing the coil’s number of turns, the magnetic field strength, or the relative motion speed between the coil and the magnet can amplify the induced EMF.
Faraday Law Formula
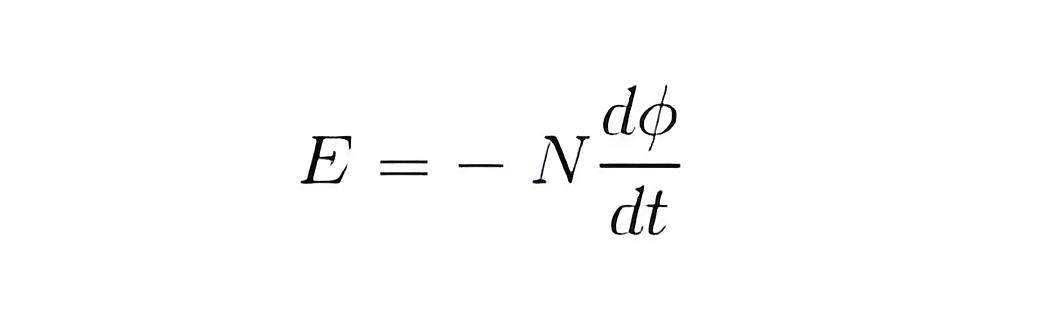
Flux Φ in Wb = B.A
B = magnetic field strength
A = area of the coil
Applications and Impact
Power transformers function based on Faraday’s law
The basic working principle of the electrical generator is Faraday’s law of mutual induction.
Induction cookers
It is also used in musical instruments like an electric guitar, electric violin, etc.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













