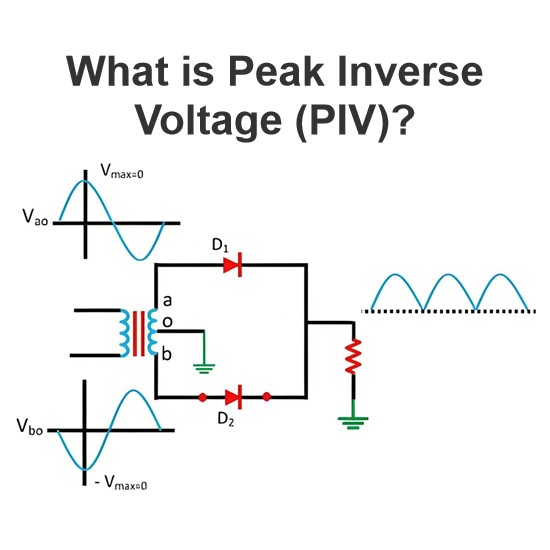
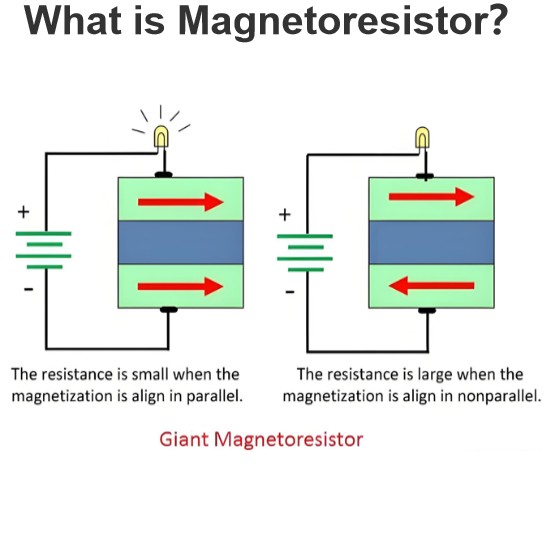
What is electrical knowledge?
Electrical knowledge covers a broad set of theoretical and practical skills related to the basic principles of electricity, circuit design, operation and maintenance of power systems, and the working principles of electronic devices. Electrical knowledge is not limited to academic theory, but also includes skills and experience in practical applications. Here is an overview of some of the core areas of electrical knowledge:
Basic concept
Circuit theory: includes the basic components of the circuit (such as power supply, load, switch, etc.), as well as the basic laws of the circuit (such as Ohm's law, Kirchhoff's law).
Basic laws of electricity: Ohm's law, Kirchhoff's law (KVL and KCL), Joule's law, etc.
Circuit analysis
Direct current circuit (DC) : Analyzes the behavior of components such as current, voltage, resistance, inductance, and capacitance in a DC circuit.
AC circuit (AC) : Study the sine wave, phase difference, impedance, inductive reactance and capacitive reactance in AC circuit.
Electronics
Semiconductor devices: including diodes, transistors (BJT, MOSFET, etc.), integrated circuits, etc.
Analog electronics: involves the design of analog circuits such as amplifiers, oscillators, and filters.
Digital electronics: including the design of logic gates, flip-flops, counters, microprocessors and other digital circuits.
Electric power system
Transmission and distribution system: involving high-voltage transmission lines, substations, distribution networks, etc.
Power equipment: including generators, transformers, circuit breakers, relays, etc.
Power quality: such as harmonic analysis, voltage fluctuations, frequency stability, etc.
Motors and drives
Motor principle: DC motor, AC motor (induction motor, synchronous motor), servo motor, etc.
Motor control: including frequency converter, soft starter, etc.
Control system
Automatic control: PID control, feedback control system, servo system, etc.
PLC programming: Application of programmable logic controller (PLC).
Electromagnetic field and wave
Electromagnetic theory: Maxwell equations, electromagnetic wave propagation, antenna principle, etc.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) : electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression, shielding technology, etc.
Computer hardware and embedded systems
Computer architecture: CPU, memory, bus, etc.
Embedded system: application of MCU, Arduino and other development platforms.
Power electronics
Converter: AC/DC, DC/AC, DC/DC, AC/AC converter.
Inverter: Inverter design for renewable energy sources such as solar and wind energy.
Safety and standards
Electrical safety: electrical protection, grounding protection, lightning protection, etc.
Electrical standards: such as IEC, IEEE, ANSI and other relevant standards and specifications.
Test and measurement
Instrument: multimeter, oscilloscope, signal generator, etc.
Data acquisition: data logger, sensor interface, etc.
Renewable energy
Solar energy: Design and installation of photovoltaic systems.
Wind energy: the working principle and technology of wind turbines.
Information Technology and Communications
Communication principle: digital communication, wireless communication, etc.
Network technology: local area Network, wide area network, Internet of Things (IoT), etc.
Software tool
CAD tools: For circuit design and simulation.
Programming language: such as Python, MATLAB and other applications in electrical engineering.
Sum up
Electrical knowledge is an interdisciplinary field that covers a wide range of topics from basic theory to advanced applications. Mastering electrical knowledge requires not only theoretical learning, but also practical experience through experiments, internships and projects.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.