What is Lenz's Law?
What is Lenz's Law?
Lenz’s Law Definition
Lenz’s Law is defined as the principle stating that the induced current in a conductor will flow in a direction such that the magnetic field it creates opposes the change in the magnetic field that produced it.
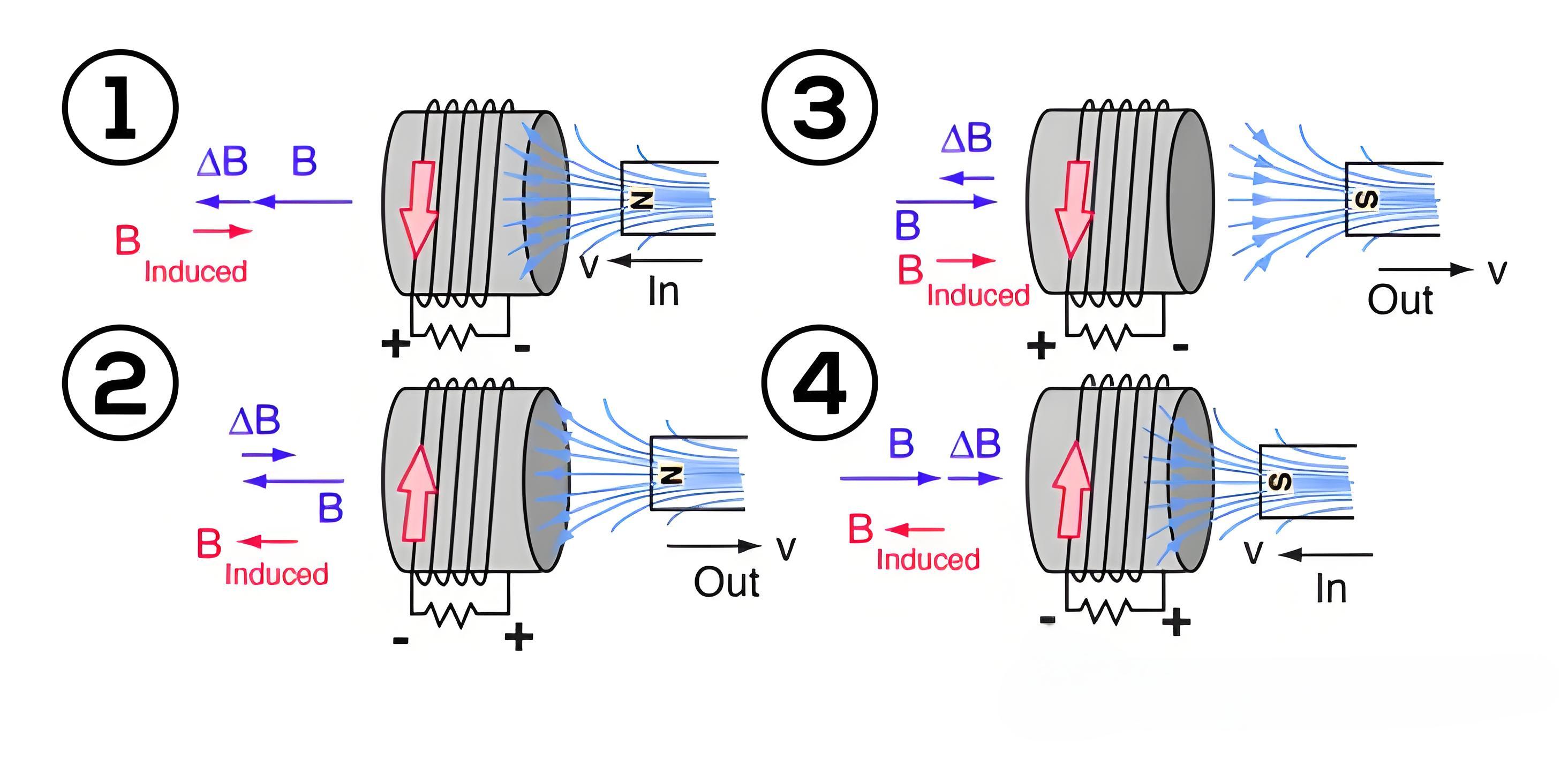
Induction Principle
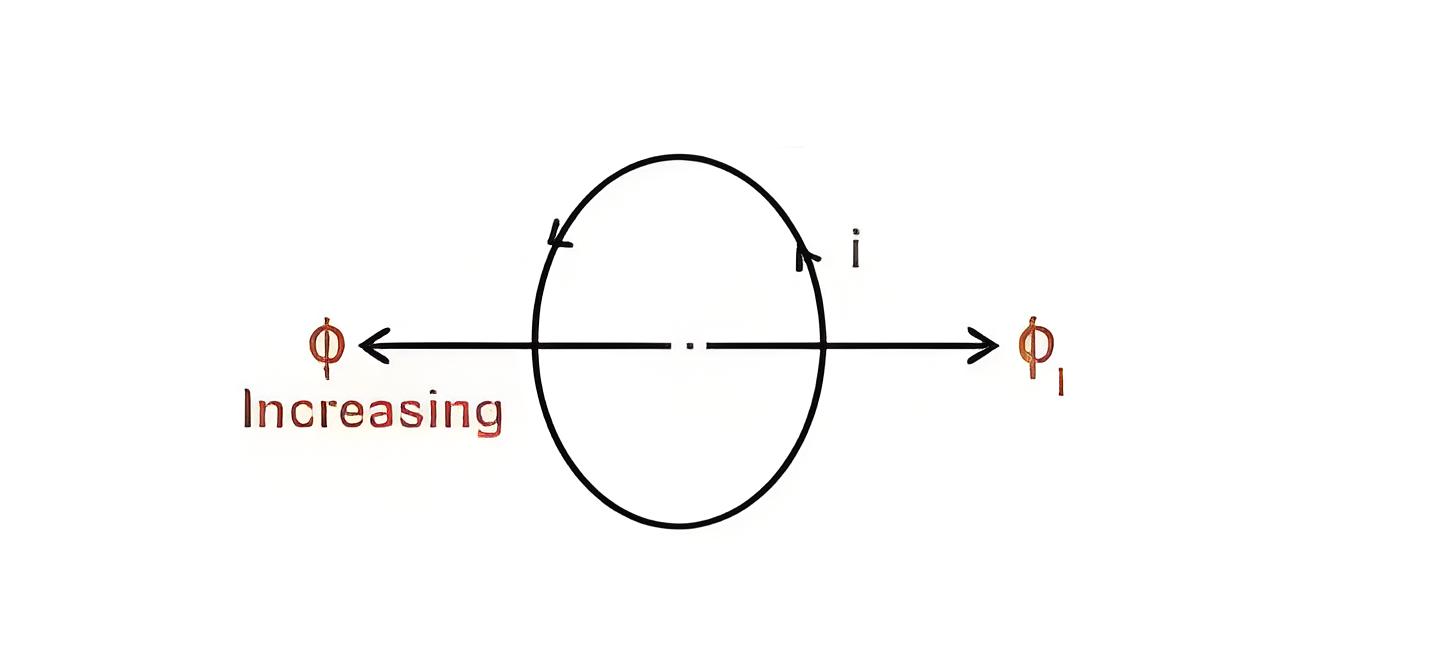
If the magnetic flux Ф linking a coil increases, the direction of current in the coil will be such that it will oppose the increase in flux and hence the induced current will produce its flux in a direction as shown below (using Fleming’s right-hand thumb rule)
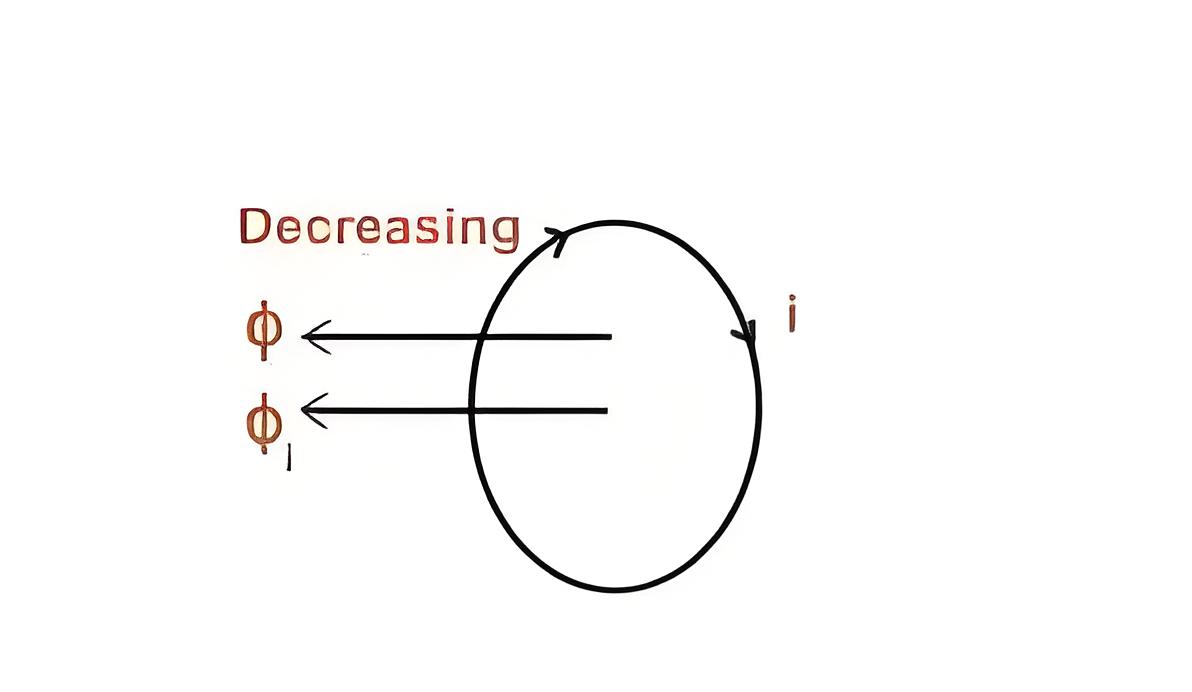
If magnetic flux Ф linking a coil is decreasing, the flux produced by the current in the coil is such, that it will aid the main flux and hence the direction of current is as shown below.
Formula Significance
The negative sign in Faraday’s law formula represents the opposing direction of the induced EMF relative to the change in magnetic flux.
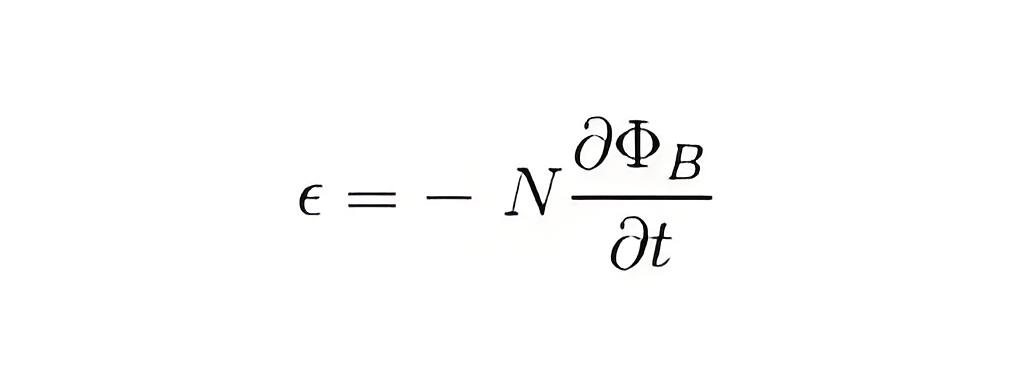
ε = Induced emf
δΦB = change in magnetic flux
N = No of turns in coil
Application Insight
Lenz’s law can be used to understand the concept of stored magnetic energy in an inductor.
This law indicates that the induced emf and the change in flux have opposite signs which provide a physical interpretation of the choice of sign in Faraday’s law of induction.
Lenz’s law is also applied to electric generators.
Lenz’s law is also used in electromagnetic braking and induction cooktops.
Conservation and Reaction
Demonstrates the principles of energy conservation and Newton’s third law by ensuring the magnetic and kinetic interactions balance out.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













