| Brand | Wone |
| Model NO. | 40.5KV 72.5KV 126KV 252KVseries high voltage earthing switch |
| Rated voltage | 40.5kV |
| Series | JW6(8) Series |
Description:
JW6/8 series high voltage Grounding Switch is composed of three single poles and operating mechanism. Each single pole consists of a base, a pillar insulator and a conducting rod. The conductive rod is installed on the base, and the static contact is installed on the top of the pillar insulator.
The operating mechanism drives the conductive rod to rotate upward from the horizontal position through the transmission element, and is stuck or inserted into the static contact to realize the closing of the grounding switch, and the opening process is the opposite.
Main Features:
The product structure is simple and reasonable, easy to assemble, transport, install and debug.
The conductive rod is made of high-strength alloy profiles with good electrical conductivity, high mechanical strength, light weight, strong anti-corrosion ability and long service life.
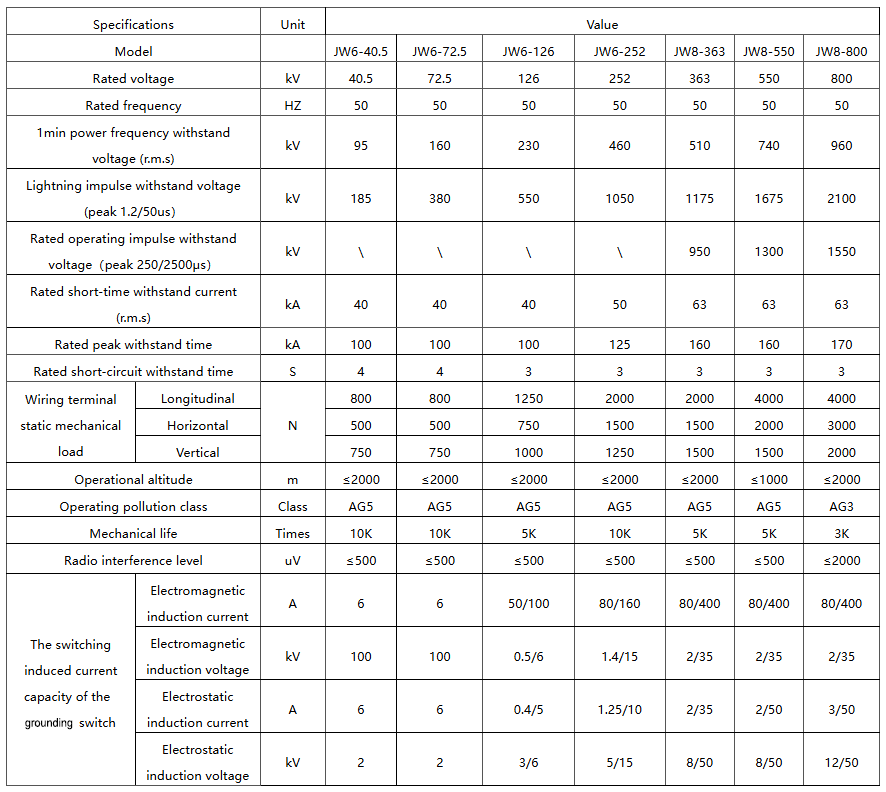
Technical parameter:
How is the indoor high-voltage AC grounding switch electrically tested?
Insulation Resistance Test: Use an insulation resistance tester to measure the insulation resistance of the grounding switch. The insulation resistance value should meet the product standards and relevant electrical codes. Generally, for indoor high-voltage AC grounding switches, the insulation resistance should be in the range of several gigohms or more to ensure good insulation performance during operation and prevent leakage accidents.
Loop Resistance Test: Measure the loop resistance of the grounding switch using a dedicated loop resistance tester to check if the contact points are in good condition. The loop resistance value should fall within the specified range. If the loop resistance is too high, it may cause significant heating when current flows through the grounding switch, affecting its normal operation.
Grounding Performance Check: Ensure that the grounding connection is reliable and that the grounding resistance meets the requirements. If the grounding resistance is too high, it may prevent the current from being effectively discharged to the ground during a fault, thus failing to provide adequate protection for maintenance personnel and equipment.



