| Brand | Pingalax |
| Model NO. | AC EV Chargers |
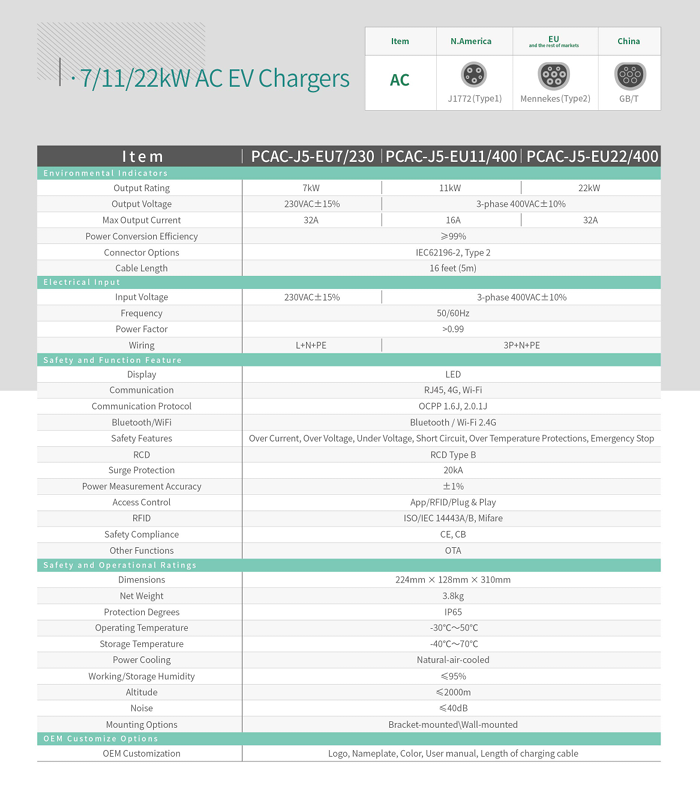
| Mounting type | Wall-mounted |
| Rated Output Rating | 11KW |
| Output Voltage | 400VAC士10% |
| Max Output Current | 16A |
| Connector Options | CCS2 |
| Cable Length | 5m |
| Methods of Communication | 4G |
| Series | AC EV Chargers |

What is the difference between DC charging and AC charging?
Charging principle:
AC charging:AC charging is through connecting to an external AC power source (such as 220V AC from a household socket). The on-board charger converts AC into DC and then charges the battery pack of the electric vehicle.In this process, the on-board charger plays a key conversion role, adjusting the external AC to DC suitable for battery charging.
DC charging:DC charging directly inputs external DC into the battery pack of the electric vehicle without going through the conversion of the on-board charger.The charging pile itself has a built-in power conversion module that can convert the AC from the power grid into DC and output it to the vehicle.
Charging speed:
AC charging:The charging speed is usually relatively slow. Generally speaking, the power of AC charging piles is relatively low. Commonly seen are 3.5kW, 7kW, etc.Taking an electric vehicle with a battery capacity of 50kWh as an example, when charging with a 7kW AC charging pile, it may take 7 to 8 hours to fully charge.
DC charging:The charging speed is much faster. The power of DC charging piles is usually higher. Commonly seen are 30kW, 60kW, 120kW or even higher.Also taking an electric vehicle with a battery capacity of 50kWh as an example, when using a 60kW DC charging pile, the battery may be fully charged in about 1 hour.






