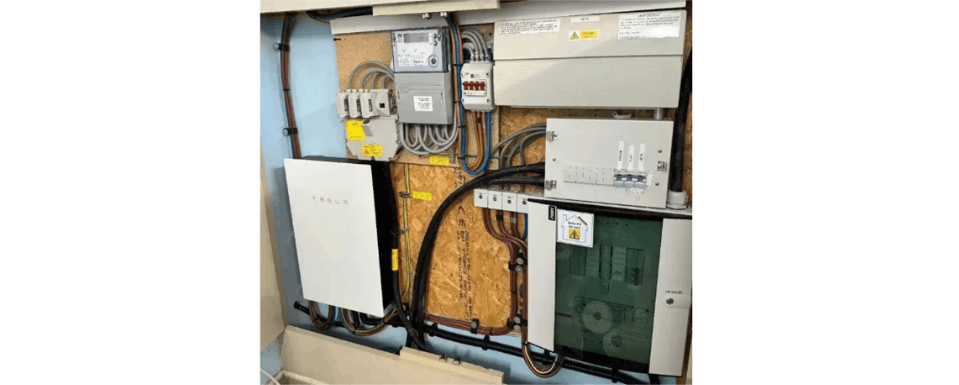
What are the impacts of environmental factors on household energy storage systems and what are the related maintenance strategies?
Felix Spark
06/26/2025
Hey there! I'm an electrical engineer specializing in Failure and Maintenance. I've dedicated my career to ensuring the seamless operation of electrical systems. I excel at diagnosing complex electrical failures, from malfunctioning industrial motors to glitchy power distribution networks. Using state - of - the - art diagnostic tools and my in - depth knowledge, I pinpoint issues quickly. On this platform, I'm eager to share my insights, exchange ideas, and collaborate with fellow experts. Let's work together to enhance the reliability of electrical setups.

What are the reasons for low insulation at the low-voltage side of a dry-type transformer?
Hi everyone, I’m Felix, and I’ve been working in electrical equipment fault repair for 15 years.Over these years, I’ve traveled across factories, substations, and distribution rooms all over the country, troubleshooting and repairing all kinds of electrical equipment. Dry-type transformers are among the most common devices we deal with.Today, a friend asked me:“What does it mean when the low-voltage side of a dry-type transformer has low insulation resistance?”Great
Felix Spark
07/01/2025

What are the causes of dry-type transformers burning out during operation?
1 Fault PhenomenonI am engaged in front - line fault maintenance work, and recently encountered problems with dry - type transformers. Dry - type transformers have a simple structure, are convenient for transportation, and easy for maintenance. They are widely used in power distribution places with relatively high environmental protection requirements. Because of their good fire - resistance, they can be installed in load - center areas to reduce voltage loss and power loss.The property manageme
Felix Spark
07/01/2025

Method for Automatic Isolation of Customer Equipment Faults by Load Switches in Distribution Networks
1 OverviewDistribution network safety has long been under - addressed, with its automation lagging substation automation . Using 10 kV intervals of existing substations to set line section points meets future grid needs . Configuration of distribution switches, section switches, and protection must match substation outgoing - line protection for reliability. Fault isolation, self - healing, and restoration are key to distribution automation .Scholars have studied smart distribution network fault
Felix Spark
06/30/2025

What You Need to Know About Load Switch Malfunctions
Hey there, I’m Blue — been working as an electrical engineer for more than 20 years now.I’ve spent most of my career designing circuit breakers, managing transformers, and helping power companies solve all sorts of electrical system challenges.Today, a friend from Southeast Asia asked me:"What are the common faults of load switches?"Great question! So let’s break it down in simple terms — no fancy jargon, just real-world stuff you might actually see on the job or during maintenance.First, What E
Master Electrician
06/30/2025