A Brief Analysis of Key Points for the Operation and Maintenance of High-Voltage SF6 Circuit Breakers

Felix Spark
05/08/2025
1 Overview
Circuit breakers can connect and disconnect circuits according to the operating mode under normal conditions. They can also quickly cut off faulty equipment based on secondary protection signals when a fault occurs, or connect the circuit to restore power supply after a transient fault is eliminated. Thus, they have the dual functions of control and protection . Currently, there are more than a hundred substations in the Pingdingshan area. In each substation, circuit breakers are required for each outgoing line, each incoming line side, and the connection of double busbars. High - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers are widely used in 110 kV and 220 kV substations due to their advantages such as strong breaking capacity, fast action speed, easy maintenance, and high stability.
High - voltage circuit breakers are mainly composed of moving contacts, stationary contacts, arc - extinguishing chambers, and conductive parts. The moving and stationary contacts are located inside the arc - extinguishing chamber and are used to interrupt current. The stationary contact remains in place, and the moving contact is powered by the operating mechanism to enable the circuit breaker to complete opening and closing operations. The operating mechanism is connected to the moving contact through a transmission mechanism and an insulating pull rod.
Although the performance of commonly used high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers is relatively complete at present, failures may still occur during operation due to changes in the power grid, external environment, and internal factors. Taking the high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers used in 220 kV substations as an example, this paper briefly discusses the common problems during their operation and corresponding handling measures.
2 Analysis of Existing Problems and Key Points of Operation and Maintenance
Multiple components of high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers, such as the operating mechanism, transmission mechanism, arc - extinguishing part, and current - conducting part, are prone to various failures during operation. In the past operation of substations in the Pingdingshan area, the following incidents have occurred:
- High - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers were forced to stop operating due to SF₆ gas leakage.
- Pressure lockout occurred due to severe oil leakage in the hydraulic mechanism, or energy storage failed due to abnormalities in the spring mechanism, resulting in the inability of high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers to interrupt current normally.
- The circuit breaker refused to operate due to problems within the mechanism itself, such as a broken control circuit, preventing it from meeting the requirements for opening and closing.
- High - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers were damaged due to porcelain insulator fracture.
- Overheating caused by current - conducting issues led to the inability of high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers to operate normally.
- The circuit breaker suffered varying degrees of damage and could not maintain normal operation due to the influence of the external environment or damage to the insulation part.
These problems can cause certain damage to high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers to varying degrees and affect their normal operation. During daily inspection and maintenance, more attention should be paid to inspecting these components of high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers to improve the power supply reliability of the power system. The following is an individual analysis of the above problems.
2.1 Arc - Extinguishing Part
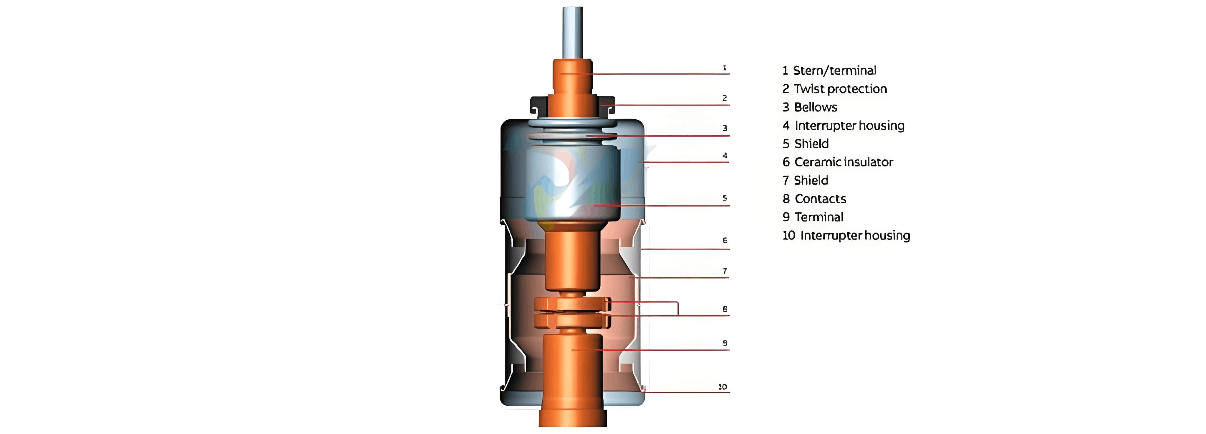
High - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers must have sufficient arc - blowing ability and dielectric recovery strength to effectively prevent arc reignition at current zero - crossing. The arc - extinguishing process of high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers takes place in the arc - extinguishing chamber, which is mainly composed of moving and stationary main contacts, moving and stationary arcing contacts, large and small nozzles, a compression cylinder, and a piston. Specifically:
- The main contacts carry the current when the circuit breaker is operating normally.
- The arcing contacts are connected in parallel with the main contacts, and their contact travel is greater than that of the main contacts. They can withstand all arc erosion during current interruption or closing, thus protecting the main contacts from damage.
- The nozzles limit the flow direction and speed of the jet gas to achieve the best arc - blowing effect.
- The piston compresses the gas in the compression cylinder when the moving contact moves, increasing the gas pressure in the cylinder to reach the optimal arc - blowing gas pressure.
During operation, SF₆ gas leakage will directly affect the stable operation of the circuit breaker. When the gas pressure drops below the threshold, the circuit breaker will issue an alarm or be locked out due to low pressure. In this case, a fault may occur, potentially expanding the power outage area.
2.2 Mechanical Part
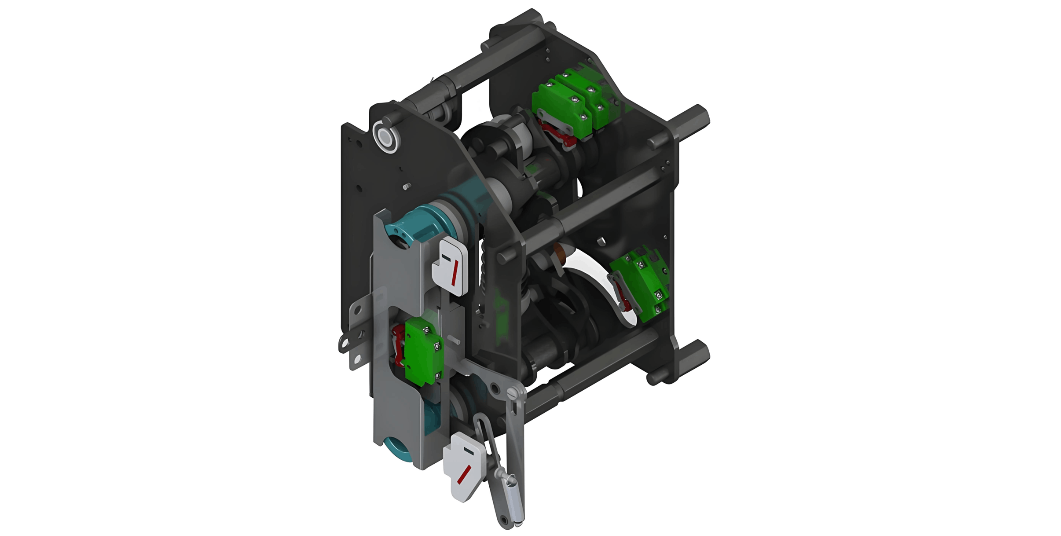
The mechanical performance of high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers directly determines their arc - extinguishing ability and affects their opening and closing speed and time. The mechanical part can be roughly divided into the operating mechanism and the transmission mechanism. According to statistical data on circuit breaker failures, 63.2% of circuit breaker failures in China are caused by the operating mechanism.
The operating mechanisms of SF₆ circuit breakers used in 110 kV and above substations in the Pingdingshan area are roughly divided into hydraulic mechanisms and spring mechanisms. Spring mechanisms are widely used due to their advantages such as simple mechanical structure, easy maintenance, fast response speed, environmental friendliness, and low cost. However, as the operating time increases, the elasticity of the spring will weaken. There may be situations where the circuit breaker fails to cut off the fault current due to the failure of the opening spring to store energy, or the reclosing fails because the closing spring fails to store energy during reclosing.
Hydraulic mechanisms have the advantages of stronger reliability, higher safety, and a longer service life. When the hydraulic value drops below the threshold, zero - pressure lockout will be activated to avoid slow opening due to pressure loss. The control system will start the motor to increase the pressure, and after a set time, the time relay will cut off the control circuit to stop the pressure increase.
In addition, transmission mechanisms such as connecting rods, crank arms, and rotating shafts play an important role in the opening and closing process. When receiving opening and closing signals, the opening and closing springs release energy and drive the contacts to complete opening and closing tasks through transmission mechanisms such as connecting rods and crank arms. If the connecting rods, crank arms, or rotating shafts are deformed or cracked, it will affect the normal transmission during the opening and closing of the circuit breaker.
2.3 Operating Environment
Outdoor - type SF₆ circuit breakers should also pay attention to the impact of changes in the operating environment during operation. For example, in strong wind conditions, the lead wires may swing significantly or foreign objects may get caught on them. When lightning strikes the power grid or the grounding system, over - voltage surges may occur, causing the circuit breaker to trip. In rainy or snowy conditions, the surface of the circuit breaker is prone to moisture, which may form corona discharge. If the surface is contaminated, more serious pollution flashover may occur. In the case of snow accumulation or icing, the joints may overheat. When the temperature changes suddenly, the oil level and gas pressure of the circuit breaker may also change suddenly, resulting in a decrease in insulation performance and affecting its opening and closing speed.
2.4 Insulation Part
The insulation part serves to isolate the equipment from the air. Commonly - used insulation materials include porcelain insulators, composite insulators, and silicone rubber insulators. Currently, the external insulation of SF₆ circuit breakers in the Pingdingshan area is mostly made of porcelain.
During operation, the insulation performance of porcelain insulators may severely decline or even be lost due to factors such as their own poor quality, unqualified installation, sudden temperature changes, or excessive over - voltage surges. If the external insulation of high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers is unevenly stressed during installation, the damage to the external insulation will worsen during long - term operation. In severe cases, cracks or breakages may occur on the surface of the porcelain.
Moreover, sudden changes in the external temperature can significantly reduce the bending and tensile strength of insulation materials. If mechanical forces are applied at this time, the insulation part may be damaged or even punctured. When the external insulation is subjected to over - voltage, partial discharge may be triggered. If there is dust or dirt on the surface of the external insulation, and the environment is humid, pollution flashover may occur under the action of a high - voltage electric field.
3 Countermeasures
Since there are many outgoing lines in 220 kV substations, and accordingly, a large number of SF₆ circuit breakers, to reduce the occurrence of the above - mentioned problems, a reasonable inspection cycle and maintenance cycle should be formulated, a complete defect handling process and equipment acceptance standard should be established, focusing on accident prevention, and a complete closed - loop management system should be established.
3.1 Formulating a Reasonable Inspection Cycle
The normal operation of circuit breakers depends on the daily inspection by operation and maintenance personnel. By formulating a reasonable inspection cycle, defects in circuit breakers can be detected in a timely manner, preventing the defects from expanding and causing accidents. The following briefly describes the key points to be noted during the inspection of 220 kV high - voltage SF₆ circuit breakers.
- Routine inspections should be carried out at least once a week. This mainly involves routine inspections of the appearance of the circuit breaker, abnormal sounds, equipment leakage, operating environment, and tracking and inspection of defects and potential hazards. Special attention should be paid to checking whether the pressure value and oil level of the high - voltage SF₆ circuit breaker are within the normal range, recording the pressure value, observing whether the oil color is normal, and whether energy storage can be carried out normally.
- Comprehensive inspections should be carried out at least once a month. Based on routine inspections, the cabinet doors of equipment in the substation are opened for inspection. Operating data such as the gas pressure value and oil level value of the circuit breaker are recorded; it is checked whether the cabinet doors of the circuit breaker are tightly closed, whether the holes are well - blocked, and whether the dehumidification and temperature - control devices can operate normally; whether the opening and closing coils have discoloration, abnormal odors, or signs of burning; whether the operating mechanism and transmission mechanism of the circuit breaker are normal; and whether the secondary wiring has overheating, looseness, or breakage.
- Inspection in the dark should be carried out at least once a month. This refers to inspections carried out at night with the lights off, focusing on checking whether the lead wires, joints, and clamps are overheating, and whether there is any discharge on the external insulation.
- Special inspections are carried out to prevent the circuit breaker from malfunctioning, refusing to operate, deforming in structure, suffering insulation damage, discharging, or experiencing pollution flashover due to changes in the external environment or the operation mode of the system, which may affect the normal operation of the circuit breaker. Specific situations have different inspection cycles.
3.2 Formulating a Reasonable Maintenance Cycle
Regular inspections are aimed at better detecting problems, while regular maintenance can better prevent small defects from developing into major accidents. The following are several common maintenance items for circuit breakers.
- Cabinet maintenance is carried out once every six months. It focuses on checking whether the sealing strips, cabinet door hinges, and handles are damaged, whether the cabinet is rusted, and whether the grounding marks are intact.
- Blocking maintenance is carried out once a month. Fire - resistant blocking materials should be used for blocking, and insulating materials such as fire - resistant boards should be used if necessary to ensure tight blocking and prevent the blocking material from collapsing.
- Maintenance of dehumidification and heating devices and lighting devices is carried out once a quarter. It is determined whether the dehumidification and heating devices are operating normally according to environmental changes. At the same time, it is checked whether the lighting devices inside the cabinet are normal, and whether their contact switches and circuit wiring are loose.
3.3 Establishing a Defect Handling Process
Defects found during inspections and maintenance should be recorded, and reported in a timely manner according to their severity. Later, maintenance personnel should promptly conduct experiments and maintenance work. After maintenance, operation and maintenance personnel are responsible for equipment acceptance, and the equipment is put into operation only after it passes the acceptance. Through the whole - process closed - loop management of discovery - filing - reporting - handling - acceptance, not only can the service life of equipment be extended, but also the occurrence of accidents can be reduced, and high - quality electric energy can be better provided to users.
3.4 Precautions for Acceptance
Circuit breakers should be accepted and pass the inspection before being put into operation after new installation or maintenance. During acceptance, it should be ensured that there are no remnants from maintenance on the circuit breaker; the porcelain insulators are clean and undamaged; the SF₆ gas pressure gauge and oil level gauge are normal; the hydraulic mechanism or spring mechanism can store energy normally; the cabinet is well - sealed, and the joints are not loose or deformed; and the position signals and abnormal alarm signals can operate correctly.
4 Conclusion
The operation and maintenance management of circuit breakers is a dynamic process. In daily work, the sense of responsibility of operation and maintenance personnel should be strengthened. They should strictly follow the regulations for corresponding inspections and maintenance, and a reasonable closed - loop management system for equipment should be formulated to ensure the normal operation of equipment and the stable operation of the power grid.

Hey there! I'm an electrical engineer specializing in Failure and Maintenance. I've dedicated my career to ensuring the seamless operation of electrical systems. I excel at diagnosing complex electrical failures, from malfunctioning industrial motors to glitchy power distribution networks. Using state - of - the - art diagnostic tools and my in - depth knowledge, I pinpoint issues quickly. On this platform, I'm eager to share my insights, exchange ideas, and collaborate with fellow experts. Let's work together to enhance the reliability of electrical setups.












