Discussion on the Maintenance Strategies of Substations and Their Optimization Measures

Felix Spark
04/26/2025
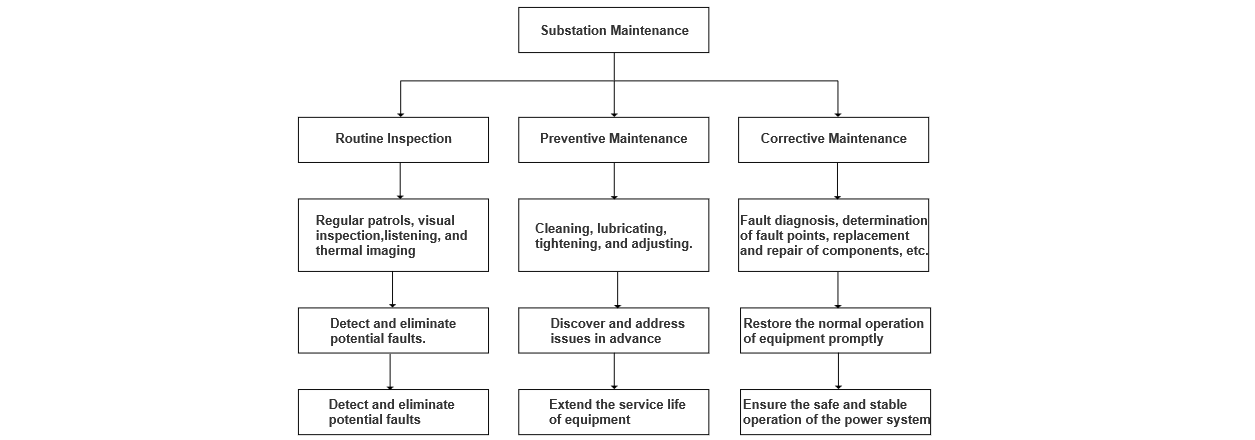
With the continuous growth of electricity demand and the increasing complexity of power systems, the operating environment and load that substation equipment faces are becoming more and more intricate. This has led to higher requirements for maintenance work. The primary objective of maintenance work is to ensure that the equipment operates in good condition through inspection, maintenance, and repair, and to prevent and eliminate potential faults that may affect the power supply. Currently, the maintenance work of substations mainly encompasses three aspects: routine inspection, preventive maintenance, and corrective maintenance.
Routine inspection involves regular patrols and detections to promptly identify any abnormal conditions of the equipment. Appropriate measures are then taken to address these issues and prevent the occurrence of faults. Preventive maintenance, on the other hand, aims to extend the service life of the equipment and enhance its operational reliability by conducting regular inspections and maintenance tasks. Corrective maintenance is carried out when the equipment malfunctions. It involves quickly diagnosing the fault, repairing it, restoring the normal operation of the equipment, and ensuring the safety and stability of the power system.
It is of great significance to propose a series of optimization strategies in response to the existing problems in current substation maintenance work. By formulating scientific maintenance plans, introducing advanced technical means, strengthening personnel training, and improving the level of informatization, the efficiency and quality of maintenance work can be effectively enhanced, the normal operation of substation equipment can be ensured, and the stable operation of the power system can be further guaranteed. This article will explore these optimization strategies in detail, analyze their implementation methods and effects, with the aim of providing valuable references and guidance for substation maintenance work.
1 Basic Contents of Substation Maintenance
Substation maintenance mainly includes the inspection, maintenance, and repair of equipment to ensure its normal operation.
1.1 Routine Inspection
Regular patrol inspections are conducted on substation equipment to detect and eliminate potential faults. These inspections usually involve visual inspections, auditory inspections, and thermal imaging inspections to ensure that the equipment is operating under normal working conditions. Through routine inspections, abnormal conditions of the equipment can be detected in a timely manner, and corresponding measures can be taken to deal with them, nipping potential problems in the bud.
1.2 Preventive Maintenance
Through regular equipment inspections and maintenance, potential problems of the equipment can be identified and addressed in advance to prevent the occurrence of faults. Preventive maintenance includes tasks such as cleaning, lubricating, tightening, and adjusting. These maintenance activities are designed to extend the service life of the equipment, reduce the failure rate, and improve the operational reliability of the equipment. For example, the regular replacement of transformer oil, the mechanical operation inspection of circuit breakers, and the calibration of protection devices.
1.3 Corrective Maintenance
When the equipment malfunctions, faults are promptly eliminated and repaired to restore the normal operation of the equipment. Corrective maintenance includes fault diagnosis, determination of the fault location, replacement or repair of faulty components, as well as the testing and restoration of the equipment after the fault. During the corrective maintenance process, it is necessary to quickly and accurately identify the cause of the fault and take effective measures to deal with it, so as to restore the normal operation of the equipment in the shortest possible time and ensure the safety and stability of the power system.
The main work processes of substation maintenance are summarized as shown in Figure 1. Through these maintenance tasks, the normal operation of substation equipment can be effectively guaranteed, and the reliability and safety of the power system can be improved. Substation maintenance is not just a simple upkeep of equipment; it is a crucial safeguard for the safe operation of the entire power system. Therefore, formulating a reasonable maintenance plan, adopting advanced maintenance technologies and means, and strengthening the training of maintenance personnel are the keys to improving the quality and efficiency of substation maintenance work.
2 Existing Problems in Current Substation Maintenance
In practical operations, there are certain issues in substation maintenance work that affect the efficiency and quality of maintenance [6-8].
2.1 Unreasonable Maintenance Plan
The maintenance plans of some substations lack scientific and rational elements. Often, they do not fully consider the actual operating conditions and fault history of the equipment. Such unreasonable maintenance plans may lead to improper scheduling of maintenance time, waste of maintenance resources, and some equipment not being maintained in a timely manner, thus affecting the efficiency and effectiveness of the overall maintenance work.
2.2 Outdated Technical Means
The maintenance of some substations still relies on traditional manual operations and simple detection tools, lacking advanced detection and diagnostic technologies. For example, many substations have not widely applied advanced technologies such as infrared thermal imaging, ultrasonic detection, and partial discharge detection. This results in some potential faults being unable to be detected and dealt with in a timely manner, affecting the quality and reliability of the maintenance work.
2.3 Uneven Personnel Quality
The technical levels and professional qualities of maintenance personnel vary widely. Some personnel lack systematic professional training and practical experience. This situation not only affects the smooth progress of maintenance work but may also lead to operational errors or improper handling during the maintenance process, thereby increasing the risk of equipment failure.
2.4 Low Level of Informatization
Some substations lack modern information management systems, and the management methods for maintenance data and information are still relatively backward. The low level of informatization leads to chaotic management of maintenance information, making it difficult to effectively record, track, and analyze the operation and maintenance history of equipment. This situation not only affects the transparency and traceability of maintenance work but also hinders the analysis of equipment failure patterns and the formulation of preventive maintenance strategies.
3 Suggestions for Optimizing Substation Maintenance Strategies
In response to the problems described above, the following suggestions for optimizing substation maintenance strategies are put forward:
3.1 Scientifically Formulate Maintenance Plans
A maintenance plan is the foundation for ensuring the orderly progress of maintenance work. To formulate a scientific maintenance plan, it is necessary to fully consider the operating status, fault history, and usage environment of the equipment. Firstly, a comprehensive assessment and condition monitoring of substation equipment should be carried out, and big data analysis technology should be used to analyze the historical operating data of the equipment to predict the fault trends of the equipment. Secondly, when formulating a maintenance plan, the importance of the equipment, operating load, and seasonal factors should be comprehensively considered, and the maintenance time should be reasonably arranged to avoid large-scale maintenance during peak electricity demand periods. Finally, the maintenance plan should be flexible and dynamically adjusted according to the actual operating conditions of the equipment to ensure the timeliness and effectiveness of the maintenance work.
3.2 Introduce Advanced Technical Means
Modern detection technologies, such as infrared thermal imaging technology, can detect the temperature distribution on the surface of the equipment in a timely manner and identify overheated parts. Partial discharge detection technology can provide an early warning when partial discharge occurs in the insulation materials of the equipment, preventing insulation failures. Ultrasonic detection technology can identify mechanical faults inside the equipment by capturing the sound signals during its operation. In addition, an online monitoring system can be applied to conduct real-time monitoring of key substation equipment, promptly obtain the operating status data of the equipment, quickly detect and deal with equipment abnormalities, and reduce the downtime due to faults.
3.3 Strengthen Personnel Training
The professional qualities and technical levels of maintenance personnel are the guarantee of the quality of maintenance work. Regular technical training for maintenance personnel should be carried out, covering the application of the latest maintenance technologies, equipment fault diagnosis methods, emergency handling skills, and safe operation procedures. The training mode can combine theoretical learning with practical operation to improve the effectiveness of the training. In addition, maintenance personnel should be encouraged to participate in technical exchanges and experience sharing activities within the industry to keep abreast of the latest technical trends and advanced experiences and improve their own technical levels. The training of maintenance personnel should also include management skills training to enhance their management capabilities in formulating and implementing maintenance plans.
3.4 Improve the Level of Informatization
Informatization is an important means to achieve scientific management of maintenance work. A modern maintenance information management system should be established to realize the digital management of maintenance information. Through the information management system, data such as the operating status, maintenance records, and fault history of the equipment can be centrally managed, facilitating data query and analysis. In addition, the information management system can also automatically generate maintenance plans and conduct intelligent scheduling, improving the scientific nature and efficiency of maintenance work.
By establishing equipment health records and timely updating the operation and maintenance data of the equipment, the operating status of the equipment can be monitored and evaluated in real time, providing data support for maintenance decisions. The information management system can also be combined with the Internet of Things technology to realize remote monitoring and intelligent diagnosis of equipment, further improving the efficiency and quality of maintenance work.
3.5 Strengthen Maintenance Management and Supervision
The management department should formulate detailed maintenance regulations and operation procedures, clarifying the responsibilities and standards of various maintenance tasks. During the maintenance process, it should be carried out strictly in accordance with the regulations and operation procedures to ensure that every maintenance link proceeds in an orderly manner. The supervision mechanism should run through the entire process of maintenance work. Through on-site supervision, inspections, and performance assessments, it is ensured that the maintenance work is carried out according to the plan. Any problems found should be rectified in a timely manner to prevent the accumulation of problems from leading to serious consequences.
3.6 Enhance Maintenance Safety
Safety issues must be highly emphasized in maintenance work. A complete safety management system should be established, and regular safety training and drills should be carried out to ensure that maintenance personnel have good safety awareness and operating skills. Necessary safety protection equipment should be equipped at the maintenance site, and safety operation procedures should be strictly followed to prevent accidents. For high-risk equipment and links, key monitoring and management should be carried out, and effective safety protection measures should be taken to ensure the safe progress of the maintenance work.
3.7 Strengthen Cooperation with Equipment Manufacturers
Cooperation with equipment manufacturers should be strengthened in maintenance work to make full use of their technical support and services. Equipment manufacturers usually have in-depth knowledge of the performance and fault patterns of the equipment and can provide technical guidance and training for maintenance work. Maintaining a good cooperative relationship with manufacturers can also enable timely access to information on equipment technology upgrades and the latest maintenance technologies, improving the technical level and efficiency of maintenance work.
In conclusion, optimizing substation maintenance strategies requires efforts from multiple aspects, as shown in Figure 2, to comprehensively improve the efficiency and quality of substation maintenance work and ensure the stable operation of the power system.
4 Conclusion
In the future, it is imperative to further intensify the research and practical application in substation maintenance work. By promoting the innovation and development of maintenance technologies and management approaches, we aim to achieve the modernization and intelligentization of substation maintenance operations. This will not only enhance the reliability and efficiency of substation equipment but also contribute significantly to the stable and sustainable operation of the entire power system.

Hey there! I'm an electrical engineer specializing in Failure and Maintenance. I've dedicated my career to ensuring the seamless operation of electrical systems. I excel at diagnosing complex electrical failures, from malfunctioning industrial motors to glitchy power distribution networks. Using state - of - the - art diagnostic tools and my in - depth knowledge, I pinpoint issues quickly. On this platform, I'm eager to share my insights, exchange ideas, and collaborate with fellow experts. Let's work together to enhance the reliability of electrical setups.