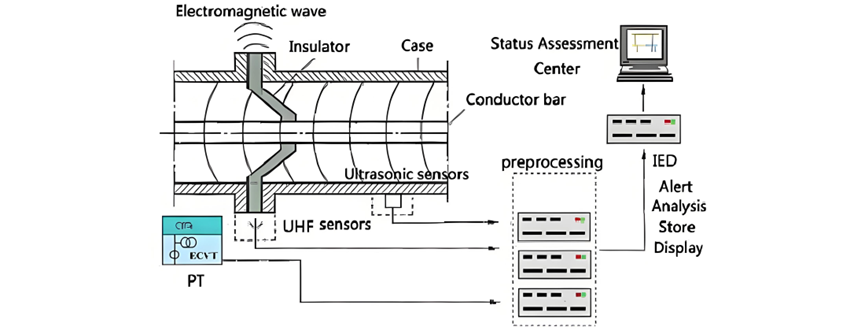
Partial Discharge (PD) Detection in GIS
Both UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) and ultrasonic methods are effective for detecting partial discharges (PD) in Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS), each with distinct advantages:
- UHF Method: Detects PD pulses via high-frequency electromagnetic waves generated by PD activity within GIS.
- Ultrasonic Method: Identifies ultrasonic waves produced by bubble shocks caused by PD.
Key Monitoring Data
The main data monitored by a GIS PD monitoring system includes:
- UHF PD signals
- Ultrasonic PD signals
- Transformer voltage signals
The online monitoring system collects these signals and generates alarm information based on the GIS’s operational status.
System Composition
A GIS PD monitoring system comprises three core components:
- Sensors: Capture PD-related signals.
- UHF PD sensors detect electromagnetic signals.
- Ultrasonic sensors measure acoustic signals.
- Data Preprocessing System: Conditions and prepares signals for analysis.
- PD Monitoring IED (Intelligent Electronic Device): Processes, stores, and displays data at the bay level.
Signal Flow and Communication
- Process Level: UHF and ultrasonic sensors acquire electrical and acoustic signals, which are conditioned and transmitted to the PD monitoring IED.
- Bay Level: The IED stores, displays, and processes data. Specific communication service mapping (per IEC 61850) defines network transmission standards for sampled values between the process and bay levels.
- Station Level: Data is reported from the bay level to the station level via predefined communication services for centralized monitoring.
System Structure
The figure illustrates the architecture of a GIS PD monitoring system compliant with IEC 61850 standards.














