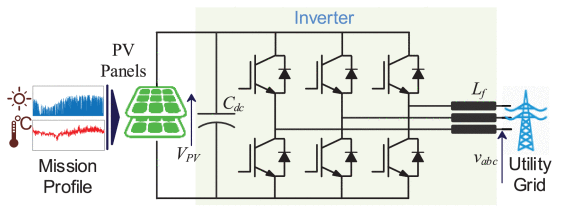
Incorporating Power Electronic Converters Reliability Into Modern Power System Reliability Analysis
This article aims to incorporate the reliability model of power electronic converters into power system reliability analysis. The converter reliability has widely been explored in device- and converter-levels according to physics of failure analysis. However, optimal decision-making for design, planning, operation, and maintenance of power electronic converters require system-level reliability modeling of power electronic-based power systems. Therefore, this article proposes a procedure to evaluate the reliability of power electronic-based power systems from the device-level up to the system-level.
1.Introduction.
Electric power system modernization is essential for reliable and secure power delivery with a low-to-zero carbon footprint. It requires deploying new technologies and infrastructure as well as deregulating the electricity sector. Some established technologies have a considerable role in power systems modernization including renewable energy resources, storages, electronic transmission and distribution systems, and e-mobility. Notably, power electronics (PE) plays an underpinning role in the energy conversion process of the aforementioned technologies . Particularly, moving toward one hundred percent renewable energies has intensified the importance of PE in the future power systems.
2.Concept of Reliability.
Reliability is defined as the ability of a system or an item to function under desired conditions within a specific period of time . According to this definition, the system/item performance must be retained within a specified interval at a target time period. Depending on a system, the reliability measures may be different. For instance, in a mission-based system, such as a spacecraft, the reliability is defined as the probability of survival during the target mission period. Thus, the first time to failure with a desired probability must be longer than the target mission period. Furthermore, in a maintainable/repairable system/item with the possibility of maintenance, the performance is measured by the availability as its reliability indicator. In these systems/items, it is important to have them in the operation state (being available) at any instance regardless of any failure occurrence before that time. This means that the system can be maintained whenever it fails and hence the only issues are the failure frequency and downtime.
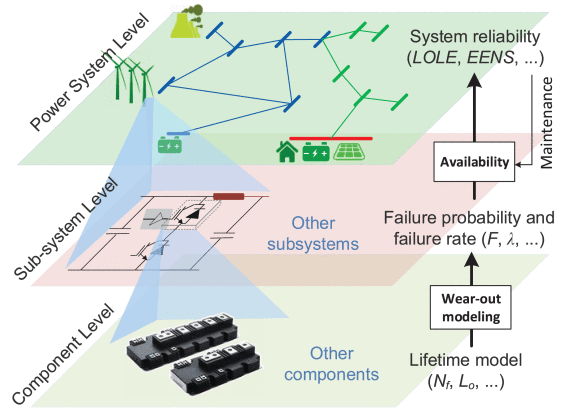
3.Converter Reliability Modeling.
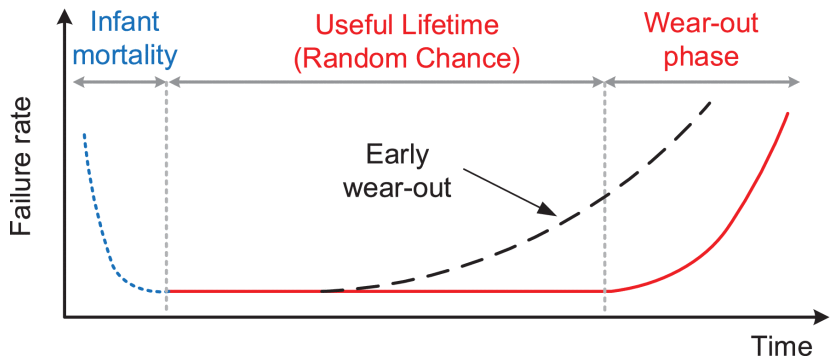
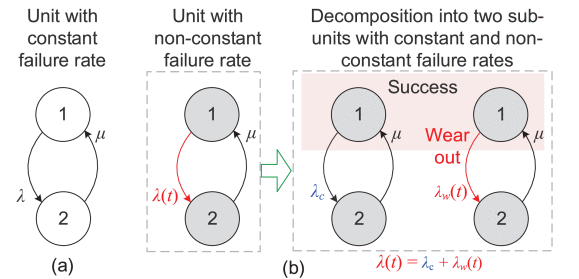
The failure characteristics of a converter, like other systems, comprise three periods including infant mortality, useful lifetime, and wear-out phase as shown in Fig. known as the bathtub curve. Usually, the infant mortality failures are related to the debugging and manufacturing processes. Hence, the converter will experience the random chance and wear-out failures within operation. The random chance failures usually have external sources such as overcurrent and overvoltage . Therefore, they are considered as exponentially distributed failures within the useful lifetime in the bathtub curve . The corresponding failure rate is usually predicted based on the historical reliability data and operational experiences.
4.Power System Reliability.
Power system reliability, the so-called adequacy is a measure of its ability to meet the electric power and energy requirements of the customers within the acceptable technical limits considering the component outages . The main measure employed in power system reliability assessment is the availability of its components. Availability is defined as the probability that an item is in operating state at any instant
5.Conclusion.
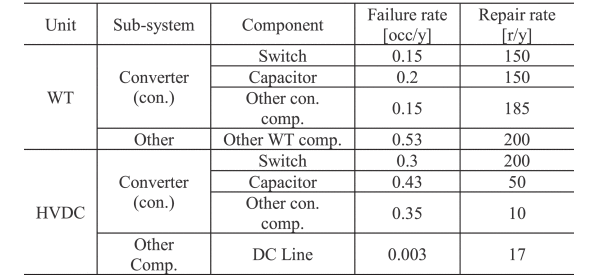
This article has proposed a procedure to bridge the power electronic and power system reliability concepts. The reliability of power electronic converters is incorporated in power system reliability analysis, which can be beneficial for optimal decision-making within planning, operation, and maintenance of modern power systems. The detailed reliability modeling of power electronic-based power systems has been presented from the device-level up to the power system-level. The impact of converter failure rates on power system performance has been illustrated for different applications.
Source: IEEE Xplore
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
IEEE (pronounced "I-triple-E") stands for the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, a global professional organization dedicated to advancing technological innovation for the benefit of humanity. Founded in 1963 through the merger of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (AIEE) and the Institute of Radio Engineers (IRE), IEEE has grown into the world’s largest technical professional society, with over 400,000 members across 160+ countries.