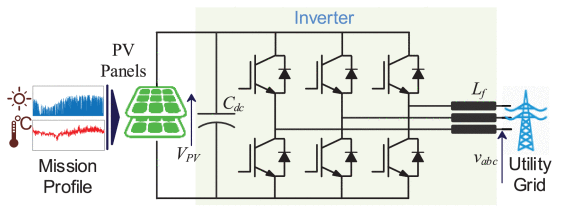
Data-driven next-generation smart grid towards sustainable energy evolution: techniques and technology review
This paper exhibits the conceptual framework of NGSG by enabling some intelligent technical features to ensure its reliable operation, including intelligent control, agent-based energy conversion, edge computing for energy management, internet of things (loT) enabled inverter, agent-oriented demand side management, etc. Also, a study on the development of data-driven NGSG is discussed to facilitate the use of emerging data-driven techniques (DDTs) for the sustainable operation of the SG.
1.Introduction.
The conventional SG cannot fully meet the requirements as it continuously changes with emerging advanced technologies. The need for clean energy has increased globally over the past decade as a result of changing environmental conditions and expanding populations and technology that may impose non-linear dynamics on the SG. The non-linearity in the smart power grid transmission and distribution systems may add new congestion, outages, fluctuation in voltage and frequency, that lead to blackouts as a result of the increasing demand for electricity . Non-renewable energy sources though being an easier, quicker, and cheaper path to generate power, they are a direct obstruction to the green environment because of high emissions . Renewable energy sources are on the rise to reduce dependency on fossil fuel-based power generation . However, the uncertainty and complexity of SGs are increasing with the addition of more distributed generation (DG), increased market size, and renewable sources.
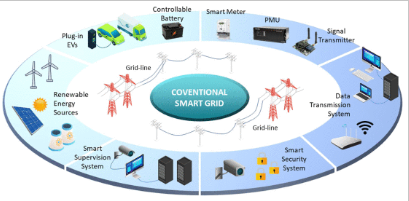
2.Smart Grid At Present: Technical Architecture.![]()
An SG enables bidirectional flow of electricity between the utility and its end users, with its smart framework structured by combining information, power technologies, and telecommunication with the prevailing electricity system. This energy technology also supports automation mechanization for efficient power distribution, storage elements, fault detection, electric vehicles, grid data supervision, combination of hybrid RESs, and flexibility of grid networks . The various components shown in Fig can be used to build the SG energy technology. They include renewable sources, a smart supervision system, a smart information system, an advanced storage system, a smart security system, sensors, and grid-lines.
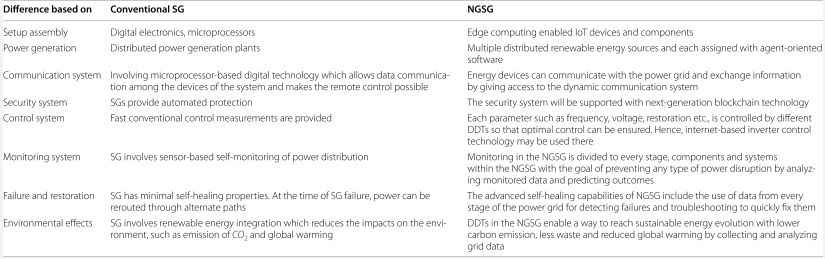
3.Add-on Technology Towards the Next-Generation Smart Grid.
NGSGs have the possibility of enabling enhanced features in the SG landscape as compared to conventional SG technologies. The security and privacy issues of the current SG systems may be better covered by an NGSG in the context of integrating more advanced features. The advance of an NGSG entirely depends on the use of data-driven techniques in its different parts. A conceptual framework of an NGSG is illustrated in Fig. It can be seen that the framework of an NGSG may consist of integrating edge computing devices, IoT enabled inverters, blockchain-based energy trading, and computationally efficient DDTs in monitoring, controlling, and forecasting. It can also be noted that a data center may appear in an NGSG to collect data from the interconnected technologies and share the data among them to ensure its interoperability. By applying DDTs, the collected data from the different sources can be analyzed intelligently to help make decisions towards sustainable energy evolution. The detailed explanation of the intelligent technologies used in an NGSG framework can be found in the following sub-sections.
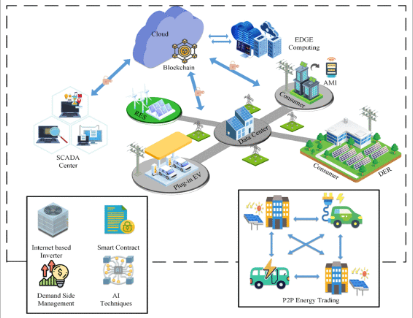
4.Data-Driven Next-Generation Smart Grid.
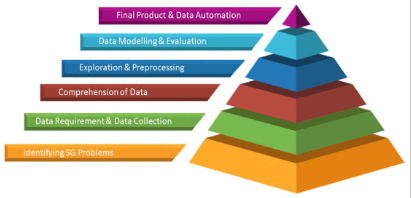
The framework of a data-driven NGSG may depend on the forming of the critical steps as shown in Fig. 5, which demonstrates how a data-driven NGSG solves critical issues and develops the final model for a data-driven NGSG. The bottom of the pyramid is the first step and the top is the last step of the process. Every step in developing the NGSG framework shown in Fig. 5 is discussed in detail in the following sub-sections.
Source: IEEE Xplore
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
IEEE (pronounced "I-triple-E") stands for the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, a global professional organization dedicated to advancing technological innovation for the benefit of humanity. Founded in 1963 through the merger of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (AIEE) and the Institute of Radio Engineers (IRE), IEEE has grown into the world’s largest technical professional society, with over 400,000 members across 160+ countries.