The main parts of an air insulated primary medium voltage switchgear and their application

Medium voltage switchgear plays a crucial role in the energy distribution process within alternating current (AC) systems, facilitating the flow of power from generation through transmission to end-users. This essential equipment is governed by specific standards that define its specifications, terminology, ratings, design criteria, construction practices, and testing protocols. For the European region, these guidelines are detailed in the following International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards:
- IEC 62271-1: Establishes common specifications for high-voltage switchgear and controlgear.
- IEC 62271-200: Focuses on AC metal-enclosed switchgear and controlgear designed for rated voltages exceeding 1 kV up to and including 52 kV.
- IEC 62271-300: Addresses gas-insulated metal-enclosed switchgear intended for rated voltages above 52 kV.
While IEC standards are globally recognized, countries such as the United States, China, and Russia may adhere to their own national standards. According to Section 3.5 of IEC 62271-1, all components of switchgear and controlgear are specified, enabling the assembly of comprehensive switchgear systems with functionalities tailored for medium voltage networks. These functions include:
- Efficiently distributing energy from higher-level transmission systems down to consumption points.
- Facilitating the switching of electrical currents.
- Conducting measurements critical for protection mechanisms, operational indicators, and billing processes.
- Safeguarding loads and equipment against faults.
- Implementing control, blocking, and interlocking features according to network operation needs.
- Enabling communication between switchgear and SCADA or DCS systems for enhanced monitoring and control.
- Ensuring the safety of personnel working within substations.
A variety of designs compliant with IEC standards are available, produced by numerous manufacturers. The IEC standard distinguishes between air-insulated and gas-insulated technologies, with design complexity varying based on the system's position within the distribution network and the sophistication required for protection and control schemes. Higher-rated switchgear typically necessitates more complex protection and control measures.
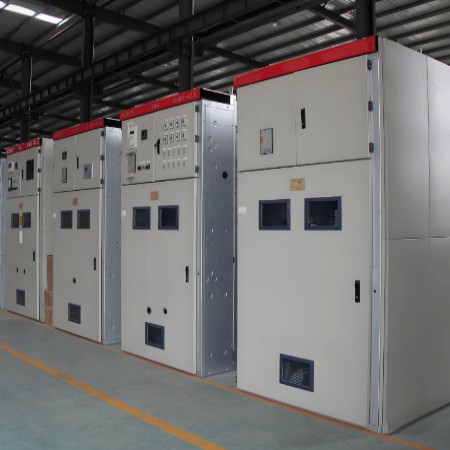
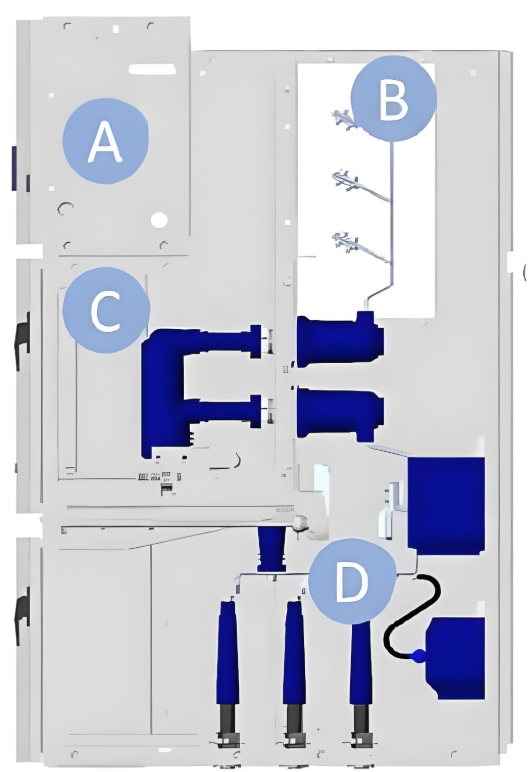
The typical architecture of primary air-insulated medium voltage switchgear (AIS) is organized into four fundamental compartments, reflecting a structured approach to achieving efficient, safe, and reliable operation within medium voltage applications. This configuration ensures optimal performance while adhering to stringent safety and operational standards.
Medium Voltage Switchgear Basic Structure Compartment
The primary structure, denoted as section B in Figures 1, 2, and 3, comprises metal sheets that provide shape, dimensions, stiffness, and robustness to the switchgear. This structure also incorporates copper components that are crucial for energy transmission and for interconnecting all compartments and apparatus within the switchgear.
This construction offers several key benefits:
- Metal-Based Segregation: The structure ensures separation between compartments according to IEC 62271-200 standards, which define different levels of accessibility. This segregation enhances safety and operational efficiency.
- Arc Withstand Capability: Alongside the metal-based segregation, the design includes arc-proof doors that provide additional protection against internal arcing events, ensuring the switchgear's ability to withstand arcs without compromising safety or functionality.
In summary, the primary structure not only gives the switchgear its physical form and strength but also integrates essential copper parts for electrical connectivity. Furthermore, it provides critical compartmentalization and arc resistance, adhering to stringent safety standards and enhancing overall system reliability. This meticulous design ensures that each component within the switchgear operates securely and efficiently, contributing to a safer and more dependable electrical distribution network.
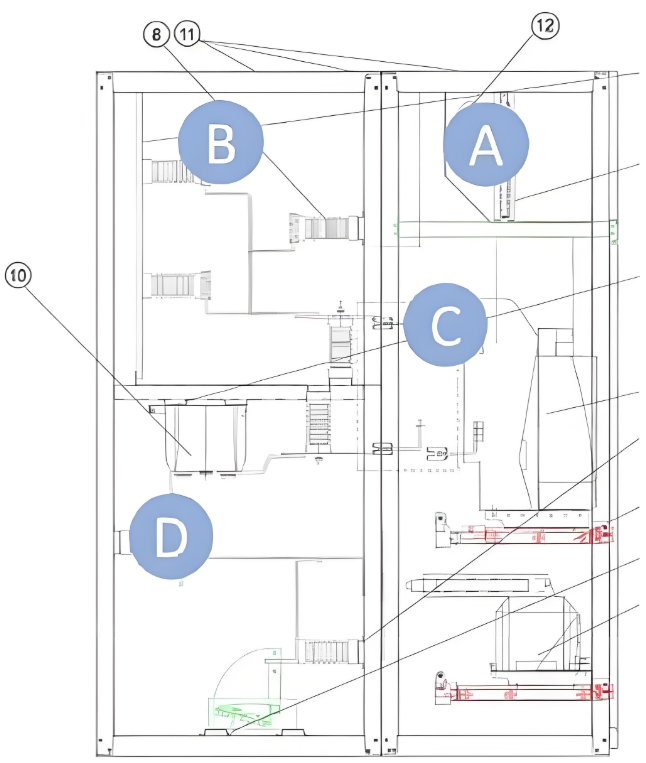
Medium Voltage Switchgear Circuit Breaker Compartment
The circuit breaker compartment, identified as section C in Figures 1, 2, and 3, houses medium voltage (MV) switching apparatus. This compartment can be equipped with various types of switching devices, including load break switches, contactors, circuit breakers, and others. The fundamental role of these switching devices is to reliably and safely open and close steady-state currents and voltages, as well as fault currents and voltages. In most primary air-insulated MV panels, circuit breakers are the preferred choice. Today, vacuum interrupting technology dominates for medium voltage applications due to its reliability and efficiency.
Medium Voltage Switchgear Cable Compartment
The cable compartment, marked as section D in Figures 1, 2, and 3, not only accommodates cable terminations but also includes sensing devices. These devices are primarily used for measuring phase currents, phase voltages, residual current, and residual voltage. The predominant technology employed for measurement purposes is the instrument transformer (IT), which operates on the established inductive principle for both current and voltage measurements. This setup ensures accurate and dependable monitoring within the switchgear system, contributing to enhanced operational safety and performance.
Through this structured approach, each component within the medium voltage switchgear plays a critical role in ensuring the safe, efficient, and reliable distribution of electrical power.













