What are Synchronous Motors?
What are Synchronous Motors?
Synchronous motor definition
A synchronous motor is an AC motor in which the rotation of the rotor is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current.
Constant speed operation
Synchronous motors operate at a constant speed called synchronous speed, which is determined by the number of poles of the motor and the frequency of power supply.
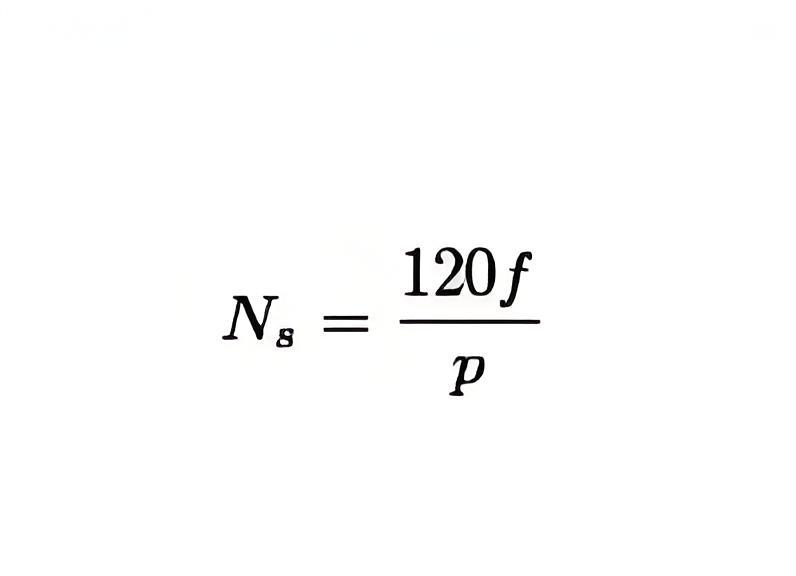
N= The Synchronous Speed (in RPM – i.e. Rotations Per Minute)
f = The Supply Frequency (in Hz)
p = The number of Poles
The structure of synchronous motor
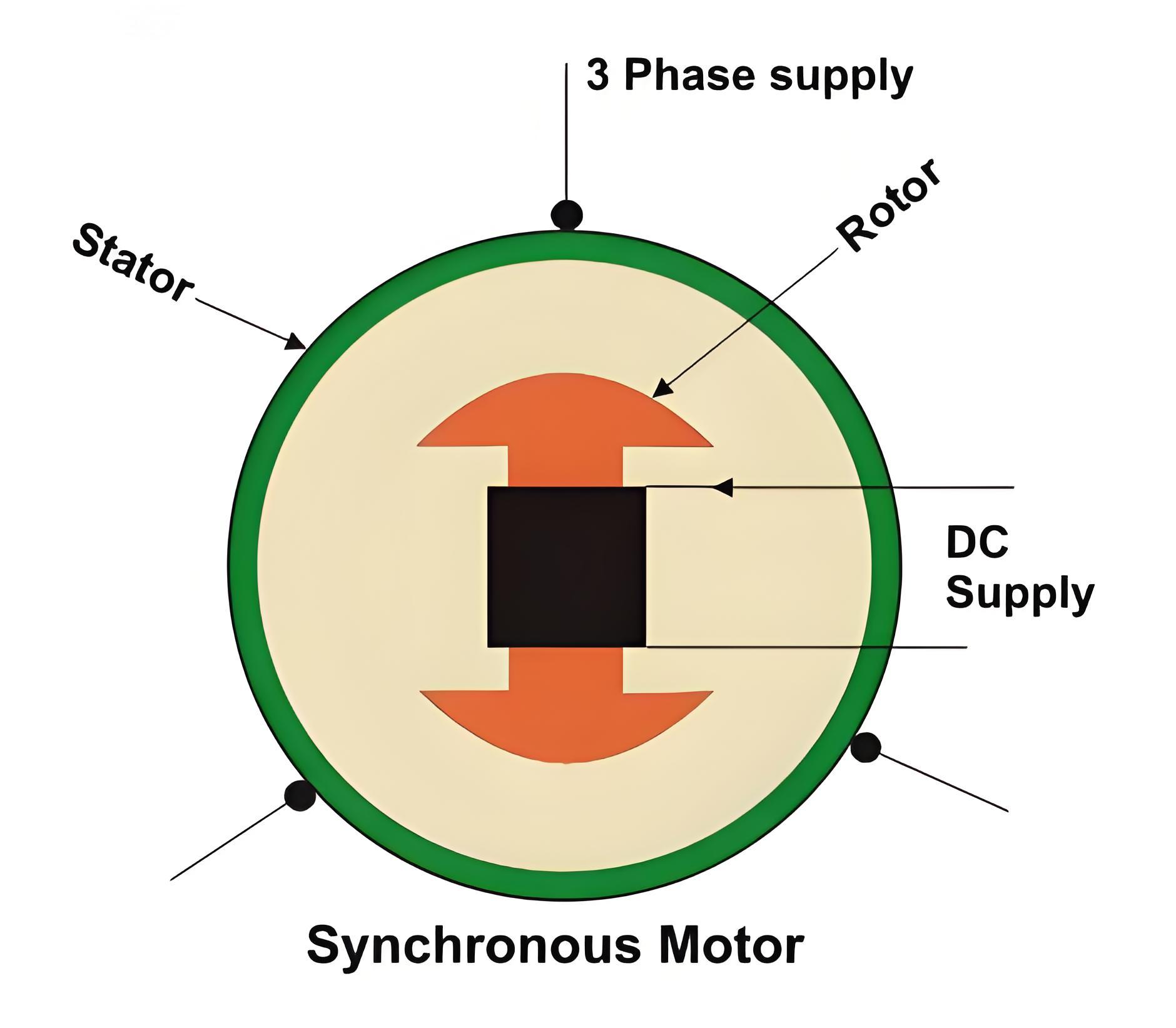
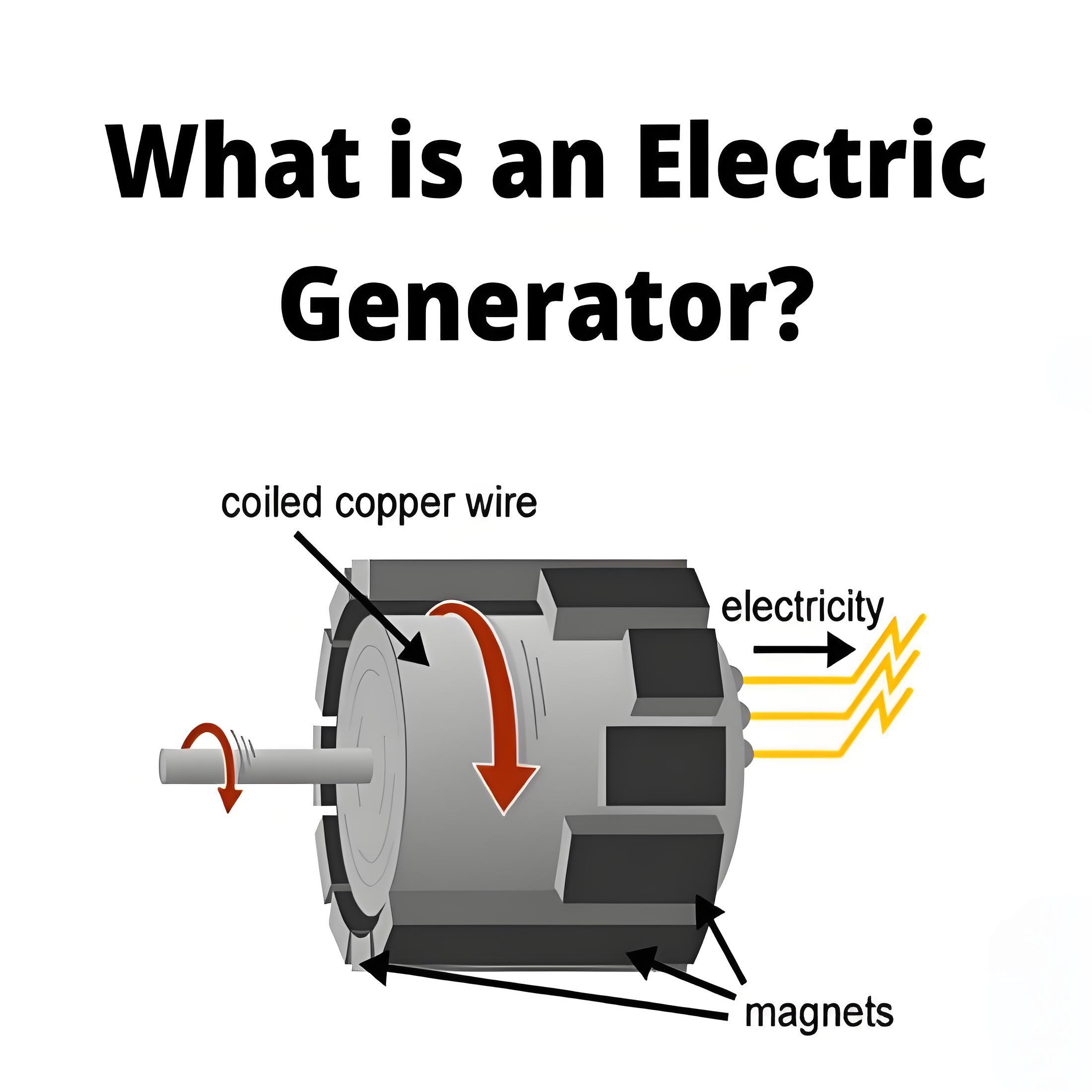
In general, its structure is almost similar to that of a three-phase induction motor, except for the fact that here we supply direct current to the rotor, for reasons we will explain later.
Now, let's first understand the basic structure of this motor. You can see from the picture above how we design this type of machine. We use three-phase power supply for the stator and DC power supply for the rotor.
The main characteristics of synchronous motor
Synchronous motors are not self-starting in nature. They need some external means to get their speed close to synchronous speed, and then they can synchronize.
The operating speed is synchronized with the power supply frequency, so for a constant power supply frequency, regardless of load conditions, they behave as constant speed motors
The motor has the unique characteristic of operating at any power factor. This allows it to be used to improve the electric power factor.
Working principle
A synchronous motor is a dual-excitation motor, that is, two electrical inputs are provided for it. The stator windings consist of a three-phase stator windings that we provide three-phase power supply, as well as DC power supply to the rotor windings.
Starting method
A motor started from an external prime mover
In this case, the synchronous motor is of convex pole type, and the additional winding is placed in the rotor pole face

Application of synchronous motor
Synchronous motors with no load on the shaft are used to improve the power factor. Due to its ability to perform at any power factor, it is used in power systems where static capacitors are expensivSynchronous motors are suitable for applications that operate at low speeds (around 500 rpm) and require high power. For the power requirements of 35 kW to 2500 KW, the corresponding three-phase induction motor size, weight and cost are very high. Therefore, it is preferred to use these motors. Explosion-proof reciprocating pump, compressor, rolling mill, etc
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.