What are the Methods of Improving Commutation?
What are the Methods of Improving Commutation?
Commutation definition
Commutation is the process of reversing the current in the coil to keep the motor running efficiently.
There are three main methods of improving commutation.
Resistance commutation
E.M.F. commutation
Compensating windings
Resistance Commutation
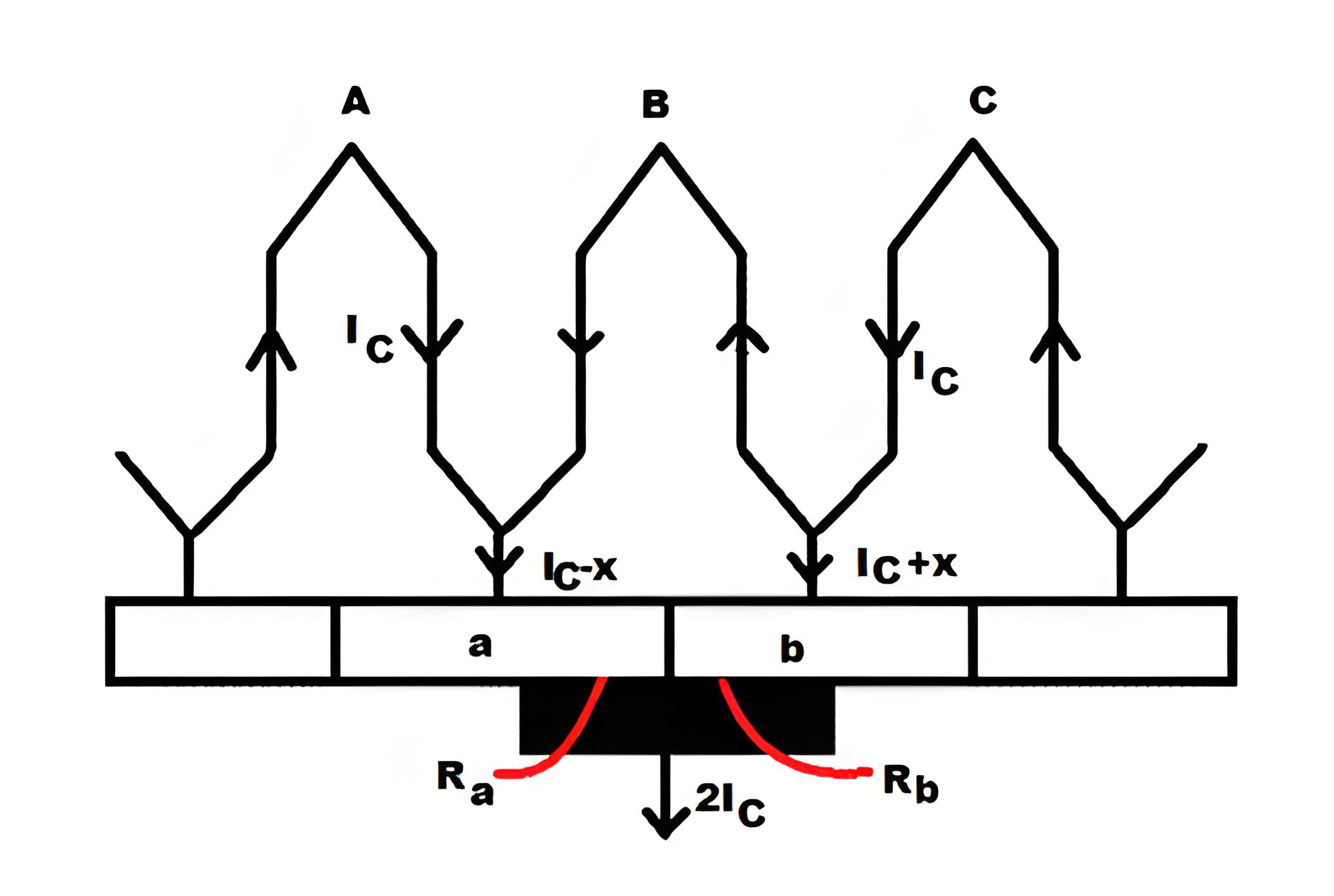
In this method of commutation we use high electrical resistance brushes for getting spark less commutation. This can be obtained by replacing low resistance copper brushes with high resistance carbon brushes.
We can clearly see from the picture that the current IC from the coil C may reach to the brush in two ways in the commutation period. One path is direct through the commutator segment b and to the brush and the 2nd path is first through the short-circuit coil B and then through the commutator segment a and to the brush. When the brush resistance is low, then the current IC from coil C will follow the shortest path, i.e. the 1st path as its electrical resistance is comparatively low because it is shorter than the 2nd path.
When high resistance brushes are used, then as the brush moves towards the commutator segments, the contact area of the brush and the segment b decreases and contact area with the segment a increases. Now, as the electrical resistance is inversely proportional to the contact area of then resistance Rb will increase and Ra will decrease as the brush moves. Then the current will prefer the 2nd path to reach to the brush.
This method ensures the quick reversal of current in the desired direction, improving commutation.
ρ is the resistivity of the conductor.
l is the length of the conductor.
A is the cross-section of the conductor (here is this description it is used as contact area).
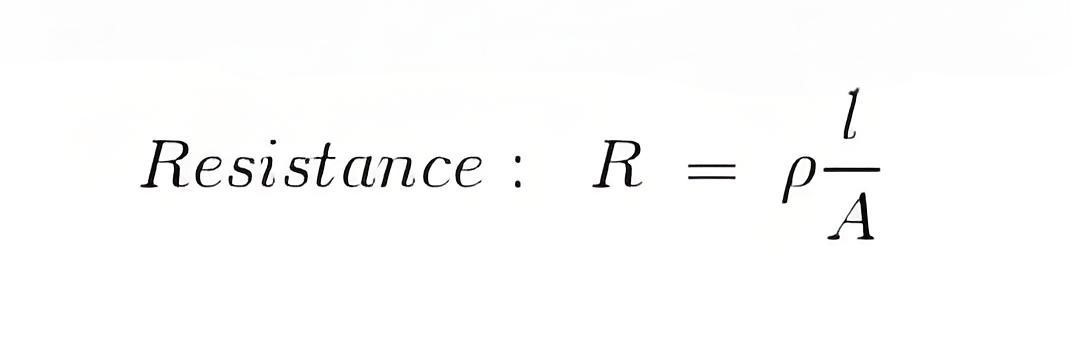
E.M.F. Commutation
The main reason of the delay of the current reversing time in the short circuit coil during commutation period is the inductive property of the coil. In this type of commutation, the reactance voltage produced by the coil due to its inductive property, is neutralized by producing a reversing emf in the short circuit coil during commutation period.
Reactance Voltage
The voltage rise in the short circuit coil due to inductive property of the coil, which opposes the current reversal in it during the commutation period, is called the reactance voltage.
We can produce reversing emf in two ways
By brush shifting.
By using inter-poles or commutating poles.
Brush Shifting Method of Commutation
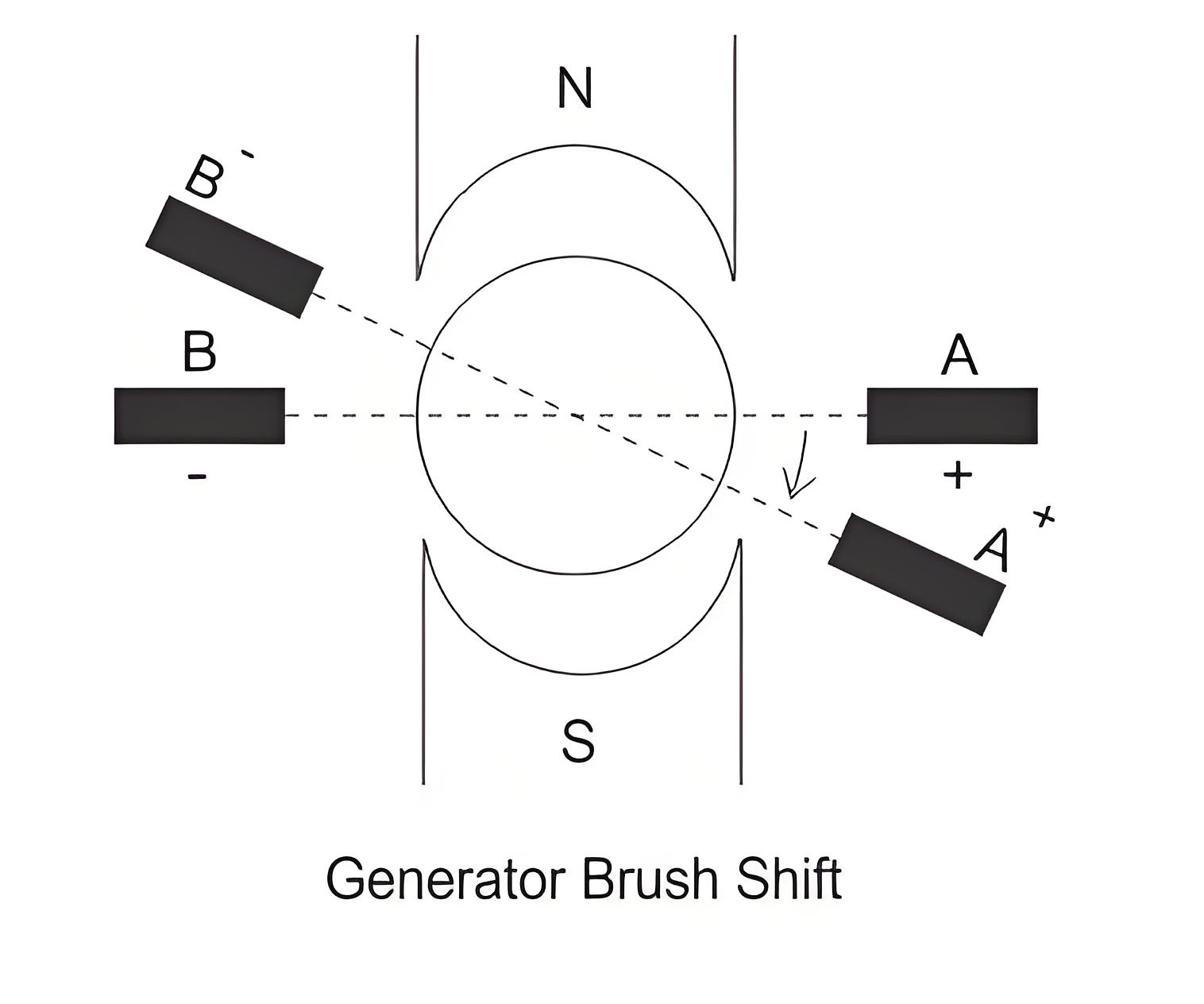
In this method of improving commutation the brushes are shifted forward direction for the DC generator and in backward direction for the motor for producing the sufficient reversing emf for eliminating the reactance voltage. When the brushes are given the forward or backward lead then it brings the short circuit coil under the influence of the next pole which is of the opposite polarity. Then the sides of the coil will cut the necessary flux form the main poles of opposite polarity for producing the sufficient reversing emf. This method is rarely used because for best result, with every variation of load, the brushes have to be shifted.
Method of Using Inter-Pole
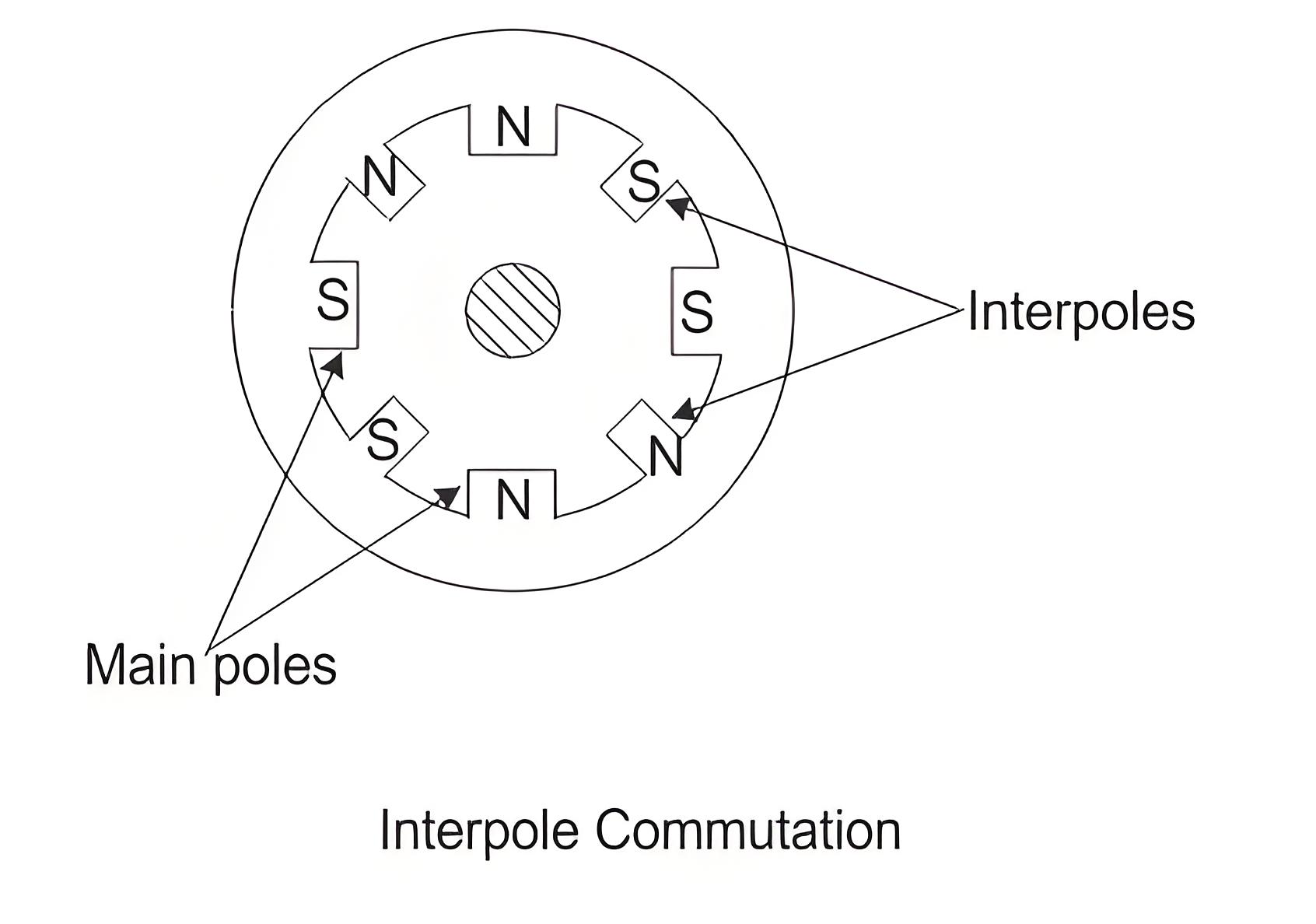
In this method, small poles called inter-poles are fixed to the yoke and placed between the main poles. For generators, their polarity matches the adjacent main poles, and for motors, it matches the preceding main poles. The inter-poles induce an emf in the short circuit coil during the commutation period, opposing the reactance voltage and ensuring spark-less commutation.
Compensating Windings
This is the most effective mean of eliminating the problem of armature reaction and flash over by balancing the armature mmf. Compensating windings are placed in slots provided in pole faces parallel to the rotor (armature) conductors.
The major drawback of compensating windings is their high cost. They are mainly used in large machines subject to heavy overloads or plugging and in small motors requiring sudden reversal and high acceleration.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.