What is DC Shunt Motor?
What is DC Shunt Motor?
DC Shunt Motor Definition
A DC shunt motor is defined as a type of DC motor where the field windings are connected in parallel to the armature winding, allowing both to receive the same voltage.
Constant Flux
The DC shunt motor is a constant flux motor because the field flux remains nearly constant due to the parallel connection of the windings.
DC Shunt Motor Equations
In a DC shunt motor, the supply current splits into two parts: Ia, flowing through the armature winding of resistance Ra and Ish, flowing through the field winding with resistance Rsh. The voltage across both windings stays the same.
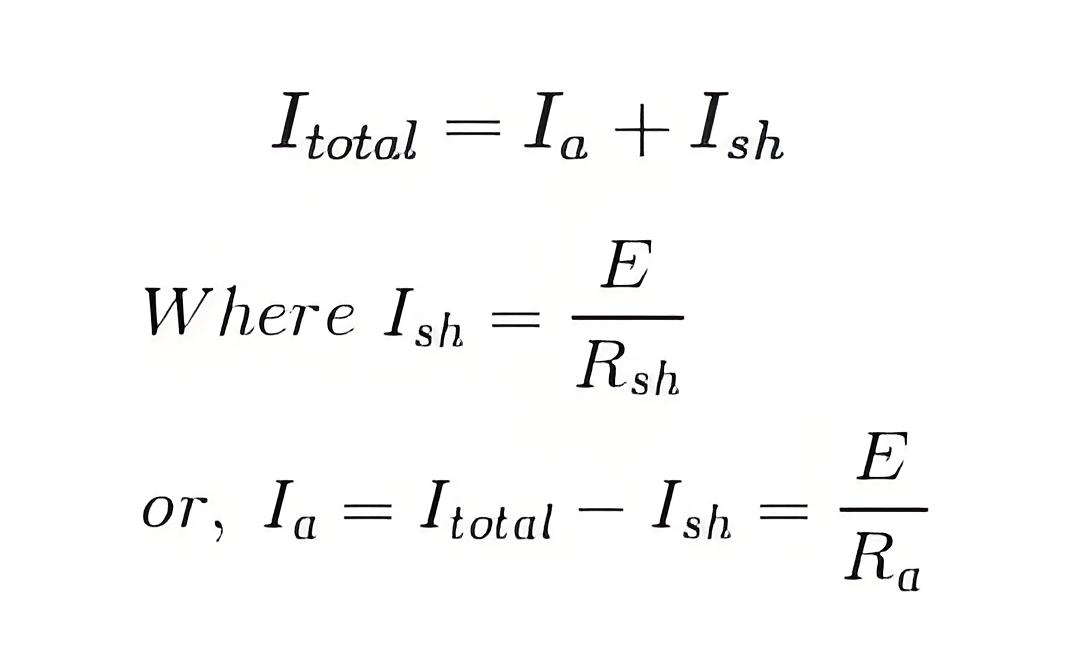
Thus we put this value of armature current Ia to get general voltage equation of a DC shunt motor.
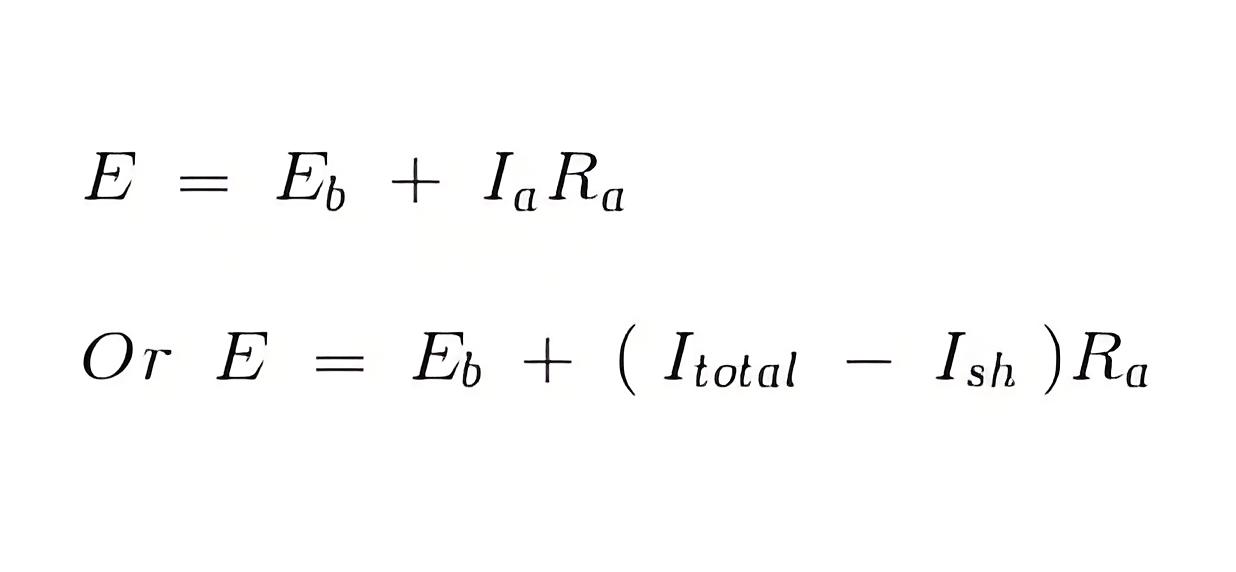
Now in general practice, when the motor is in its running condition, and the supply voltage is constant and the shunt field current given by,
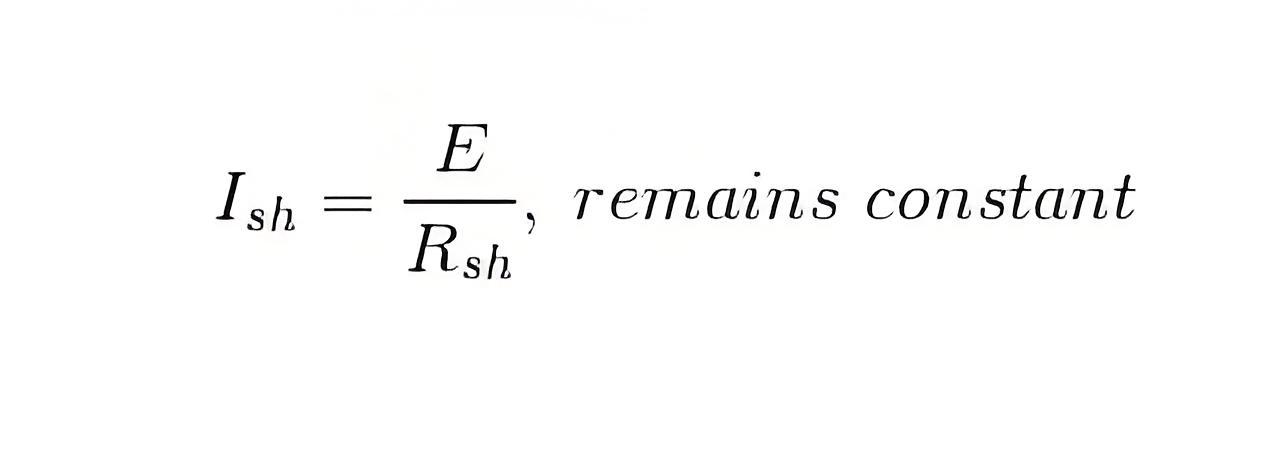
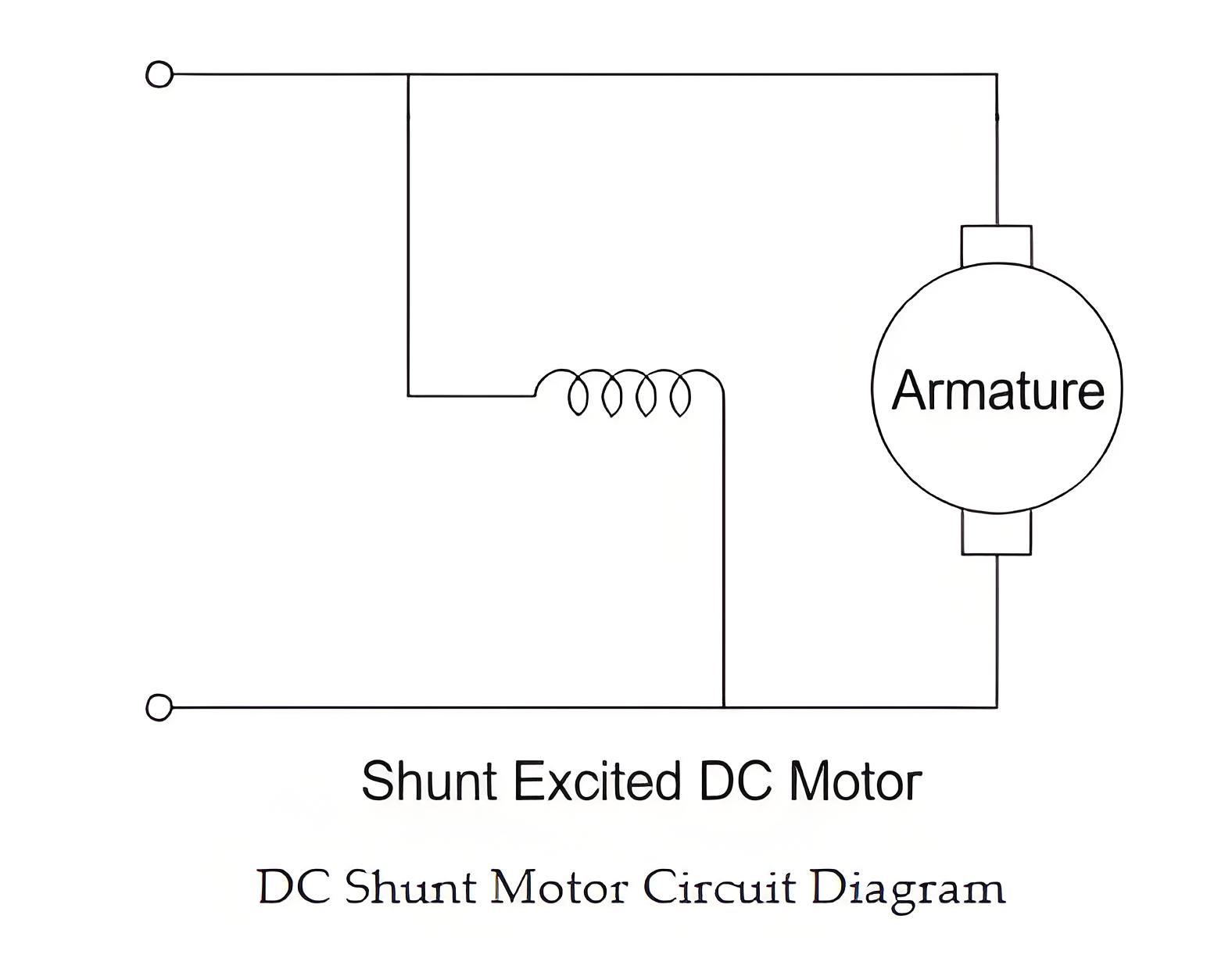
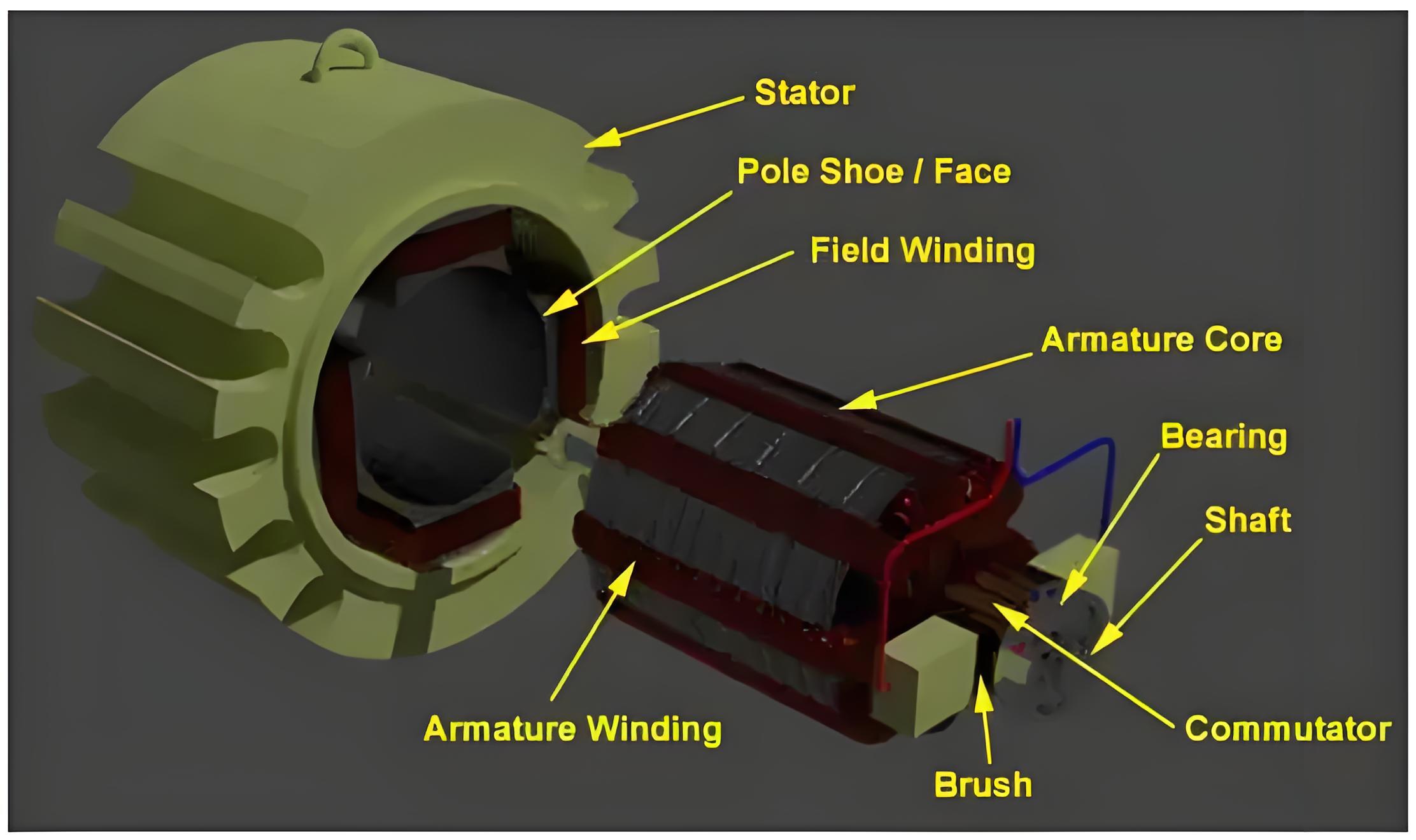
Construction of a Shunt Wound DC Motor
The construction of a dc shunt motor is pretty similar to other types of DC motor, as shown in the figure below
Self-Speed Regulation
DC shunt motors can self-regulate their speed when the load changes, maintaining a steady speed without external modifications.
Torque and Speed Relationship
In a DC shunt motor, the torque is proportional to the armature current, which helps the motor adjust its speed when the load varies.
Industrial Use
DC shunt motors are popular in industrial applications where constant speed operation is essential, thanks to their self-regulating speed feature.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.