What is are Losses in DC Machine ?
What is are Losses in DC Machine ?
DC Machine Losses Definition
In a DC machine, losses refer to the input power that doesn’t convert into useful output power, reducing efficiency.
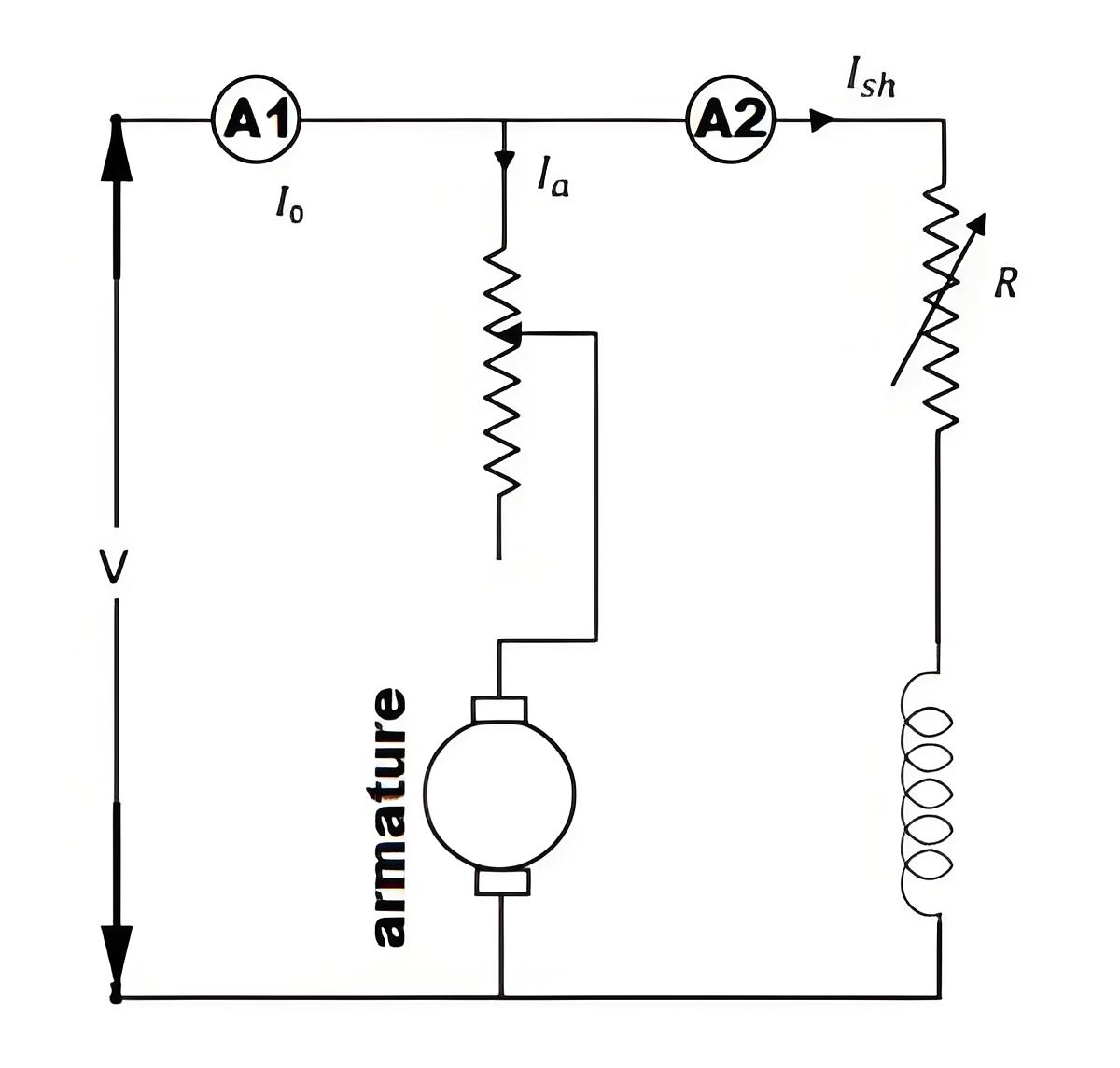
Copper Losses
These occur in the windings due to resistance and are divided into armature loss, field winding loss, and brush contact resistance loss.
Armature copper loss = Ia2Ra
Where, Ia is armature current and Ra is armature resistance.
These losses are about 30% of the total full load losses.
Core Losses
These include hysteresis loss, due to the constant reversal of magnetization in the armature, and eddy current loss, caused by induced emf in the iron core.
Mechanical Losses
The losses associated with mechanical friction of the machine are called mechanical losses. These losses occur due to friction in the moving parts of the machine like bearing, brushes etc, and windage losses occur due to the air inside the rotating coil of the machine. These losses are usually very small about 15% of full load loss.
Hysteresis Loss in DC Machine
This specific type of core loss occurs due to the reversal of magnetization in the armature core, consuming energy.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.