What is Compound Wound DC Motor?
What is Compound Wound DC Motor?
Compound Wound DC Motor Definition
A compound wound DC motor (also known as a DC compound motor) is defined as a self-excited motor using both series and shunt field coils to combine the benefits of high starting torque and good speed regulation.
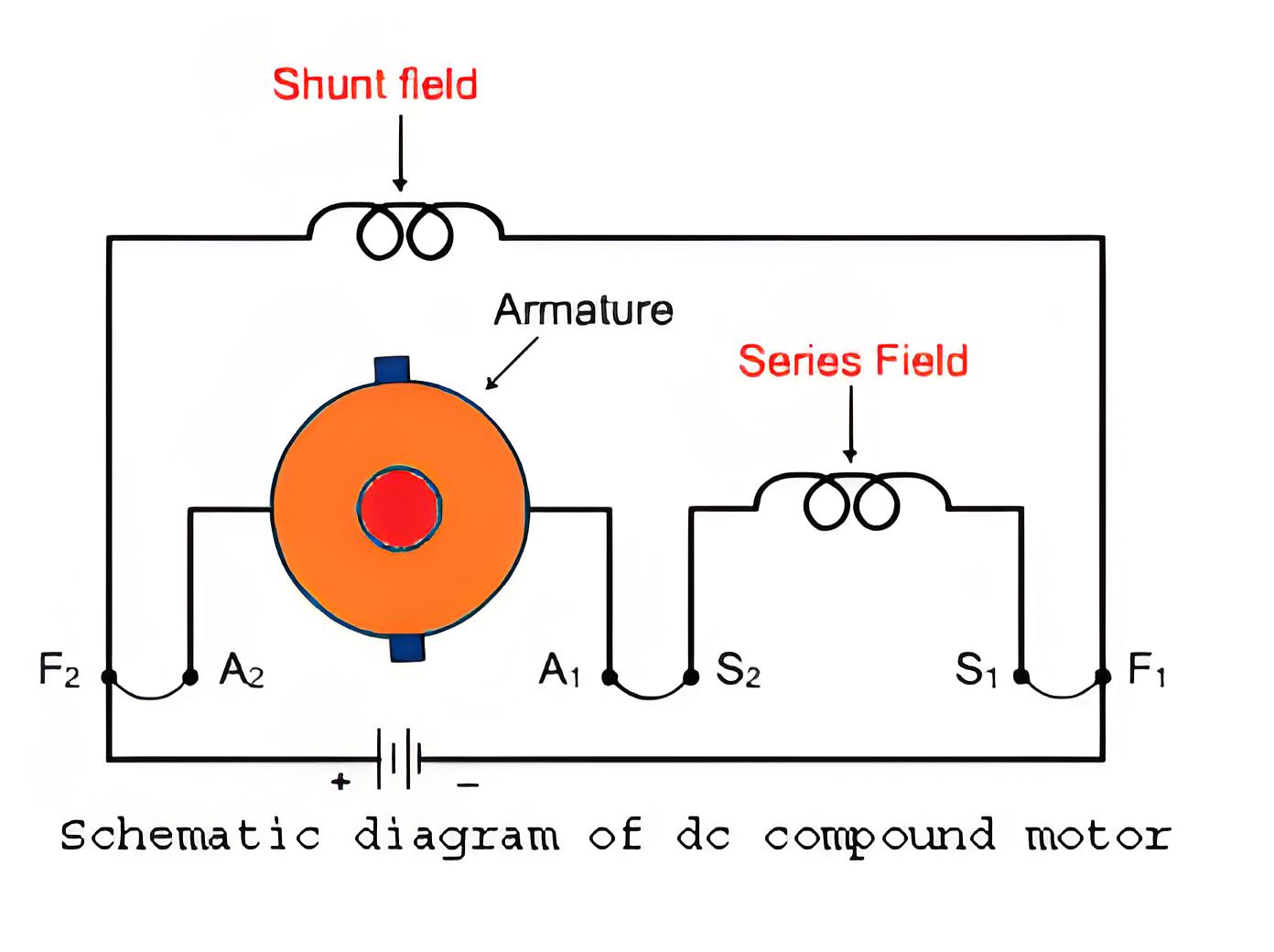
Types of Compound Wound DC Motors
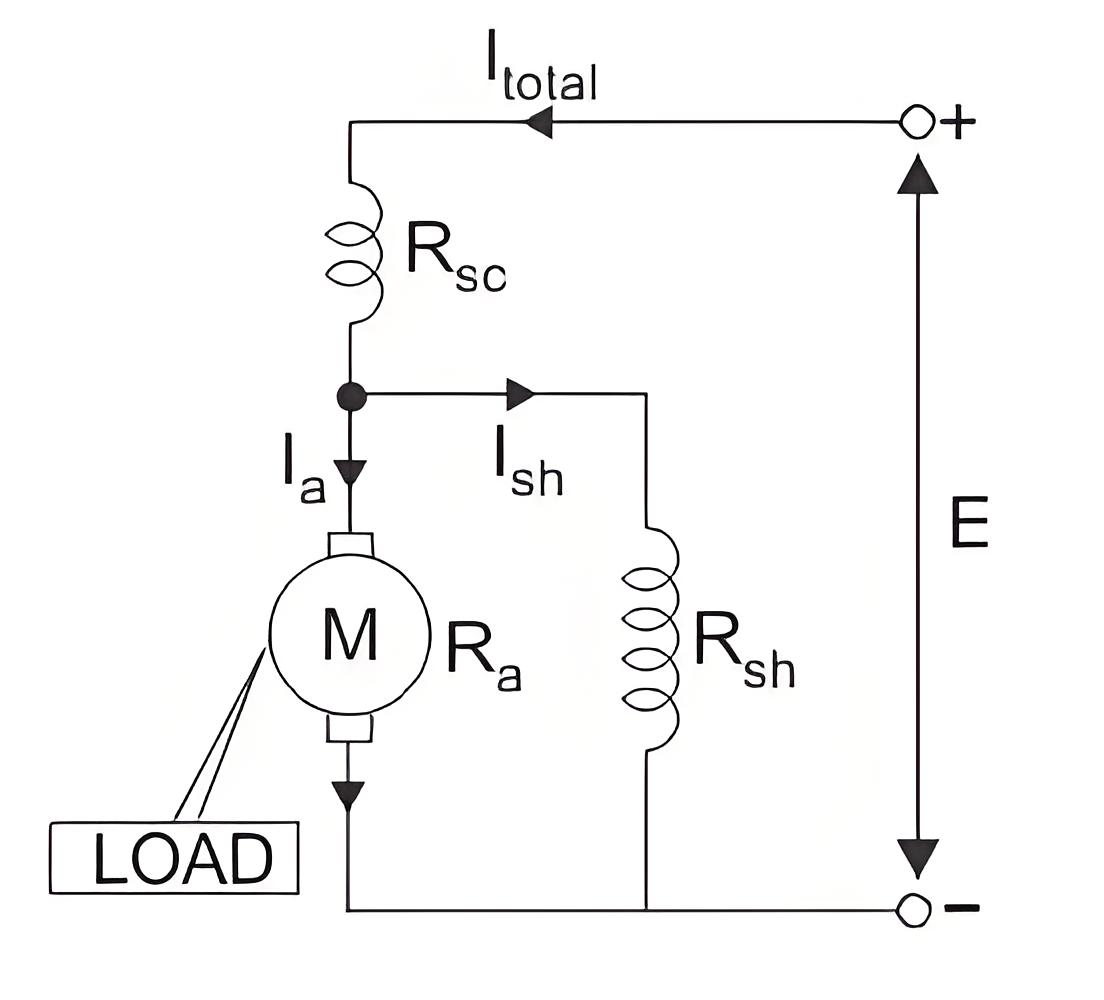
Long Shunt Compound Wound DC Motor
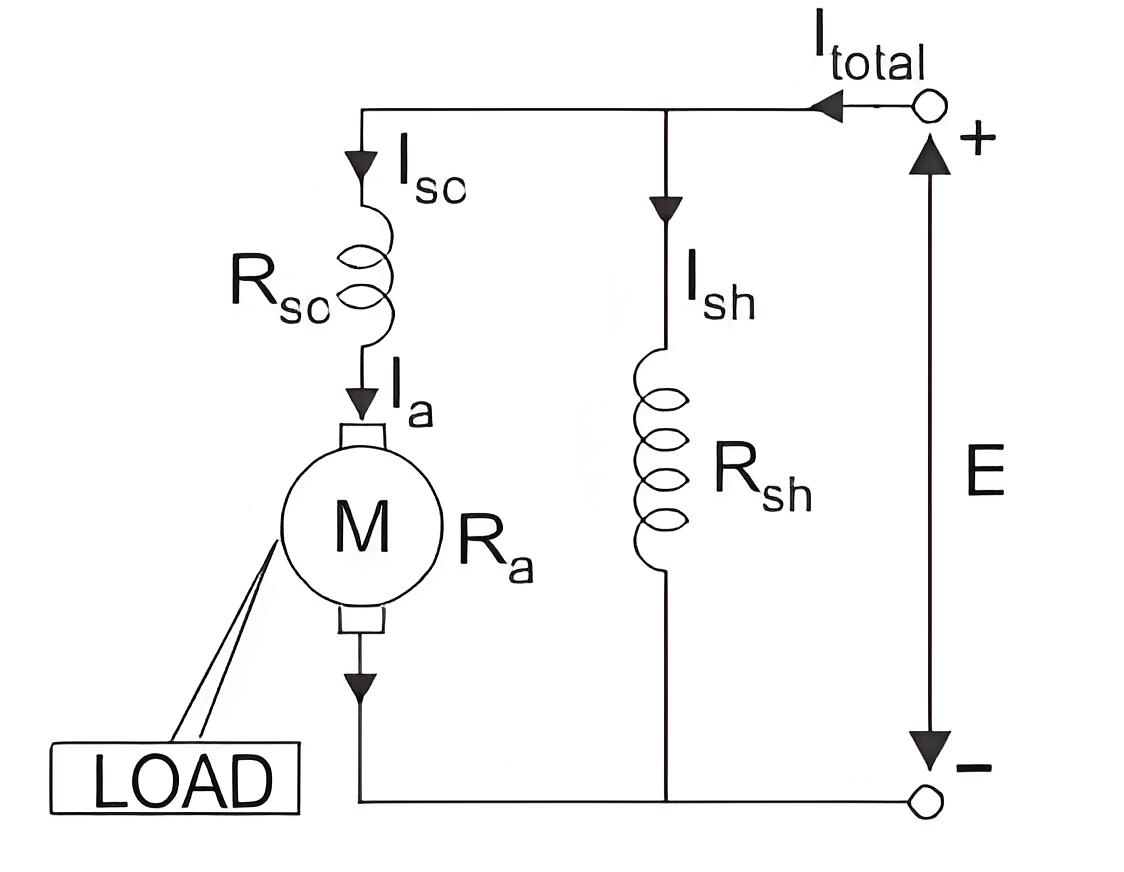
Voltage and Current Equation of Long Shunt Compound Wound DC Motor
Let E and Itotal be the total supply voltage and current supplied to the input terminals of the motor. And Ia, Ise , Ish be the values of current flowing through armature resistance Ra, series winding resistance Rse and shunt winding resistance Rsh respectively.Now we know in shunt motor.And in series motor
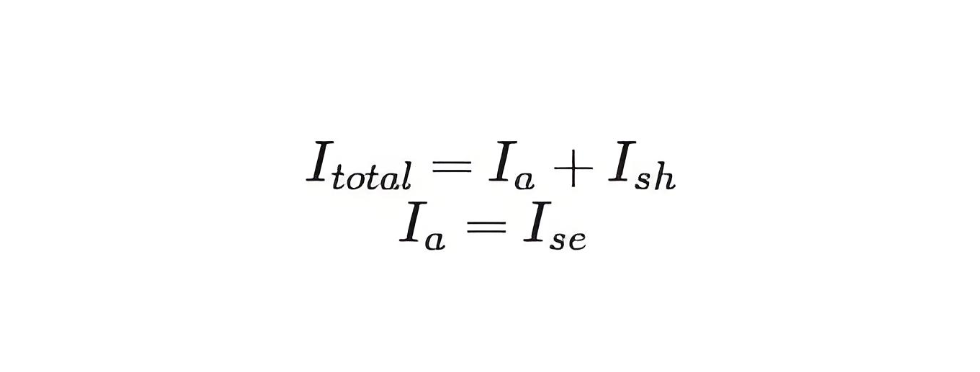
Therefore, the current equation of a compound wound DC motor is given by
And its voltage equation is,
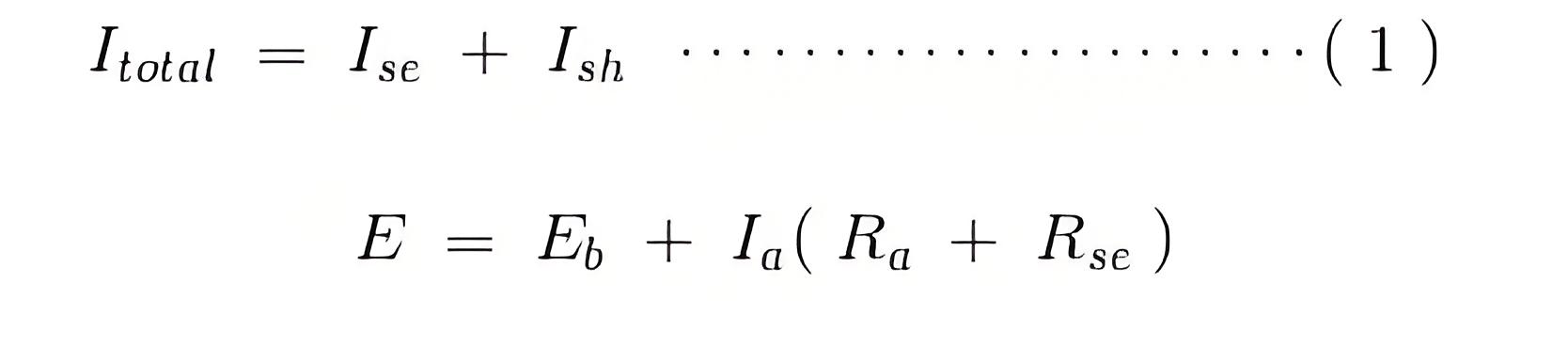
Short Shunt Compound Wound DC Motor
Apart from the above mentioned classification, a compound wound DC motor can further be sub divided into 2 types depending upon excitation or the nature of compounding. i.e.
Voltage and Current Equations
The voltage and current equations for compound wound DC motors can be derived using Kirchhoff’s laws, tailored to each motor type’s configuration.
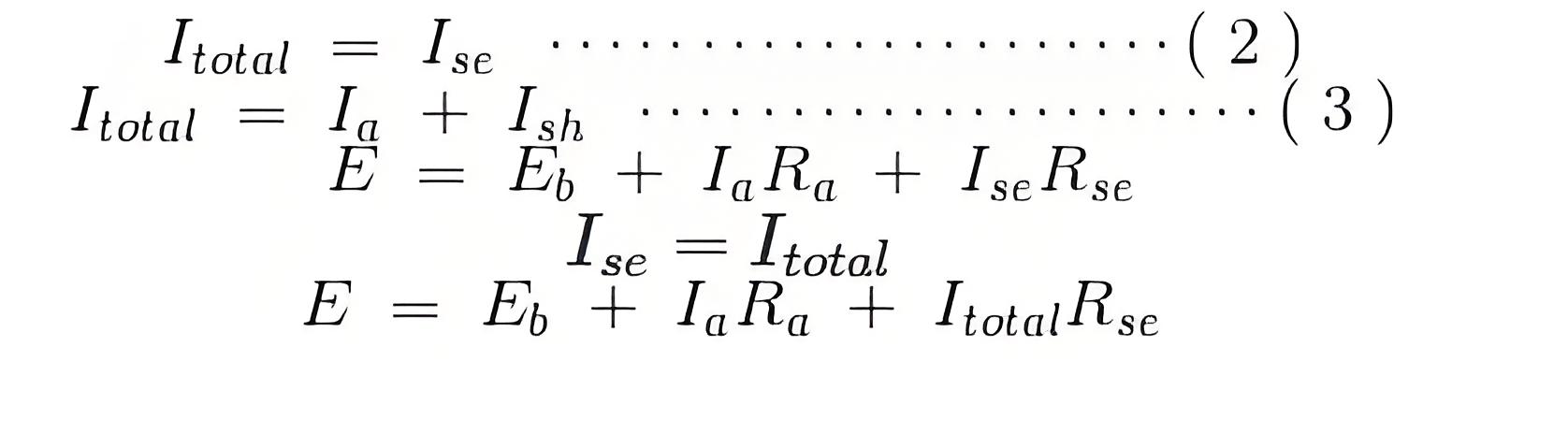
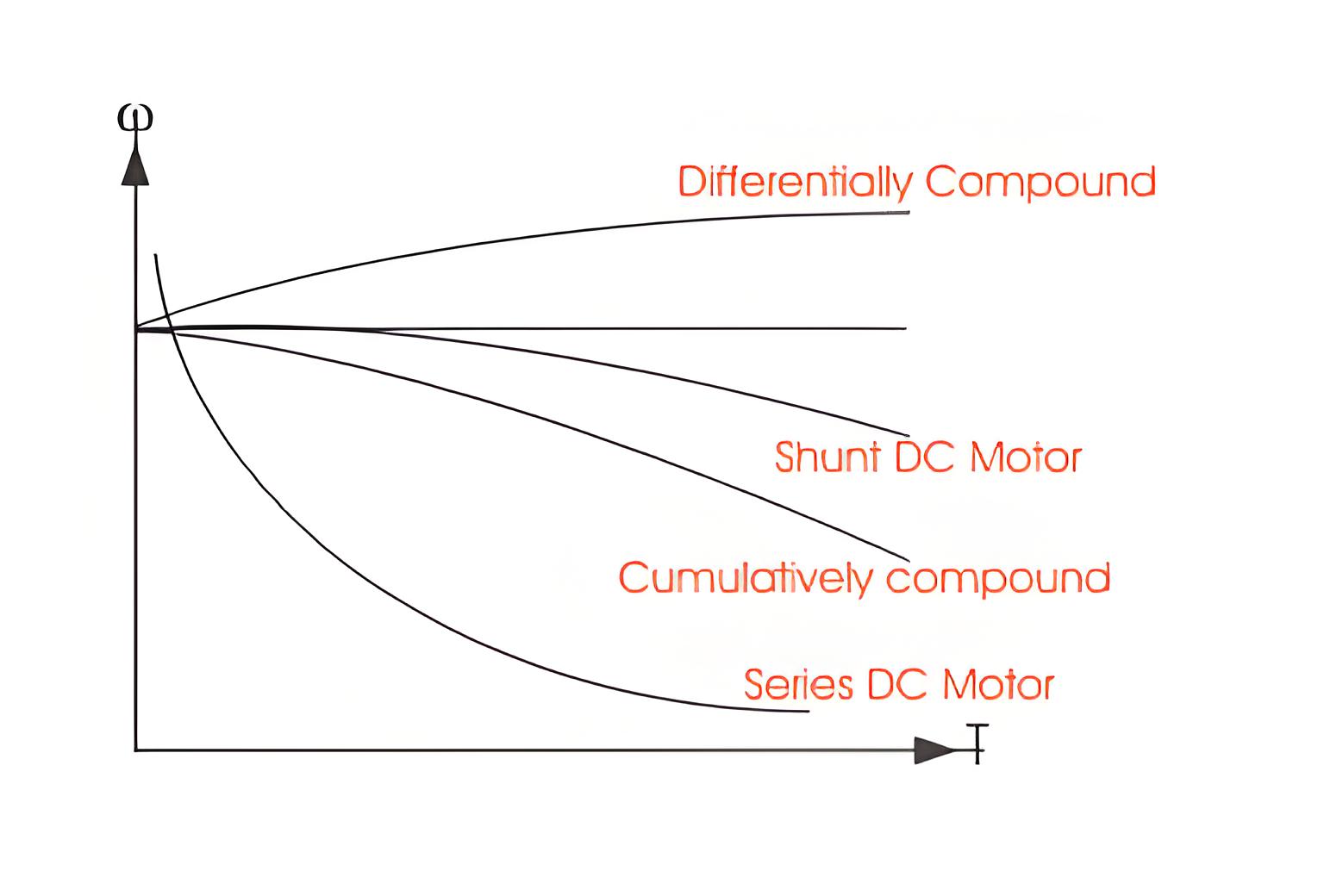
Cumulative Compounding
In cumulatively compounded motors, the shunt field flux supports the main field flux, enhancing the motor’s performance.
Differential Compounding
Differentially compounded motors have shunt field flux that opposes the main field flux, reducing overall flux and making these motors less practical for most applications.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.