What is a Centrifugal Switch?
What is a Centrifugal Switch?
Centrifugal Switch Definition
A centrifugal switch is an electrical component that activates based on the centrifugal force generated by a motor’s rotating shaft to control motor start-up.
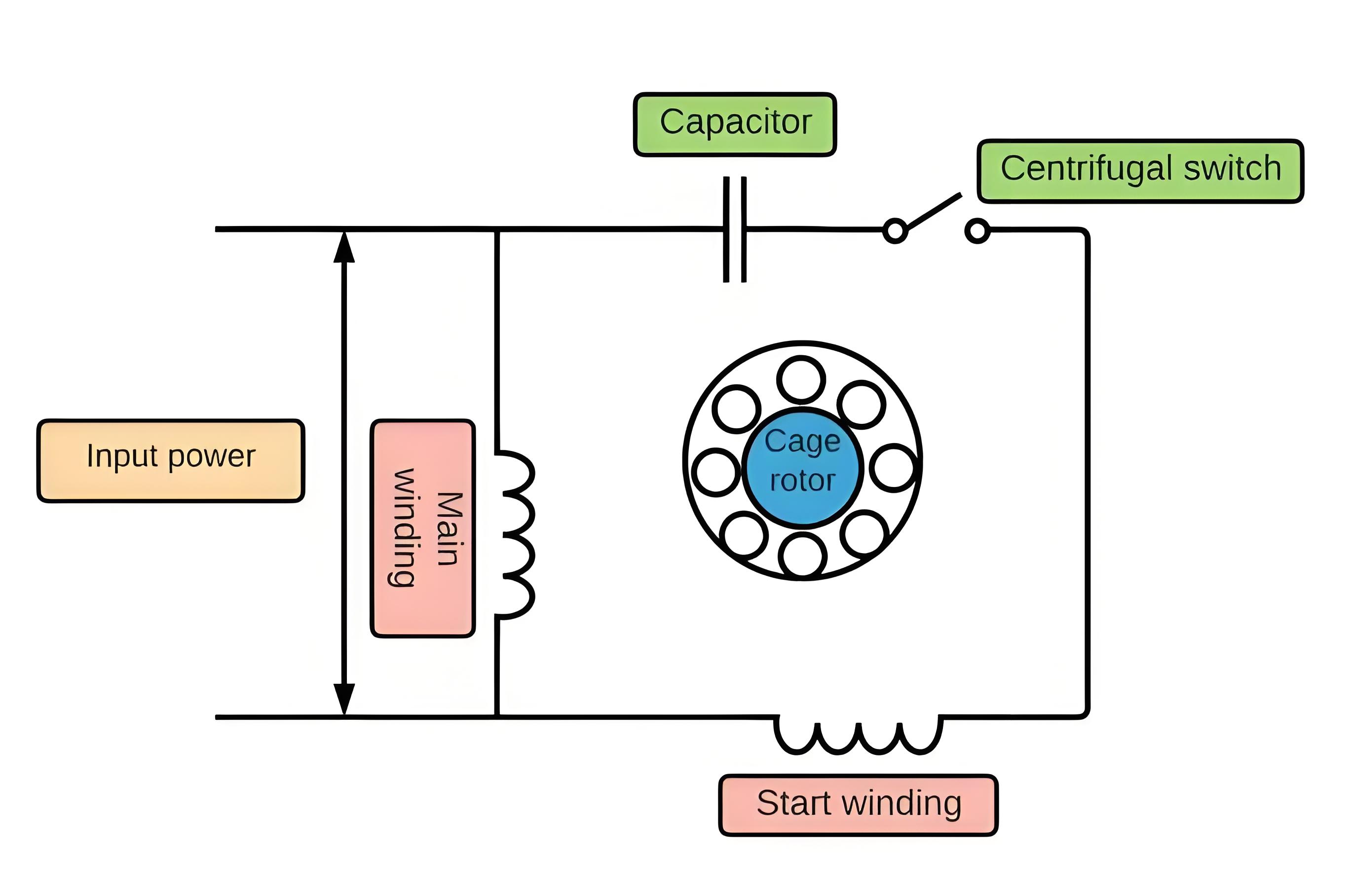
Operational Mechanism
A single-phase AC engine has a centrifugal switch inside its case, which is attached to the engine shaft. When the engine is off and motionless, the switch is closed.
When the engine is switched on, the switch drives electricity to the capacitor and the extra coil winding in the engine, increasing its starting torque. As the engine’s revolutions increase per minute, the switch opens, as the engine no longer needs a boost.
A centrifugal switch solves a problem associated with single-phase AC electric motors. They do not develop enough torque on their own to start turning from a dead stop.
A circuit switches on the centrifugal switch, providing the requisite boost to start the motor. The switch turns off the boost circuit until the motor reaches its running speed, and the motor runs normally.
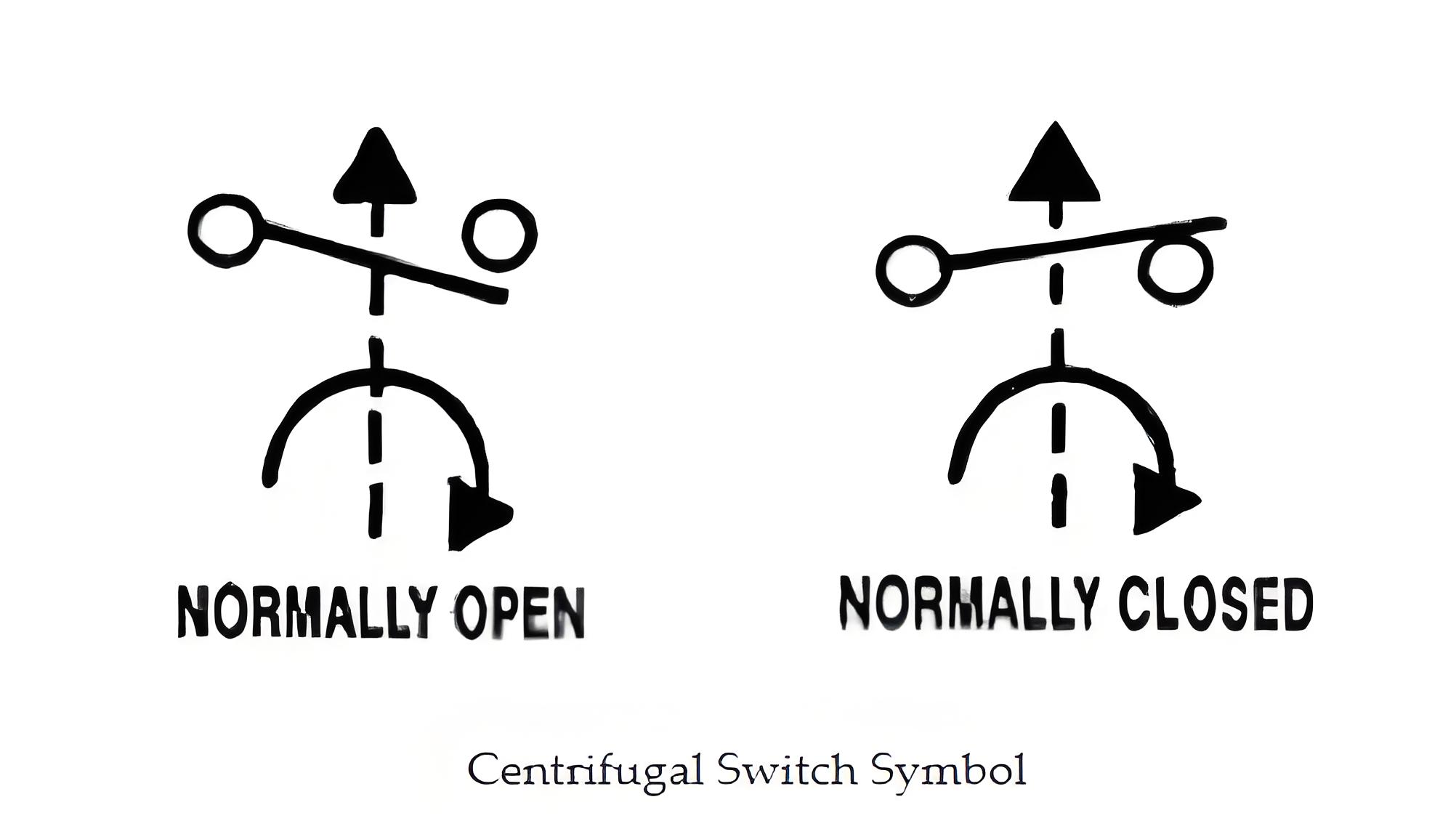
Symbol and Schematic
The symbol of a centrifugal switch in electrical schematics represents its function and connection within an electrical or electronic circuit.
Testing Protocols
Throughout its life cycle, the process should be uniform.
For simplicity of design and low production cost, the number of components of the equipment should be minimal.
It should have marginal elements of friction.
Without causing any significant design changes, the cut-out/cut-in ratio should be readily modifiable.
The switch is readily accessible as the communication unit of the switch is present on the outside of the motor frame. So, without dismantling the motor assembly, the switch can be tested, washed, and replaced.
Impact of Malfunction
If the centrifugal switch fails to disconnect after the motor starts, it can cause the starting winding to burn out, highlighting the importance of proper switch function for motor longevity.
Applications of a Centrifugal Switch
Defense against Overspeed in motors, generators, etc.
Used in DC motors, conveyors, escalators, lifts, etc.
These are also used in devices such as blowers, fans as well as conveyors to detect under-speed.
Material losses are often used in systems where the loss of speed could lead to damage of the device.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.