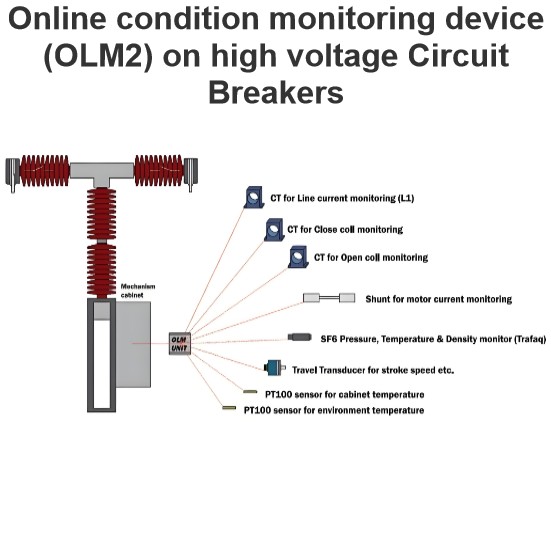
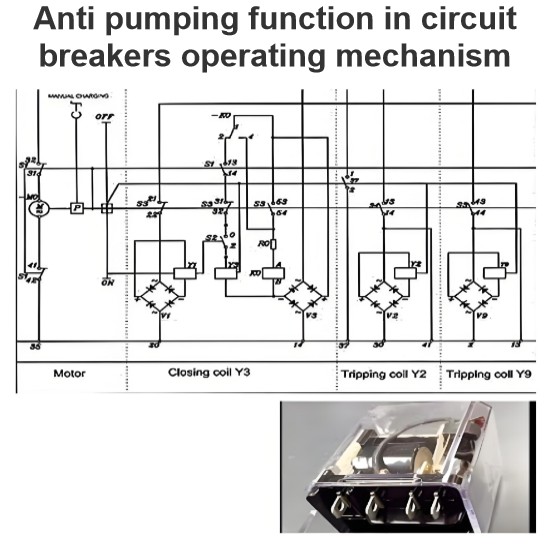
Online monitoring of high voltage circuit breaker parameters with optical fibre techniques
Sensing Principles
Sensing principles involve detecting changes in the state of light polarization due to various physical phenomena. These include:
• Pockels Effect: Changes in polarization caused by an electric field.
• Faraday Effect: Changes in polarization caused by a magnetic field.
• Photoelasticity: Changes in polarization due to mechanical stress.
• Thermochromic Effects: Changes in light characteristics due to temperature variations.
• Mechanical Vibration: Changes in the spatial distribution of light caused by mechanical vibrations.
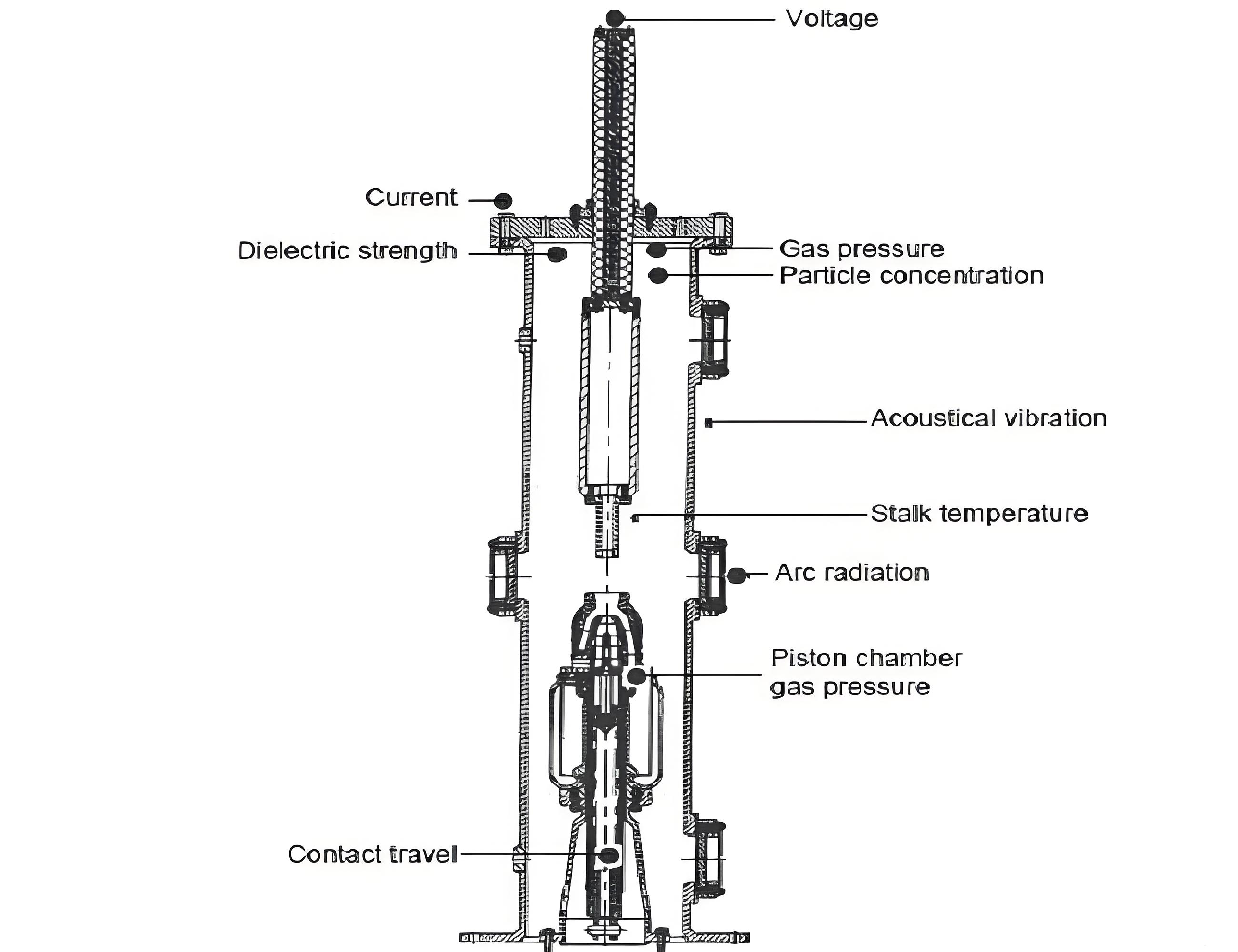
High Voltage Gas Blast Interrupter with Optical Fiber Chromatic Sensors
The figure illustrates a schematic diagram of a high voltage gas blast interrupter, highlighting various types of optical fiber chromatic sensors deployed for monitoring different parameters. These sensors include:
• Gas Pressure Sensors: Monitoring gas pressures in the interrupter tank and piston chamber using Fabry-Perot pressure sensors.
• Contact Potential Sensors: Measuring the potential difference across contacts.
• Fault Current Sensors: Detecting fault currents within the system.
• Temperature Sensors: Monitoring the temperature of the contact stalk.
• Contact Travel Sensors: Using chromatic linear scales to measure the movement of contacts.
• Mechanical Vibration Sensors: Detecting vibrations during operation.
• Arc Radiation Sensors: Monitoring radiation emitted by arcs during interruption.
Time Variation Data During Circuit Breaker Operation
The time variation data for key parameters during circuit breaker operation are as follows:
• Piston Chamber Pressure: Measured using a Fabry-Perot pressure sensor.
• Contact Travel: Monitored using a chromatic linear scale.
• Mechanical Vibration: Detected during the breaker's operation.
These datasets provide valuable insights into the conditions that occur during the fault current interruption process. By analyzing this information together, a better understanding of the interrupter's operation can be achieved, leading to improved performance and reliability.
Translation and Polished Version
Sensing Principles
Sensing principles involve detecting changes in the state of light polarization due to various physical phenomena. These include:
• Pockels Effect: Changes in polarization caused by an electric field.
• Faraday Effect: Changes in polarization caused by a magnetic field.
• Photoelasticity: Changes in polarization due to mechanical stress.
• Thermochromic Effects: Changes in light characteristics due to temperature variations.
• Mechanical Vibration: Changes in the spatial distribution of light caused by mechanical vibrations.
High Voltage Gas Blast Interrupter with Optical Fiber Chromatic Sensors
The figure shows a schematic diagram of a high voltage gas blast interrupter, indicating various types of optical fiber chromatic sensors that have been deployed. These sensors include:
• Gas Pressure Sensors: Monitoring gas pressures in the interrupter tank and piston chamber using Fabry-Perot pressure sensors.
• Contact Potential Sensors: Measuring the potential difference across contacts.
• Fault Current Sensors: Detecting fault currents within the system.
• Temperature Sensors: Monitoring the temperature of the contact stalk.
• Contact Travel Sensors: Using chromatic linear scales to measure the movement of contacts.
• Mechanical Vibration Sensors: Detecting vibrations during operation.
• Arc Radiation Sensors: Monitoring radiation emitted by arcs during interruption.
Time Variation Data During Circuit Breaker Operation
The time variation data for key parameters during circuit breaker operation are as follows:
• Piston Chamber Pressure: Measured using a Fabry-Perot pressure sensor.
• Contact Travel: Monitored using a chromatic linear scale.
• Mechanical Vibration: Detected during the breaker's operation.
Such data taken together provide insight into the various conditions that occur during the fault current interruption process, so that an improved understanding of the interrupter operation can be obtained.