Different types of breakers and switches to be used in grids
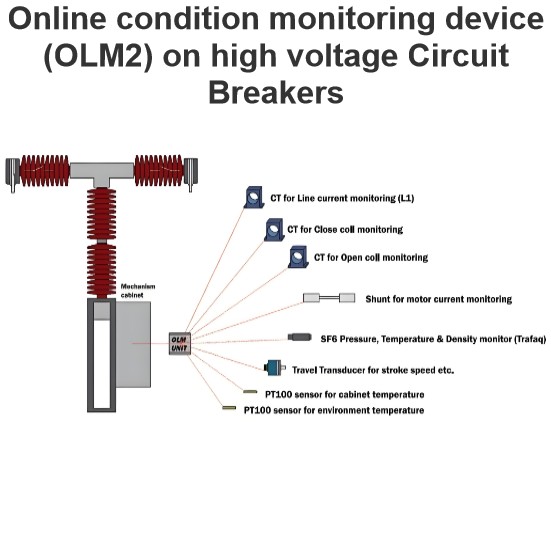
Circuit Breakers
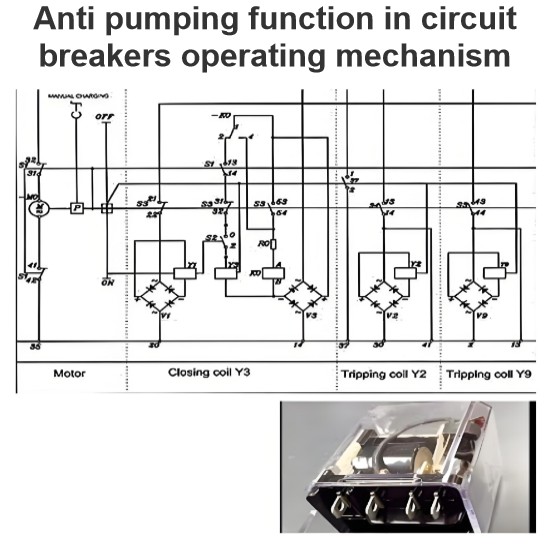
Circuit breakers (CBs) are designed to switch on and off any type of current up to their rated current. This includes both load currents and short-circuit currents. CBs installed in overhead systems should be capable of performing successful and unsuccessful auto-reclosing operations.
Load Break Switches
Load break switches (LBS) can handle switching load currents under normal operating conditions but lack the capability to switch short-circuit currents. They are suitable for normal load management but not for fault conditions.
Disconnecting Switches
Disconnecting switches (DSs) can only be operated under no-load conditions. They are used to switch currents from busbars without load and no-load currents of low-rated transformers. Interlocking with circuit breakers (CBs) is necessary to ensure safe operation.
Earthing Switches
Earthing switches (ESs) are used for grounding equipment. It is common to combine ESs with DSs for safety purposes.
Fuses
Fuses are typically installed in low voltage (LV) and medium voltage (MV) systems. They interrupt currents by melting a specially designed conductor and must be replaced after operation. In LV systems, fuses are often combined with disconnecting switches (DSs).
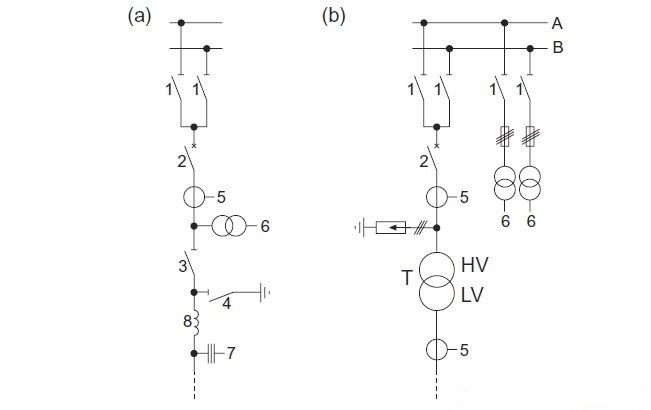
Typical Feeder Arrangement for HV Switchgear
The following describes two typical arrangements for HV switchgear feeders, as shown in the diagram:
(a) Overhead Line Feeder with Double Busbar
- Busbar DS: A disconnecting switch connected to the busbar.
- CB: A circuit breaker that can handle load and short-circuit currents.
- Feeder DS: A disconnecting switch connected to the feeder line.
- ES: An earthing switch for grounding.
- CT: Current transformer for measuring current.
- VT: Voltage transformer for measuring voltage.
- CVT: Capacitive voltage transformer for additional measurements.
- Blocking Reactor: Used to limit fault currents or provide reactive power compensation.
(b) Transformer Feeder with Double Busbar
- Busbar DS: A disconnecting switch connected to the busbar.
- CB: A circuit breaker that can handle load and short-circuit currents.
- Feeder DS: A disconnecting switch connected to the transformer feeder.
- ES: An earthing switch for grounding.
- CT: Current transformer for measuring current.
- VT: Voltage transformer for measuring voltage.
- CVT: Capacitive voltage transformer for additional measurements.
- Blocking Reactor: Used to limit fault currents or provide reactive power compensation.
Diagram Explanation
The diagrams illustrate two configurations:
- Overhead Line Feeder with Double Busbar: This setup allows for flexibility in switching between different lines and provides redundancy through the double busbar system.
- Transformer Feeder with Double Busbar: This configuration ensures reliable operation and maintenance of transformers by providing a redundant path through the double busbar system.
Both configurations include essential components like circuit breakers, disconnecting switches, earthing switches, current transformers, voltage transformers, capacitive voltage transformers, and blocking reactors to ensure safe and efficient operation of the HV switchgear.