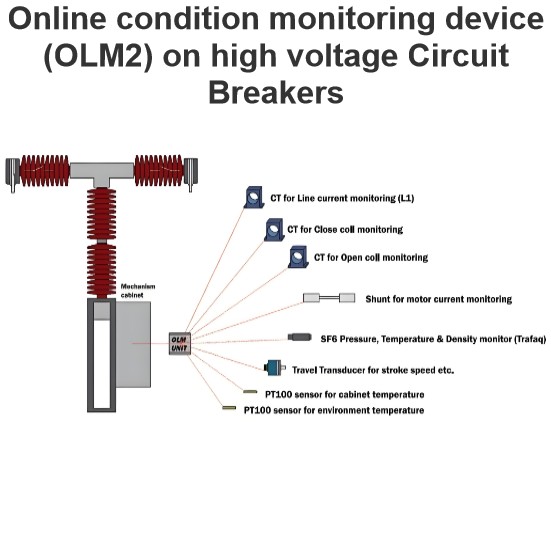
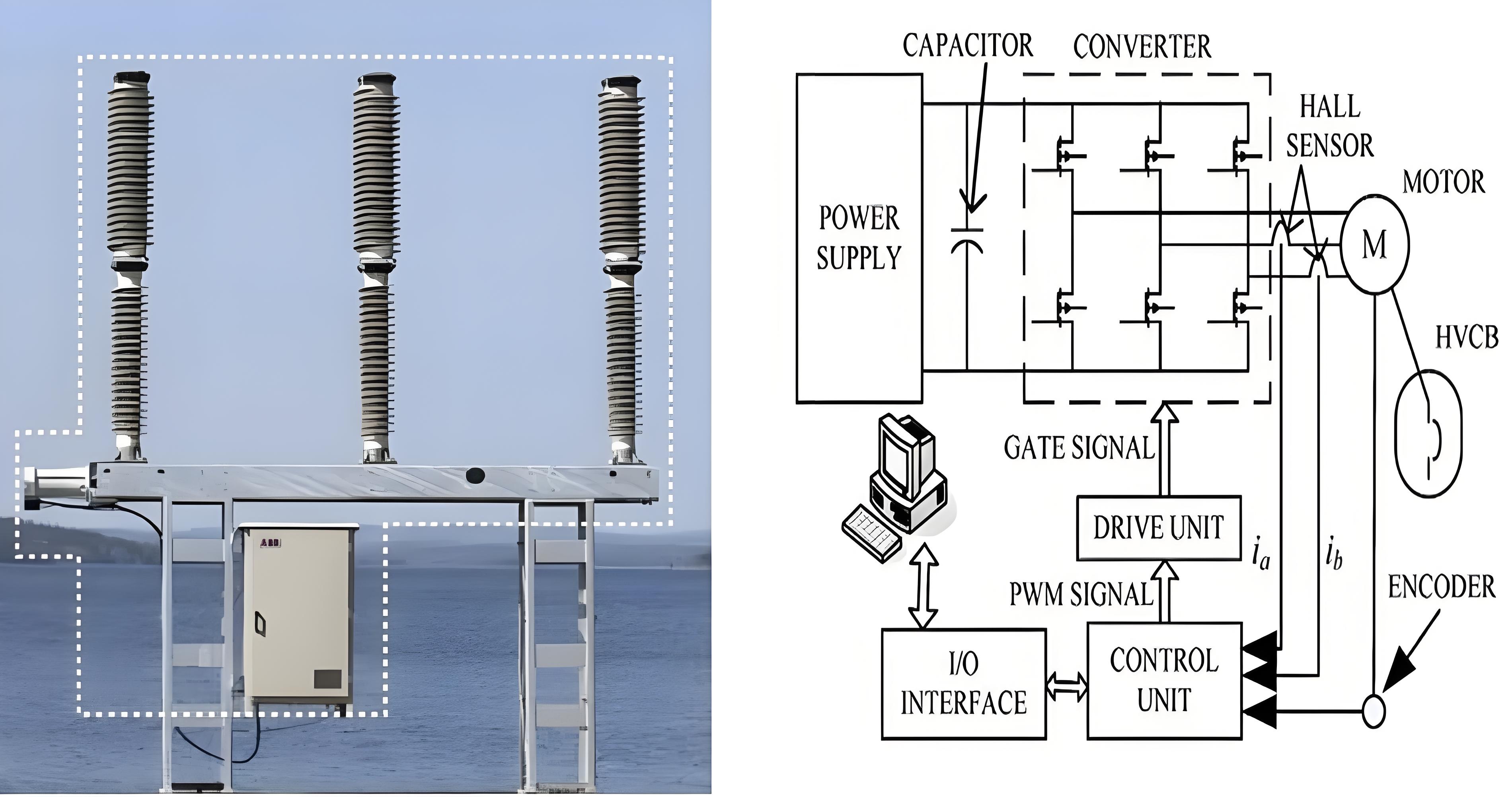
Motor drive mechanism for HV CB
Edwiin
01/10/2025
Major Advantages of Motor Drives
Motor drives offer several significant advantages:
- Elimination of Wearing Components: Reduces maintenance needs and extends equipment lifespan.
- Reduction in Operating Forces: Lowers the physical effort required to operate machinery.
- Substantial Reduction in Noise Levels: Enhances operational comfort and reduces noise pollution.
- Increased Reliability: Improves system stability and reduces downtime.
Components of a Motor Drive Mechanism
The motor drive mechanism primarily consists of:
- AC/DC Power Supply: Converts electrical energy into a form suitable for driving the motor.
- Energy Buffer Capacitors: Act as energy storage units to provide large transient currents during operation, minimizing the impact on the power supply.
- Converter: Composed of Intelligent Power Modules (IPMs), which convert electrical energy into the appropriate form for motor use.
- Control Unit: Manages the overall operation of the drive system.
- Motor: Typically a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) used for applications requiring rapid torque response and high-performance operation.
Key Features and Sensors
- Energy Buffer Capacitors: These capacitors store energy to meet the high transient current demands during circuit breaker (CB) operation, thereby reducing the strain on the power supply.
- Converter: Utilizes IPMs for efficient and reliable power conversion.
- Hall Sensors: Measure stator current to monitor motor performance and ensure precise control.
- Optical Encoder: Installed on the motor shaft, it measures motor speed and rotor position, providing critical feedback for control algorithms.
Vector Control Method for PMSM
The vector control method is employed to manage the PMSM effectively:
- Basic Concept: Decomposes the stator current into two components:
- Magnetic Field-Generating Component: Controls the magnetic field strength.
- Torque-Generating Component: Controls the torque output.
- Separate Control: By treating these components separately, the motor can be controlled similarly to a DC machine, allowing for precise speed and torque regulation.
Speed and Torque Control
In PMSM systems, speed and torque are independently controlled:
- Speed Control: Adjusts the rotational speed of the motor based on the application requirements.
- Torque Control: Manages the force applied by the motor to achieve desired performance levels.
Conclusion
Motor drives, particularly those utilizing PMSMs with advanced vector control methods, offer enhanced performance, reliability, and efficiency. The integration of energy buffer capacitors, intelligent converters, and precise sensors ensures smooth and dependable operation, making them ideal for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.