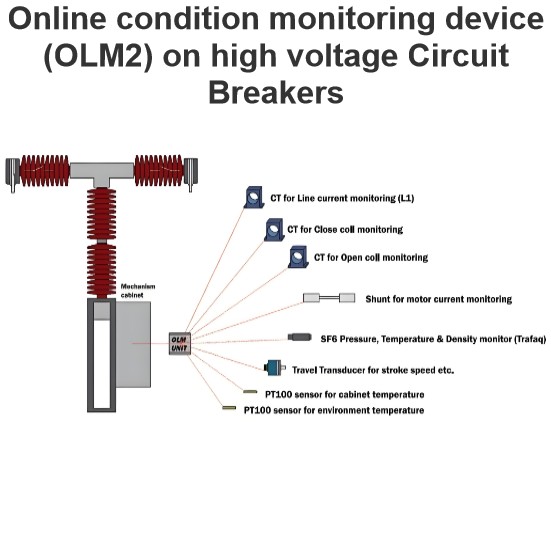
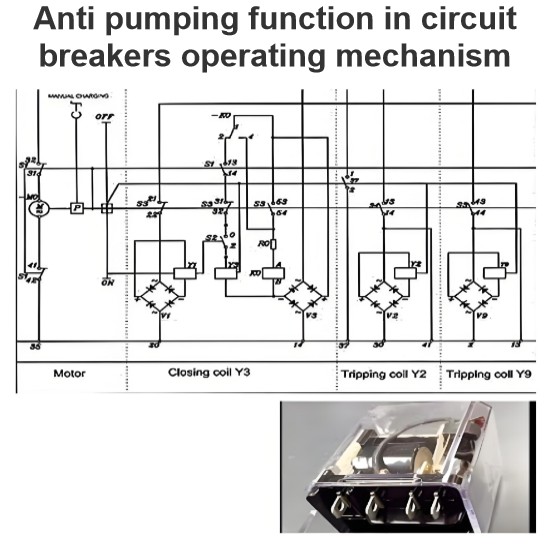
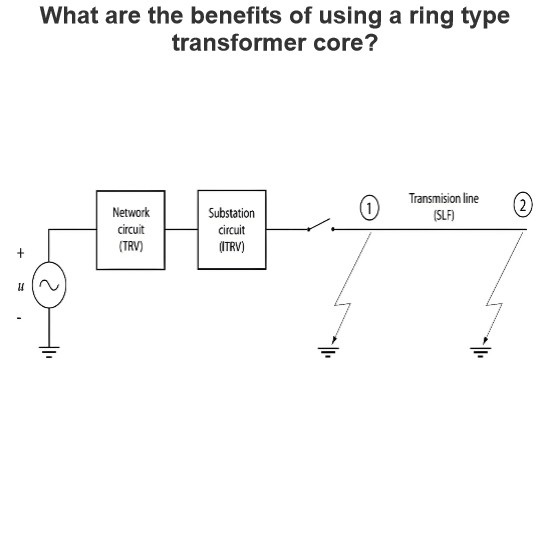
Pneumatic operating mechanism in switchgears
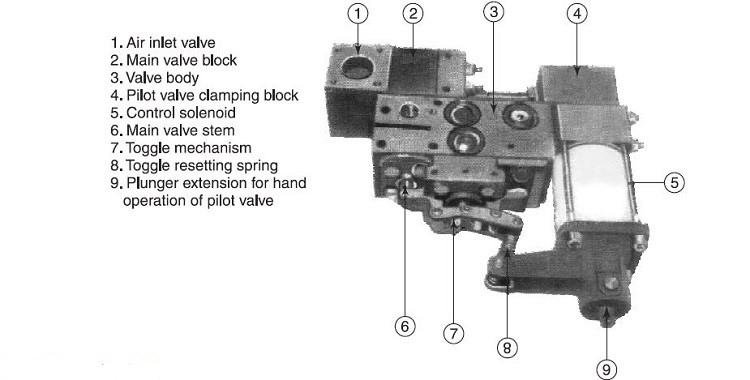
Pneumatic Mechanisms in High-Voltage Air Blast Circuit Breakers
Pneumatic mechanisms are commonly used with air blast circuit breakers to facilitate the opening and closing operations. In some designs, these mechanisms are entirely pneumatic, eliminating the need for solid mechanical links between the operating mechanism and the contacts. Other designs use an air piston to drive the closing linkage and charge the opening springs.
Typical Pneumatic Mechanism in HV Air Blast Circuit Breakers
Closing Sequence:
Air Supply:
- Air is supplied through a filter in the air-inlet block (1) to the inlet manifold and main valve block (2). From there, it travels through a connecting pipe to the pilot valve block (4).
- Under normal conditions, all valves are closed, and there is no pressure within the main body of the unit.
Initiating the Closing Operation:
- During the closing operation, the solenoid (5) is energized, which opens the pilot valve.
- Pressurized air then enters the body (3), forcing down a servo-piston onto a bell crank. This action, transmitted through a toggle mechanism (7), raises the main valve stem (6), thereby opening the main valve.
Completion of the Closing Operation:
- Once initiated, the closing movement must be completed. A one-way ball valve ensures that the main valve remains open until the circuit breaker mechanism stroke is fully executed, independent of the electrical control system.
- The pressurized air passes through the now-open main valve to the circuit breaker's closing cylinder, completing the closing sequence.
Key Components and Their Functions:
- Air-Inlet Block (1): Filters and supplies air to the system.
- Main Valve Block (2): Controls the flow of pressurized air to the closing cylinder.
- Pilot Valve Block (4): Regulates the initial flow of air to activate the main valve.
- Solenoid (5): Energizes to open the pilot valve.
- Servo-Piston: Converts pneumatic force into mechanical motion.
- Bell Crank and Toggle Mechanism (7): Transmits the force from the servo-piston to raise the main valve stem.
- Main Valve Stem (6): Opens the main valve to allow air flow to the closing cylinder.
- One-Way Ball Valve: Ensures the main valve stays open until the closing operation is complete.
This mechanism ensures reliable and controlled operation of high-voltage air blast circuit breakers, maintaining safety and performance standards in critical applications.