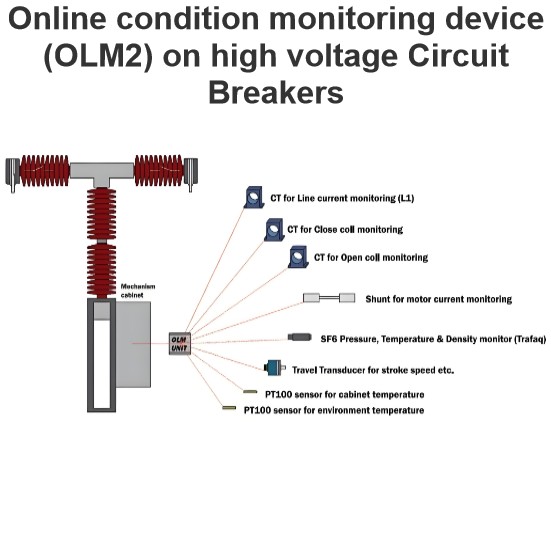
Transient Electromagnetic Emissions(TEE) measurement methods in switchgears
Edwiin
12/21/2024
TEE Detection Methods During CB Switching Operations
During circuit breaker (CB) switching operations, transient earth voltages (TEEs) are generated by electric discharges within each interrupter. These TEEs, caused by disruptive discharges such as pre-strikes, re-ignitions, and restrikes, exhibit high amplitude and a broadband frequency range. To detect and analyze these TEEs, three primary methods have been developed:
- TEE Detection with UHF Antennas
- Description: This method employs four passive ultra-high-frequency (UHF) antennas. The principle is based on triangulation to locate the source of emission, allowing for per-interrupter analysis in live-tank CBs and per-pole analysis in dead-tank CBs.
- Application: Suitable for both live-tank and dead-tank CBs.
- Advantages: Provides precise location of the discharge source, enabling detailed analysis of individual interrupters or poles.
- Setup: The UHF antennas are strategically placed around the CB to capture the emitted signals, which are then analyzed to determine the origin of the TEE.
- TEE Detection with Capacitive Sensors
- Description: This method is more suited for dead-tank CBs. It uses an active high-frequency antenna (AA) placed near the CB and three broadband passive antennas (PA), which act as capacitive sensors of the electric field, positioned under each phase conductor.
- Application: Primarily used for dead-tank CBs.
- Advantages: The capacitive sensors can effectively capture the electric field changes caused by TEEs, providing a non-intrusive way to monitor the CB's performance.
- Setup: The AA is placed close to the CB, while the three PAs are positioned next to each phase conductor. This arrangement allows for the detection of TEEs across all phases, ensuring comprehensive monitoring.
- General Test Arrangement (a): The AA and PAs are arranged around the CB to capture the TEE signals.
- Positioning of AA and Three PAs (b): The AA is placed near the CB, and the three PAs are positioned under each phase conductor of a 275 kV dead-tank CB.
- TEE Detection with PD Couplers
- Description: This method extends the first method (UHF antennas) to dead-tank CBs with two interrupters in series. It uses high-sensitivity antennas, known as partial discharge (PD) couplers, to detect TEEs.
- Application: Suitable for dead-tank CBs with multiple interrupters in series.
- Advantages: The PD couplers offer higher sensitivity, making them ideal for detecting TEEs in complex CB configurations.
- Setup: The PD couplers are placed in strategic locations to capture the TEE signals from each interrupter, allowing for detailed analysis of the CB's performance.
Applicability
All three methods can be applied to both high-voltage (HV) and medium-voltage (MV) circuit breakers, depending on the specific requirements and CB design.
Example Setup for Method 2
The following setup illustrates the configuration for TEE detection using capacitive sensors (Method 2):
- General Test Arrangement (a): The active high-frequency antenna (AA) is placed near the CB, while three broadband passive antennas (PAs) are positioned under each phase conductor. This arrangement ensures that TEEs from all phases are captured.
- Positioning of AA and Three PAs (b): The AA is placed close to the 275 kV dead-tank CB, and the three PAs are positioned under each phase conductor. This setup allows for the detection of TEEs across all phases, providing a comprehensive view of the CB's performance during switching operations.