What is a DAC?
What is a DAC?
Overview of Digital-to-Analog Converters
Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC), also known as D/A converter, is abbreviated as DAC. It is a device that converts digital quantities into analog ones. DAC is essentially composed of four parts: weighted resistor network, operational amplifier, reference power supply, and analog switch.
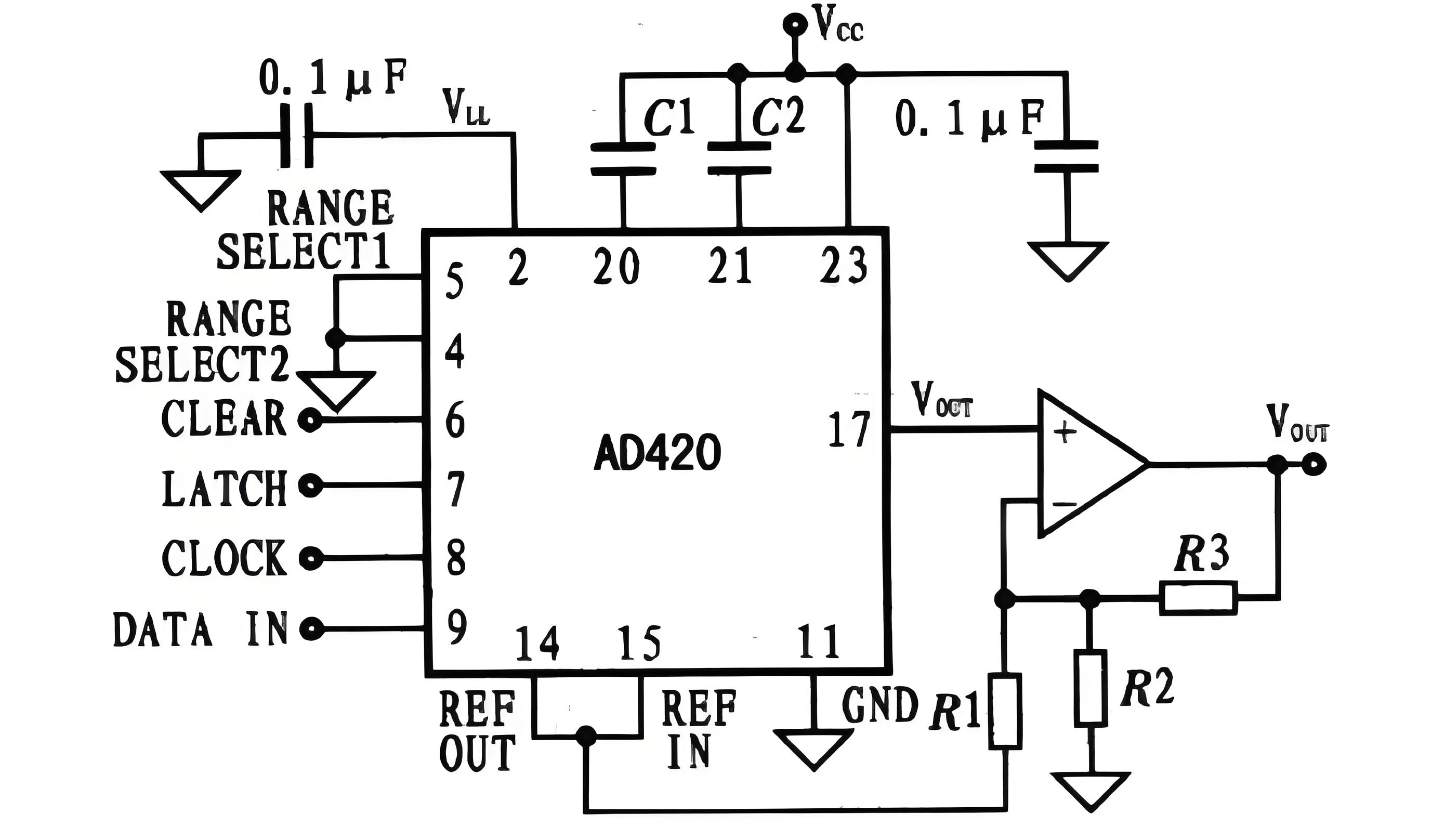
Working Principle
The DAC is mainly composed of digital registers, analog electronic switches, weighted-resistor networks, power amplifiers, and reference voltage sources (or constant current sources). The digital numbers used for digital storage control the corresponding positions of the analog electronic switches respectively, causing the weighted-resistor network at the position where the digit is 1 to generate a current value proportional to its position weight. The power amplifier's requirements for each current value are calculated and converted into voltage values.
Application
DACs are often used as output channels in process control computer systems, connected to actuators to achieve automatic control of the production process. In addition, DAC circuits are also used in the design of digital-to-analog converters that utilize feedback technology.
Classification
There are various types of DACs, including parallel comparison type, integration type, and ∑-Δ type. Each type has its own characteristics and applicable scenarios. For example, the parallel comparison type DAC is the fastest, but it is difficult to achieve high resolution; the integration type ADC is suitable for low-speed, precision measurement fields; the ∑-Δ type ADC adopts incremental coding, making it suitable for high-speed conversion scenarios.
Technical Indicators
The technical indicators of DAC include the number of bits, resolution, conversion accuracy and conversion speed, etc. The number of bits determines the range of maximum and minimum values that the DAC can represent for analog quantities. Resolution refers to the smallest change in analog quantity that the DAC can distinguish, usually expressed in least significant bits (LSB). Conversion accuracy is the closeness between the actual value of the analog quantity output by the DAC and its theoretical value. Conversion speed refers to the time required for the DAC to complete a conversion.
Trend Development
With the development of digital technology, DACs are becoming more and more integrated and advanced in technical indicators. In the future, DACs will continue to develop towards high speed, high precision, and low power consumption to meet the needs of more fields.
In summary, digital-to-analog converters are important electronic components that play a significant role in modern control, communication, and detection fields. With the advancement of technology, the performance of DACs will become increasingly outstanding, and their application range will be even broader.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













