What is a ADC ?
What is a ADC ?
Analog to Digital Converter Definition
An Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) is a device that changes a continuous analog signal into a discrete digital signal.
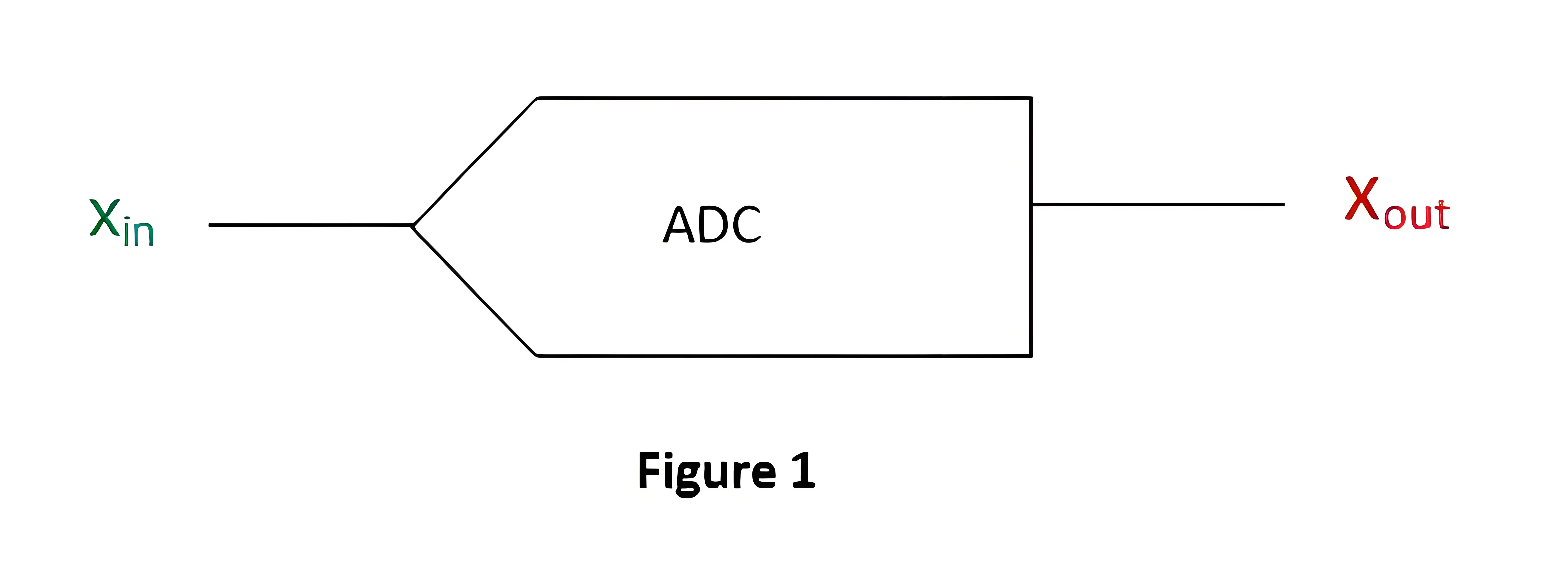
ADC Process
Sampling and Holding
Quantizing and Encoding
Sampling and Holding
In Sampling and Holding (S/H), the continuous signal is sampled and held steady for a short period. This removes variations in the input signal that could affect conversion accuracy. The minimum sampling rate must be twice the maximum frequency of the input signal.
Quantizing and Encoding
For understanding quantizing, we can first go through the term Resolution used in ADC. It is the smallest variation in analog signal that will result in a variation in the digital output. This actually represents the quantization error.
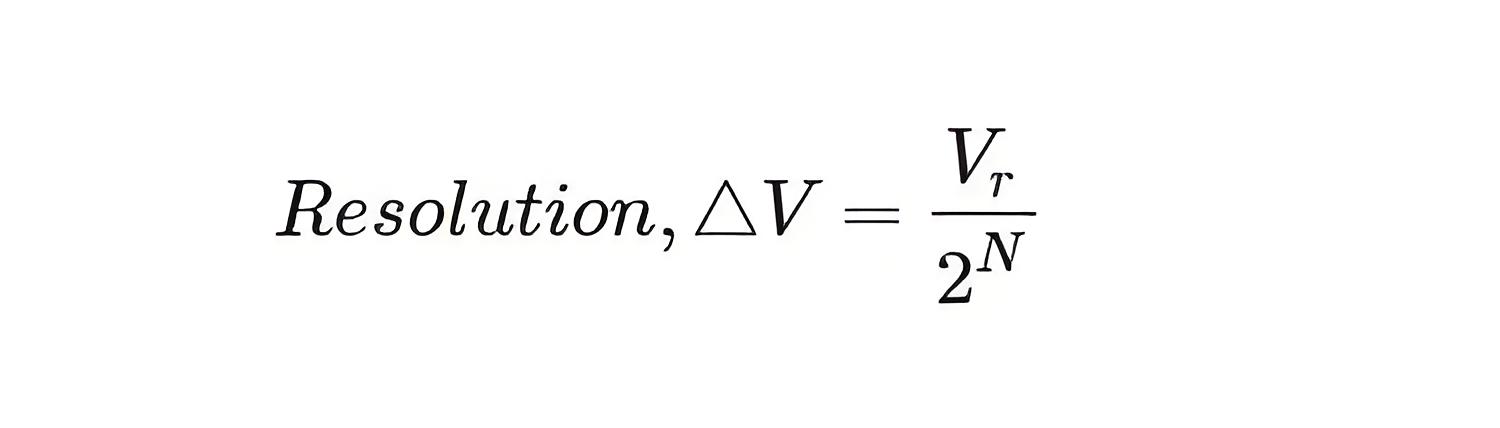
V → Reference voltage range
2N → Number of states
N → Number of bits in digital output
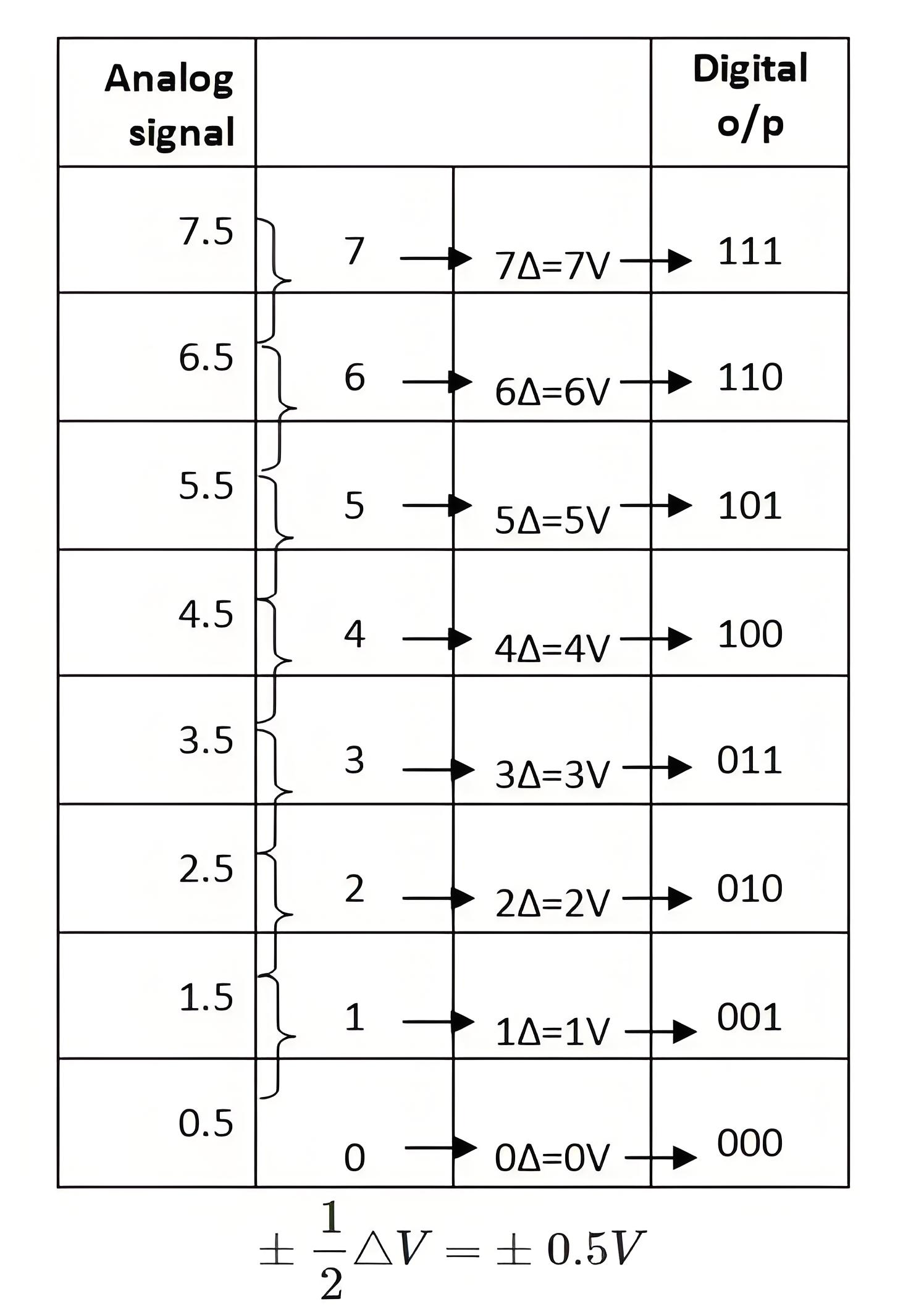
Quantizing is the process of dividing the reference signal into several discrete levels, or quanta, and then matching the input signal to the correct level.
Encoding assigns a unique digital code to each discrete level (quantum) of the input signal. The process of quantizing and encoding is demonstrated in the table below.
From the above table we can observe that only one digital value is used to represent the whole range of voltage in an interval. Thus, an error will occur and it is called quantization error. This is the noise introduced by the process of quantization. Here the maximum quantization error is
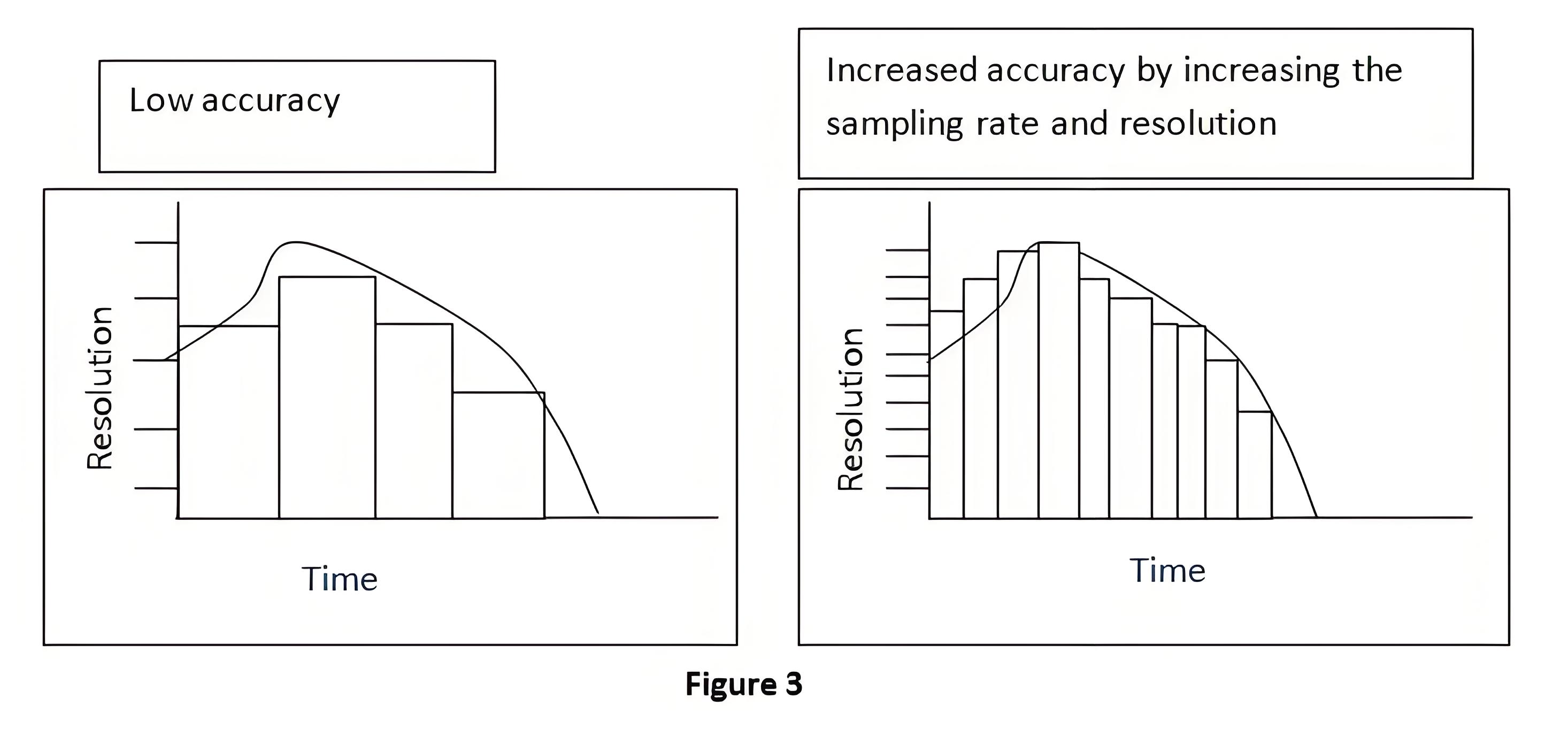
Improving ADC Accuracy
To improve ADC accuracy, two methods are commonly used: increasing the resolution and increasing the sampling rate. This is shown in figure below (figure 3).
Types and Applications of ADCs
Successive Approximation ADC: This converter compares the input signal with the output of an internal DAC at each successive step. It is the most expensive type.
Dual Slope ADC: It have high accuracy but very slow in operation.
Pipeline ADC: It is same as that of two step Flash ADC.
Delta-Sigma ADC: It has high resolution but slow due to over sampling.
Flash ADC: It is the fastest ADC but very expensive.
Other: Staircase ramp, Voltage-to-Frequency, Switched capacitor, tracking, Charge balancing, and resolver.
Application of ADC
Used together with the transducer.
Used in computer to convert the analog signal to digital signal.
Used in cell phones.
Used in microcontrollers.
Used in digital signal processing.
Used in digital storage oscilloscopes.
Used in scientific instruments.
Used in music reproduction technology etc.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













