What is Synchronous Condenser?
What is What is Synchronous Condenser?
Synchronous Condenser Definition
A synchronous condenser is defined as a synchronous motor running without a mechanical load, used to improve the power factor of power systems.
Improving Power Factor
Suppose due to a reactive load of the power system the system draws a current Ithree phase synchronous motorL from the source at a lagging angle θL in respect of voltage. Now the motor draws a IM from the same source at a leading angle θM.
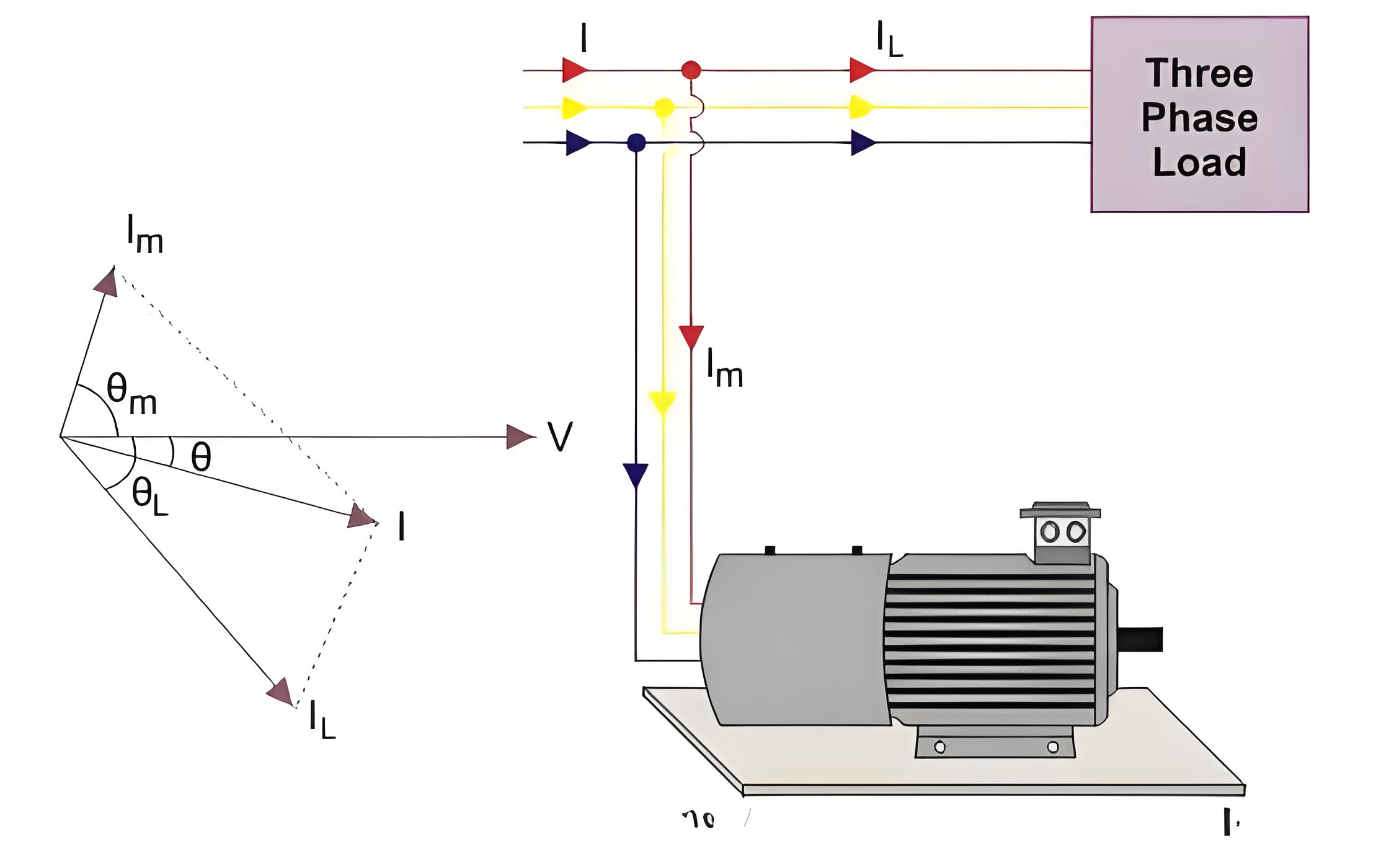
Now the total current drawn from the source is the vector sum of the load current IL and motor current IM. The resultant current I drawn from the source has an angle θ in respect of voltage. The angle θ is less than angle θL. Hence power factor of the system cosθ is now more than the power factor cosθL of the system before we connect the synchronous condenser to the system.
A synchronous condenser is a more advanced technique for improving power factor than a static capacitor bank. However, for systems below 500 kVAR, it is not as economical as a capacitor bank. For major power networks, we use synchronous condensers, but for lower-rated systems, we usually employ capacitor bank.
One advantage of a synchronous condenser is that it allows smooth, continuous control of the power factor. In contrast, a static capacitor bank can only improve the power factor in steps, not allowing fine adjustments.The short circuit withstand-limit of the armature winding of a synchronous motor is high.
Although, synchronous condenser system has some disadvantages. The system is not silent since the synchronous motor has to rotate continuously.
An ideal load less synchronous motor draws leading current at 90o(electrical).
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.