Stator Earth Fault Protection of Alternator
Stator Earth Fault Protection Definition
Stator earth fault protection limits ground fault current to minimize damage to the stator core and winding.
Ground Impedance Role
Grounding the stator with high impedance can reduce fault current but may lower relay sensitivity, requiring additional sensitive relays.
Resistance Neutral Earthing
In this method, the stator’s neutral point is grounded through a resistor, which is connected with a current transformer and protective relay.
Relay Types
Depending on the connection method, either an inverse time relay (for direct substation connection) or an instantaneous armature attracted relay (for star-delta transformer connection) is used.
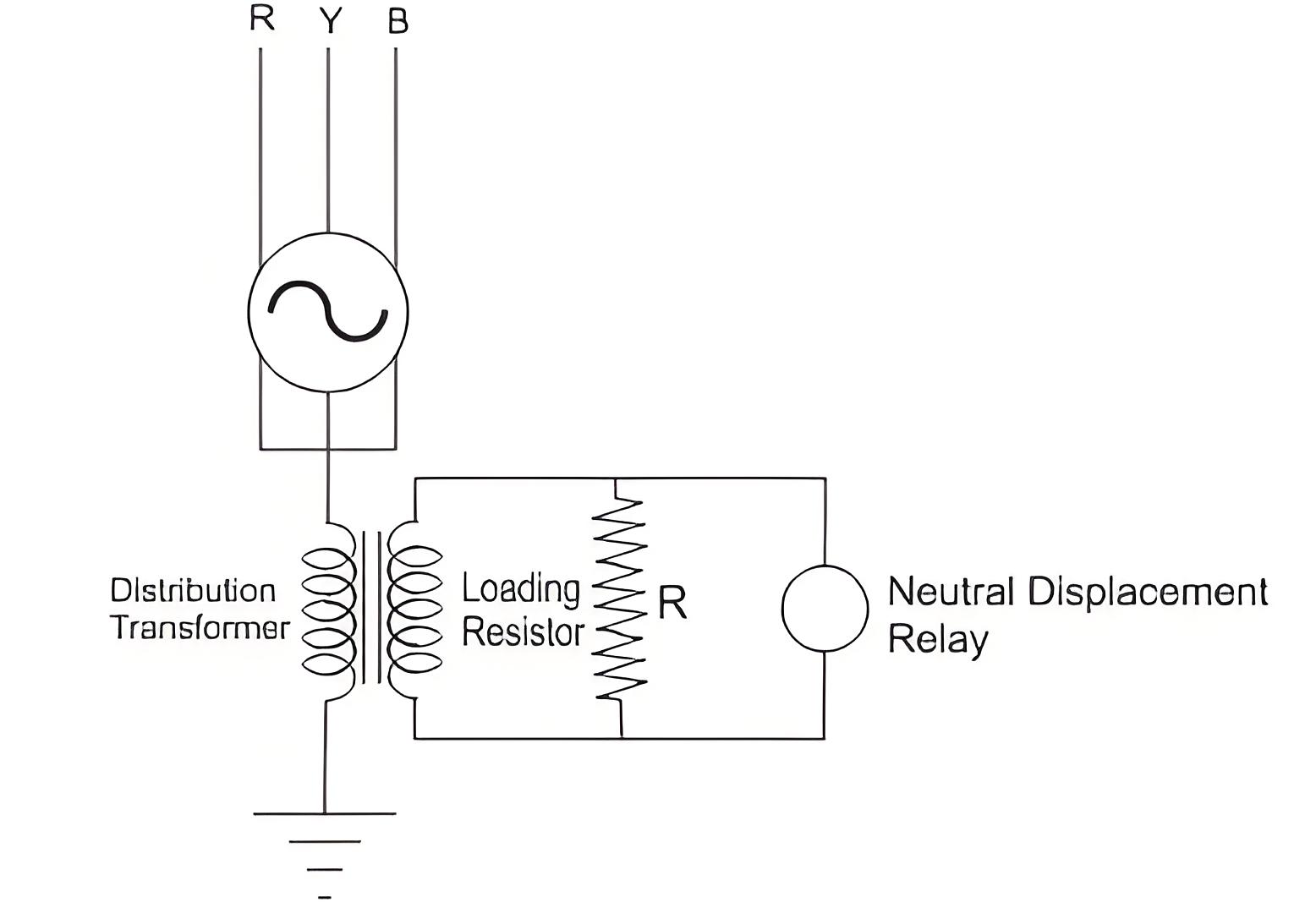
Alternative Grounding Method
A distribution transformer and resistor setup can also ground the stator, with an overvoltage relay ensuring protection.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













