What is Inter Turn Fault Protection?
What is Inter Turn Fault Protection?
Inter Turn Fault Definition
Inter turn faults happen when the insulation between conductors in the same stator winding slot is damaged.
Detection Methods
These faults can be detected using stator differential protection or stator earth fault protection.
Importance of Stator Inter Turn Protection
High voltage generators and modern large generators need stator inter turn protection to prevent faults.
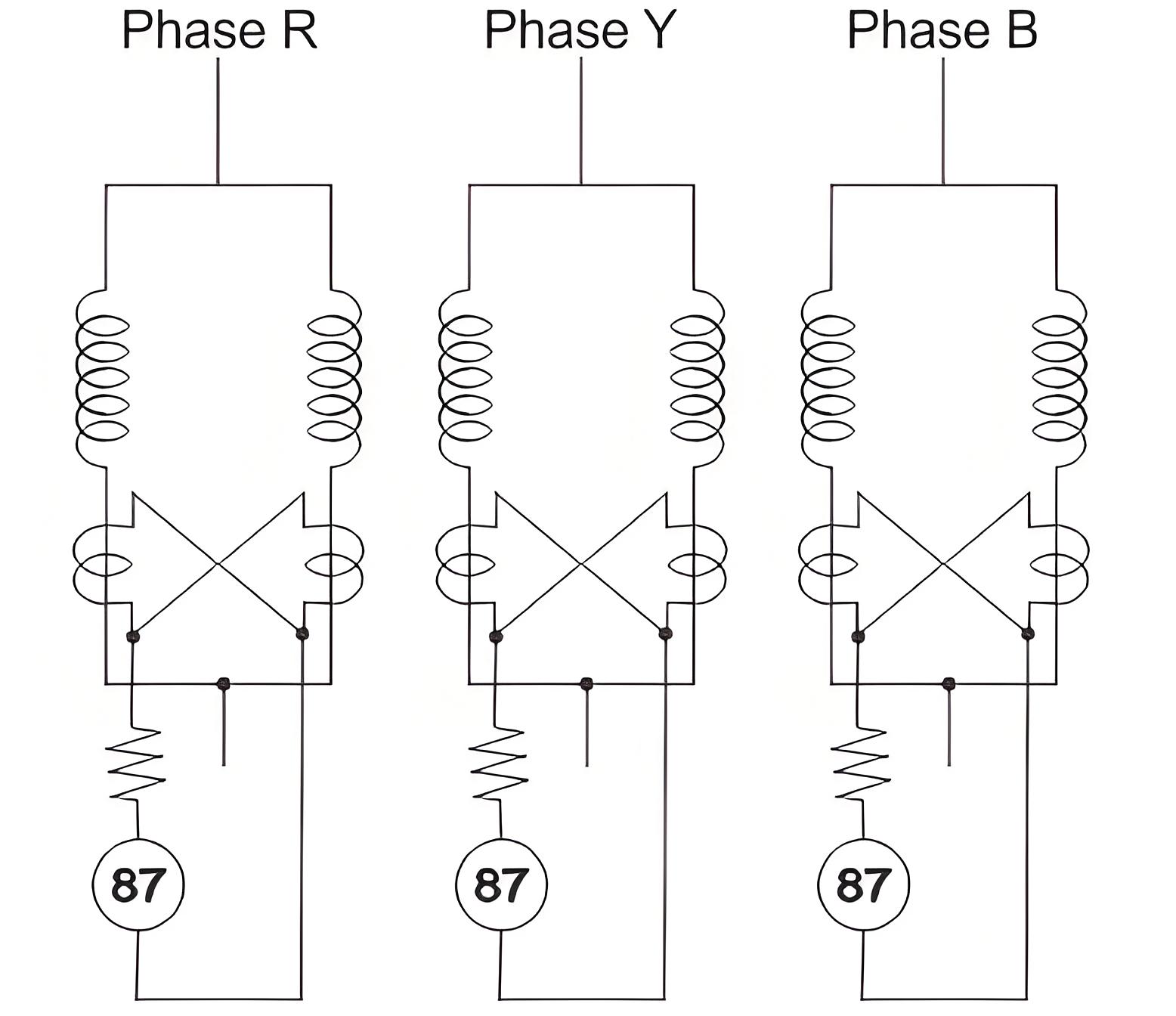
Cross Differential Method
Ross differential methods is most common among them. In this scheme the winding for each phase is divided into two parallel paths.
Each path is fitted with identical current transformers (CTs), and their secondaries are cross-connected. This cross-connection is because the currents at the primary of both CTs are entering, unlike differential protection of transformer where current enters from one side and exits the other.
A differential relay and series stabilizing resistor are connected across the CT secondary loop. If an inter turn fault occurs in any path of the stator winding, it creates an imbalance in the CT secondary circuits, triggering the 87 differential relay. Cross differential protection should be applied individually to each.
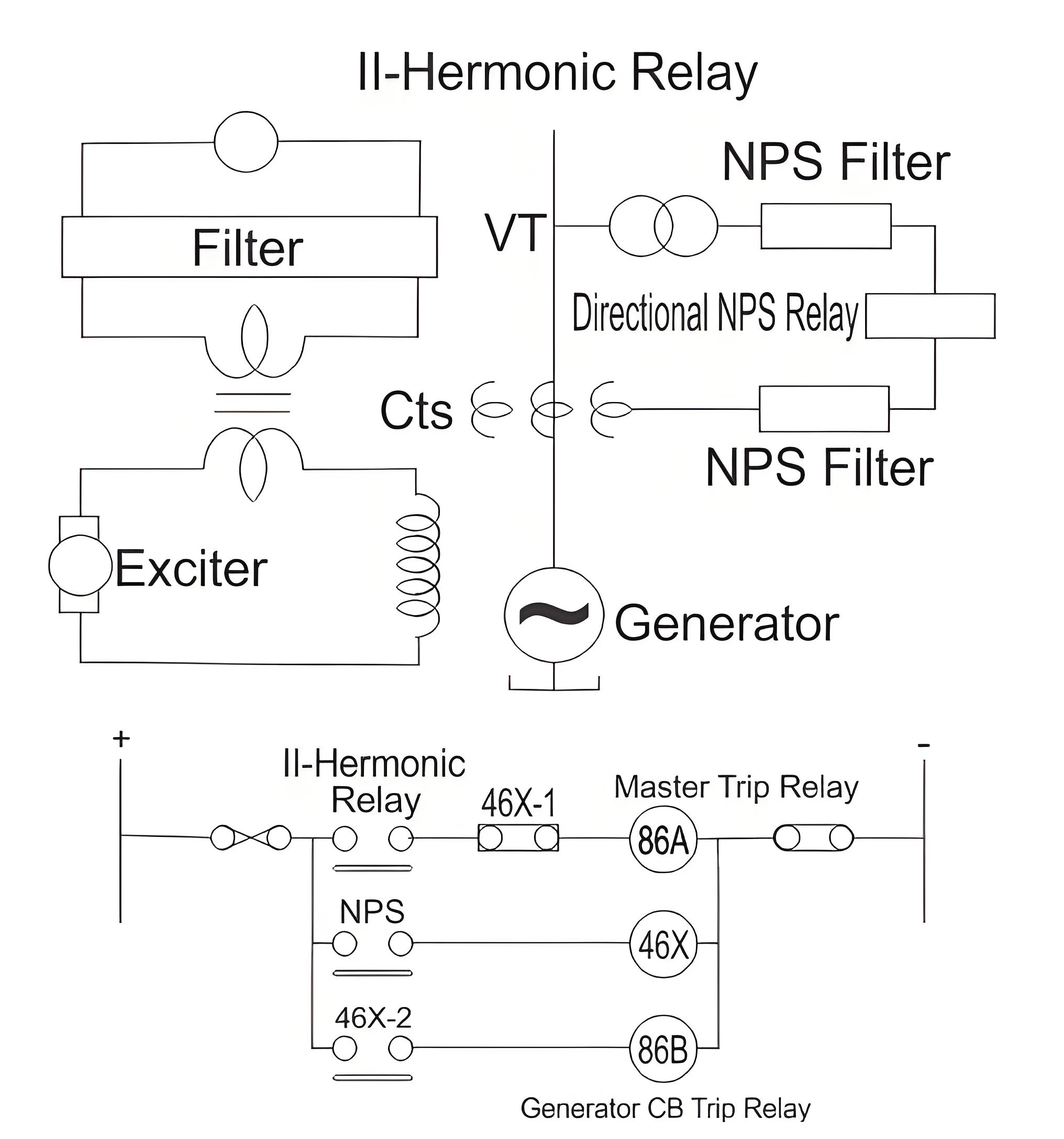
Alternative Protection Scheme
This scheme provides complete protection against internal faults of all synchronous machines irrespective of the type of the winding employed or the kind of methods for connection. An internal fault in the stator winding generates second harmonic current, included in the field winding and exciter circuits of the generator. This current can be applied to a sensitive polarized relay via a CT and filter circuit.
The scheme operation is controlled by a direction of negative phase sequence relay, in order to prevent operation during external unbalanced faults or asymmetrical load conditions. Should there be any asymmetry external to the generator unit zone, the negative phase sequence relay prevents a complete shutdown, only allowing the main circuit breaker to be tripped, to prevent the rotor damage due to the over rating effects of second harmonic currents.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













