What is Gas Insulated Switchgear?
What is Gas Insulated Switchgear?
GIS Definition
Gas Insulated Switchgear is defined as a metal-enclosed switchgear that uses SF6 gas as the primary insulation between live parts and the earthed metal enclosure.
Key components of a GIS include
Circuit breakers
Disconnectors
Bus bars
Transformers
Earth switches
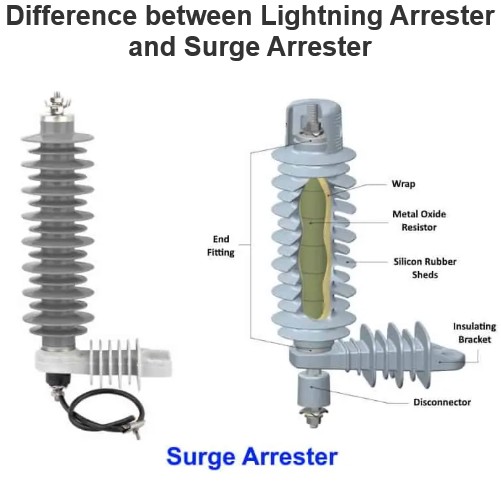
Surge arresters
High Dielectric Strength
The use of SF6 gas allows GIS to operate at higher voltages without breakdown, providing efficient and reliable power system management.
Space Efficiency
GIS reduces the physical footprint required for switchgear by up to 90%, making it ideal for space-constrained environments.
Safety Features
By encapsulating its components in a sealed metal enclosure, GIS enhances safety by minimizing exposure to live parts and reducing arc flash hazards.
Types and Models of Gas-Insulated Switchgear
Isolated phase GIS
Integrated three-phase GIS
Hybrid GIS
Compact GIS
Highly integrated system (HIS)
Advantages
Space saving
Safety
Reliability
Maintenance
Disadvantages
Cost
Complexity
Availability
Versatile Applications
Urban or industrial areas
Power generation and transmission
Renewable energy integration
Railways and metros
Data centers and factories
Conclusion
Gas-insulated switchgear is a type of electrical equipment that uses a gas, such as SF6, as the primary insulation and arc extinguishing medium. It consists of metal-enclosed compartments that house various components of a power system, such as circuit breakers, disconnectors, bus bars, transformers, earth switches, surge arresters, etc.
GIS is a modern and advanced technology that can provide efficient and reliable solutions for power systems. However, it is important to understand its characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, and applications before choosing the type of switchgear for a specific project.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.