What is an ELCB?
What is an ELCB?
ELCB Definition
An Earth-leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installations (both residential and commercial) with high Earth impedance to prevent electric shocks. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circuit if a dangerous voltage is detected.
ELCBs help detect current leaks and insulation failures in the electrical circuits that would cause electrical shocks to anyone coming into contact with the circuit.There are two types of earth leakage circuit breakers—a voltage ELCB and a current ELCB.
Voltage ELCB
The working principle of a voltage ELCB is straightforward. One terminal of the relay coil connects to the equipment’s metal body, while the other terminal connects directly to the earth.
If insulation fails or a live wire touches the metal body, a voltage difference appears between the coil terminal and the earth. This difference causes current to flow through the relay coil.
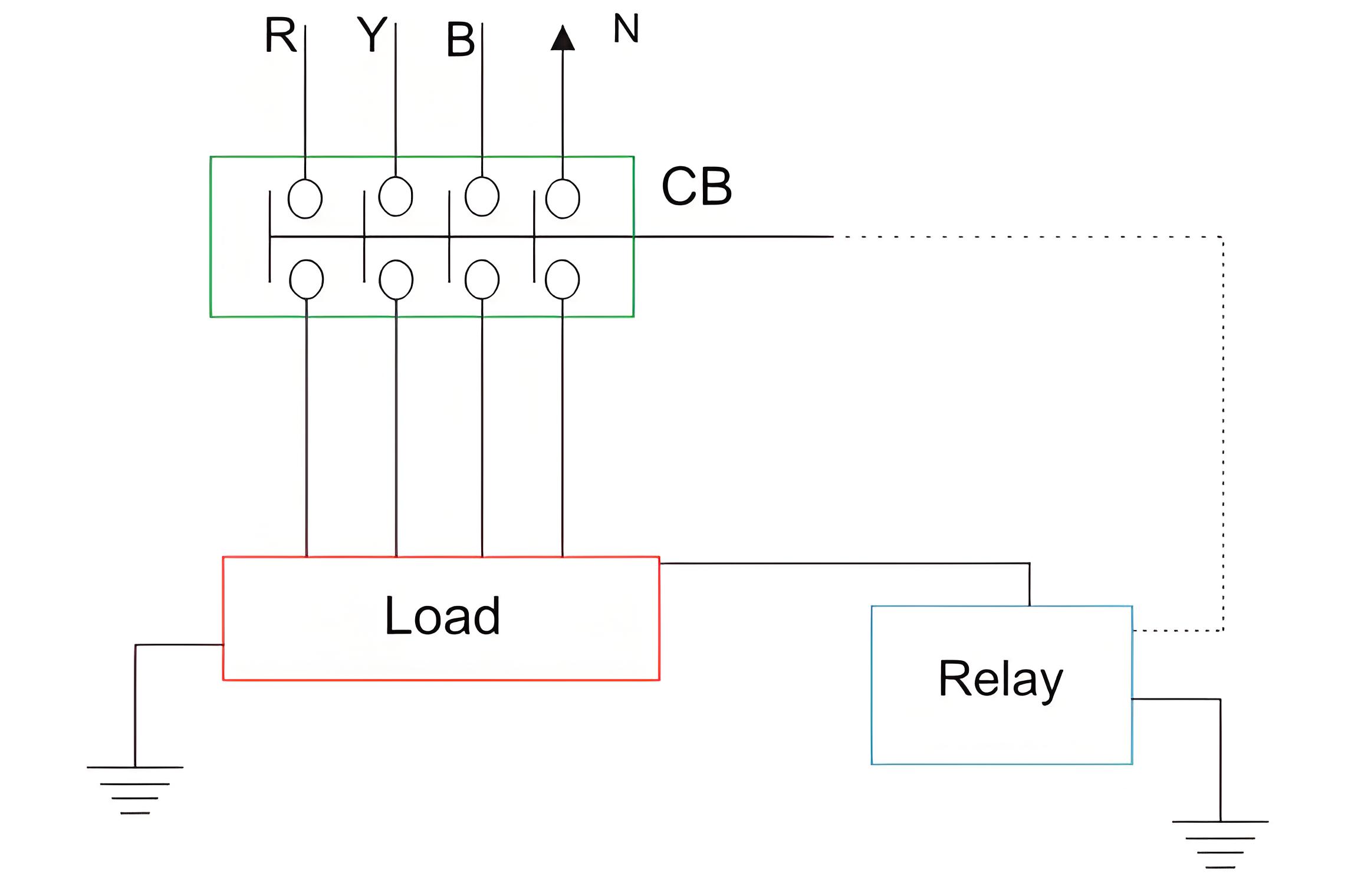
If the voltage difference crosses, a predetermined limit, the current through the relay becomes sufficient to actuate the relay for tripping the associated circuit breaker to disconnect the power supply to the equipment.
The typicality of this device is, it can detect and protect only that equipment or installation with which it is attached. It cannot detect any leakage of insulation in other parts of the system. Study our Electrical MCQs to learn more about the operation of ELCBs.
Current ELCB (RCCB)
The working principle of current earth leakage circuit breaker or RCCB is also very simple as voltage operated ELCB but the theory is entirely different and residual current circuit breaker is more sensitive than ELCB.
ELCBs come in two types: voltage-based and current-based. Voltage-based ELCBs are often called simple ELCBs, while current-based ones are known as RCDs or RCCBs. In RCCBs, a current transformer (CT) core is energized by both phase and neutral wires.
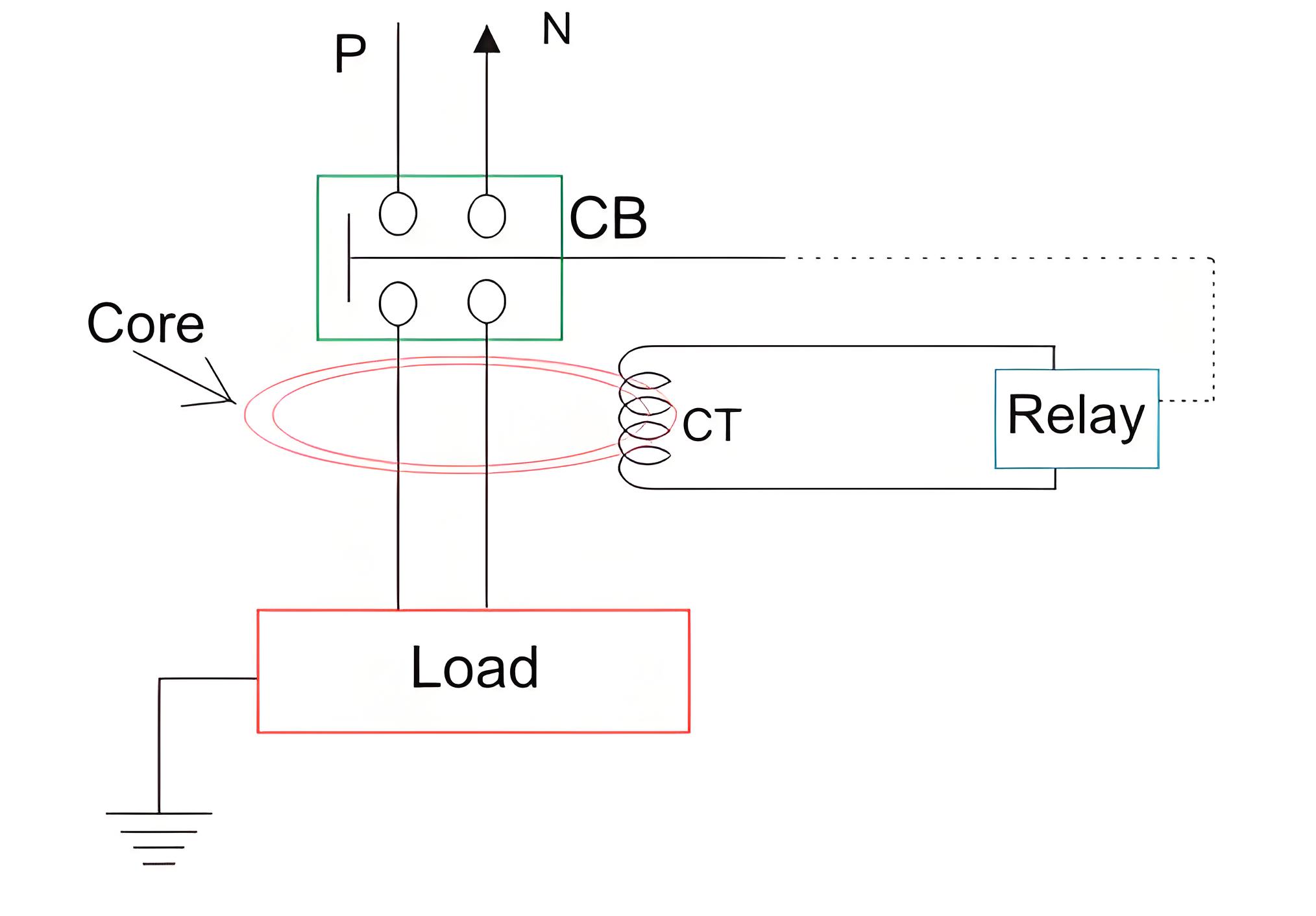
Single Phase Residual Current ELCB. The polarity of the phase winding and neutral winding on the core is so chosen that, in normal condition mmf of one winding opposes that of another.
As it is assumed that, in normal operating conditions the current goes through the phase wire will be returned via neutral wire if there’s no leakage in between.
As both currents are same, the resultant mmf produced by these two currents is also zero-ideally.The relay coil is connected with another third winding wound on the CT core as secondary. The terminals of this winding are connected to a relay system.
In normal operating condition there would not be any current circulating in the third winding as here is no flux in the core due to equal phase and neutral current.
When an earth leakage occurs, some of the phase current may pass to the earth through the leakage path instead of returning via the neutral wire.Hence the magnitude of the neutral current passing through the RCCB is not equal to phase current passing through it.
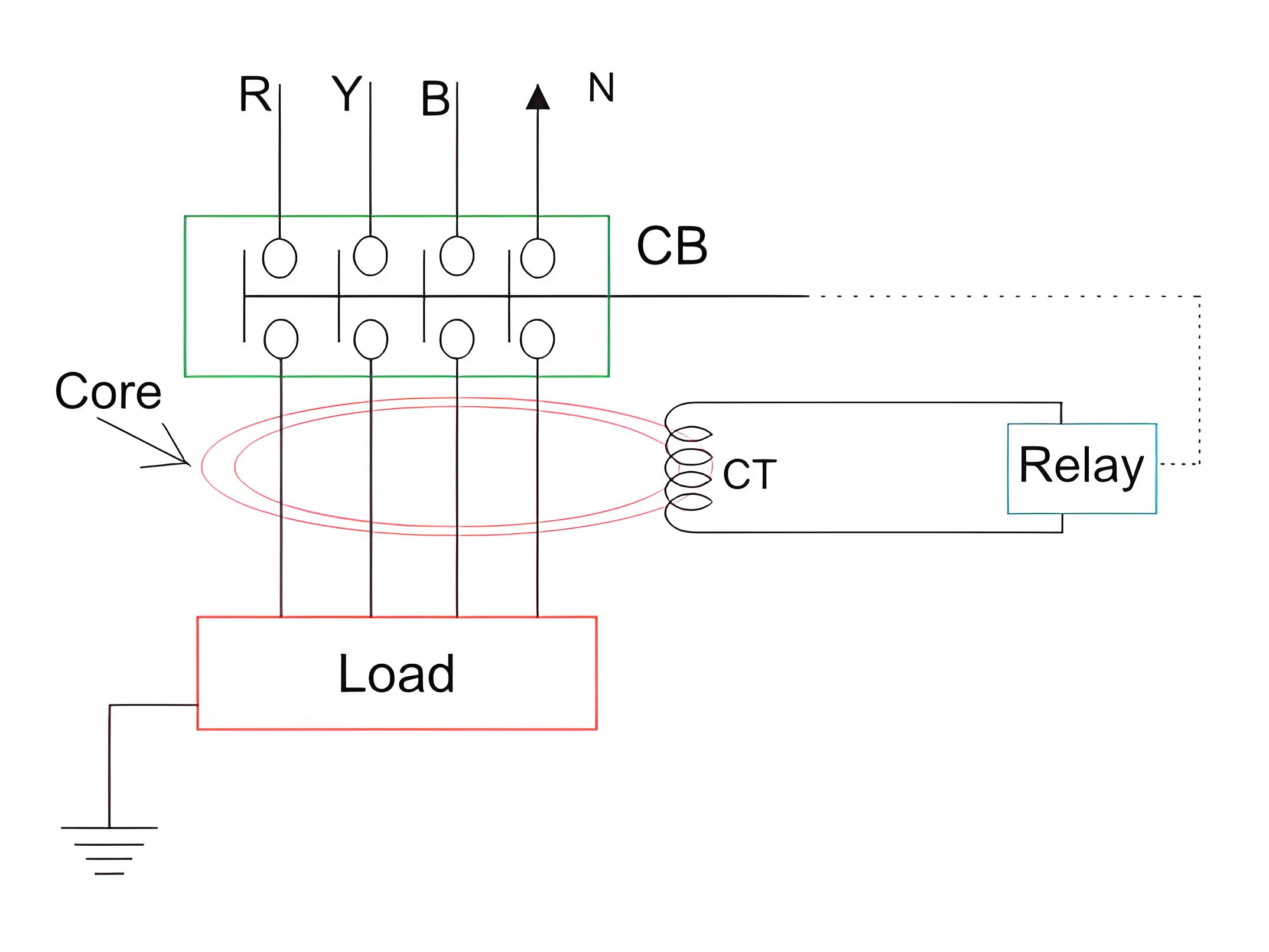
When the imbalance exceeds a set value, the current in the third winding becomes high enough to activate the electromagnetic relay.This relay causes tripping of the associated circuit breaker to disconnect the power supply to the equipment under protection.
Residual current circuit breaker is sometimes also referred as residual current device (RCD) when we consider the device by disassociating the circuit breaker attached to RCCB. That means, the entire parts of RCCB except circuit breaker are referred as RCD.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













