Signal Flow Graph of Control System
Signal Flow Graph Definition
A signal flow graph simplifies control system diagrams by using nodes and branches instead of blocks and summing points.
Rules for Drawing Signal Flow Graph
The signal always travels along the branch towards the direction of indicated arrow in the branch.
The output signal of the branch is the product of transmittance and input signal of that branch.
Input signal at a node is summation of all the signals entering at that node.
Signals propagate through all the branches, leaving a node.
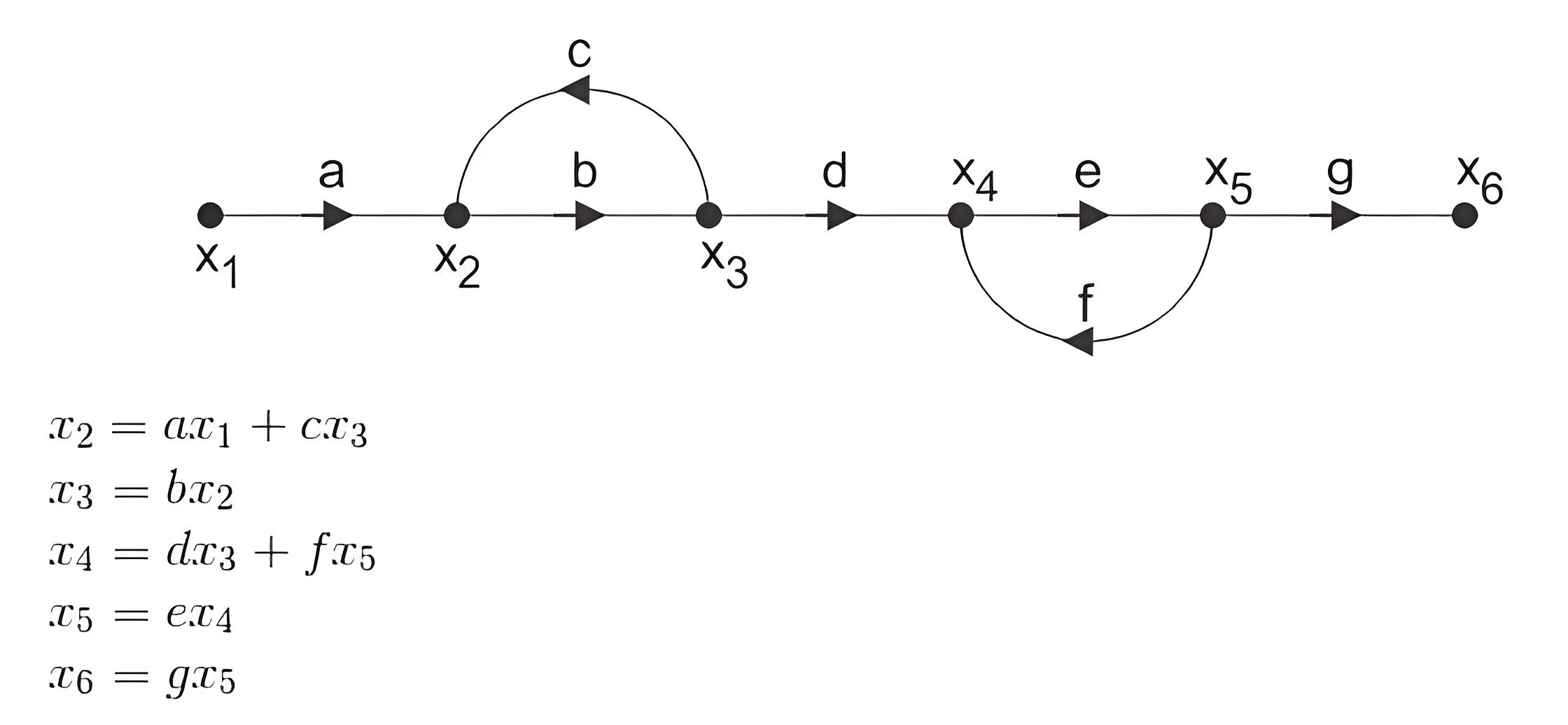
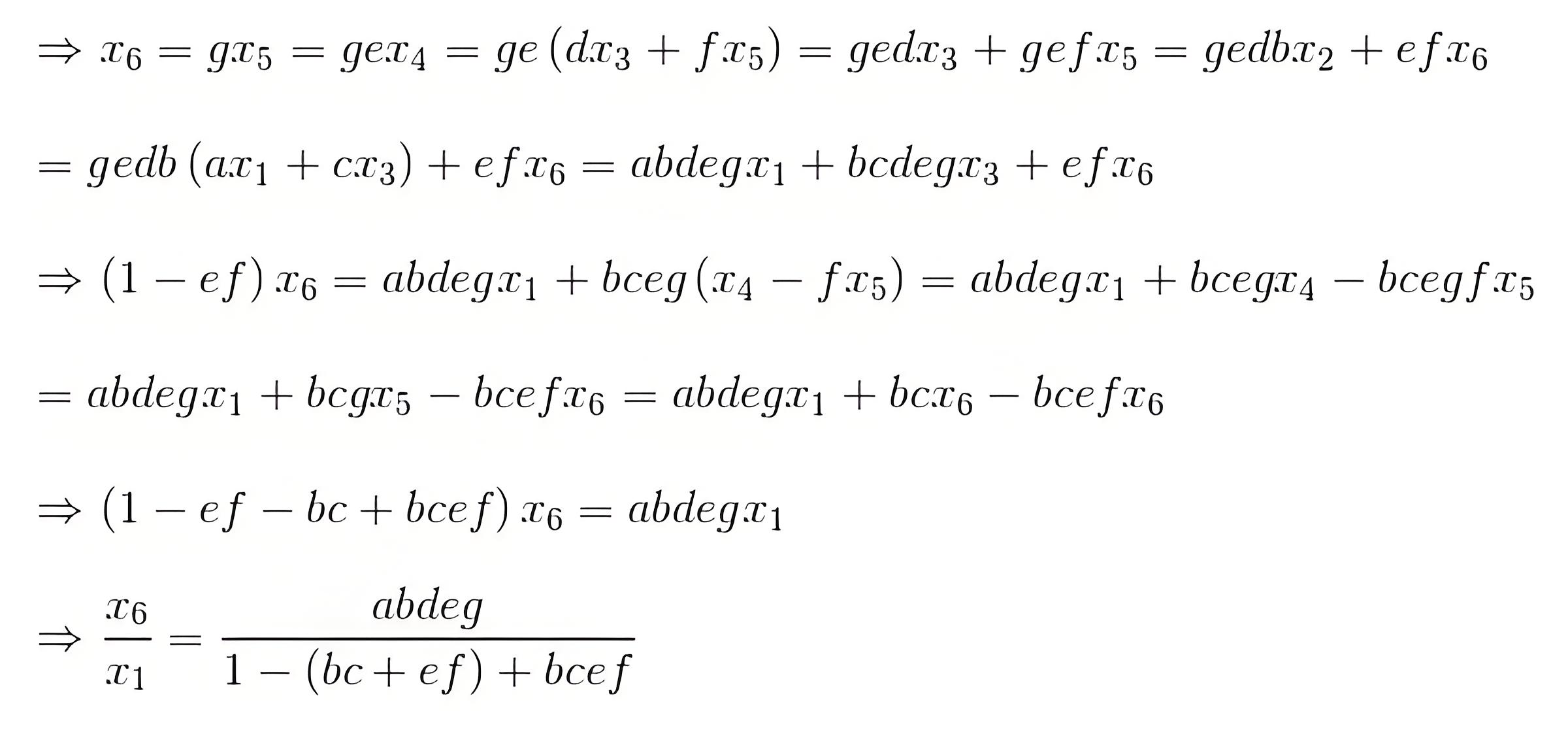
Simple Process of Calculating Expression of Transfer Function for Signal Flow Graph
First, calculate the input signal at each node of the graph. This is done by summing the products of transmittance and the variables at the other ends of branches pointing to the node.
Now by calculating input signal at all nodes will get numbers of equations which relating node variables and transmittance. More precisely, there will be one unique equation for each of the input variable node.
By solving these equations we get, ultimate input and output of the entire signal flow graph of control system.
Lastly by dividing inspiration of ultimate output to the expression of initial input we calculate the expiration of transfer function of that signal flow graph
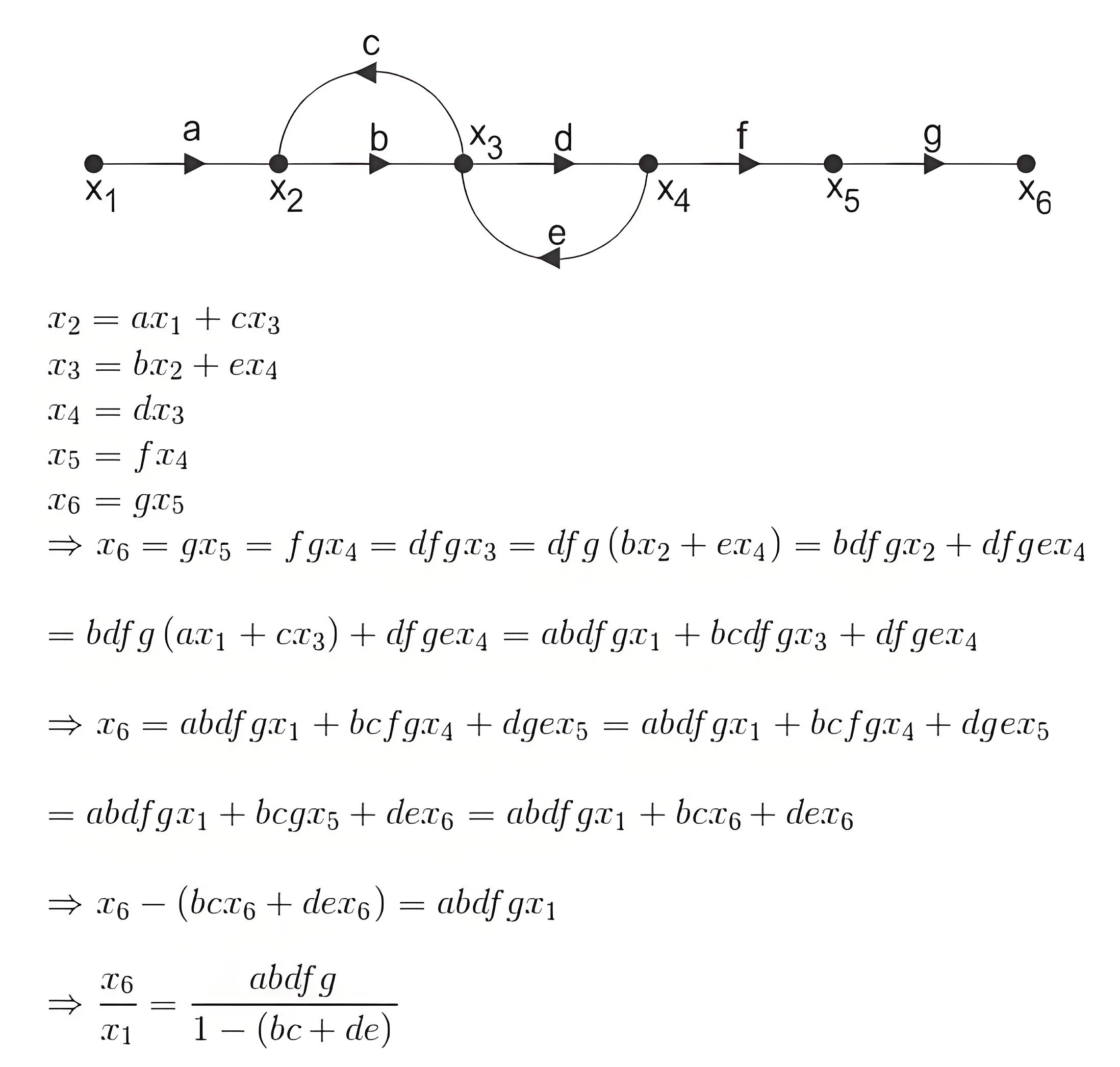
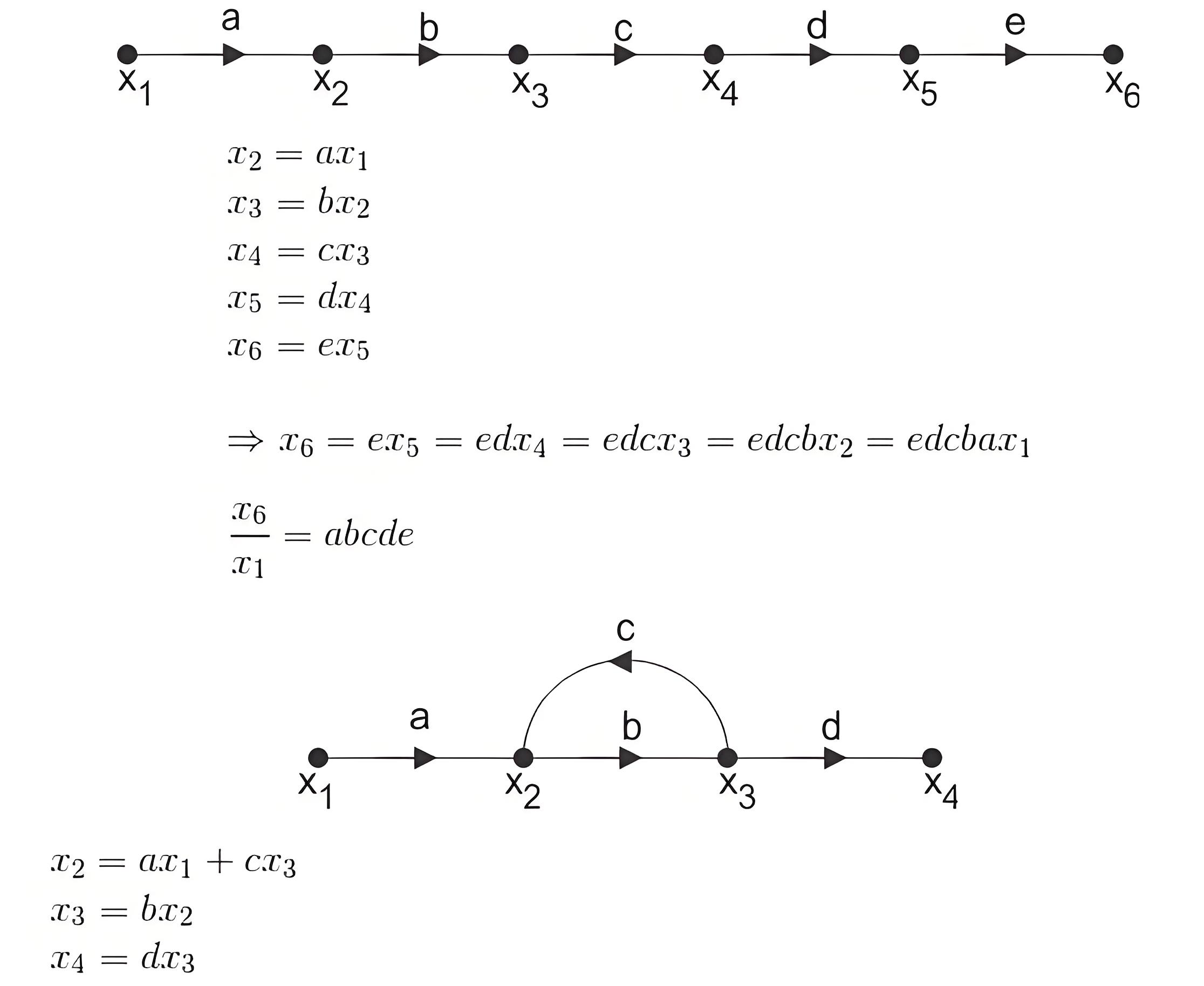
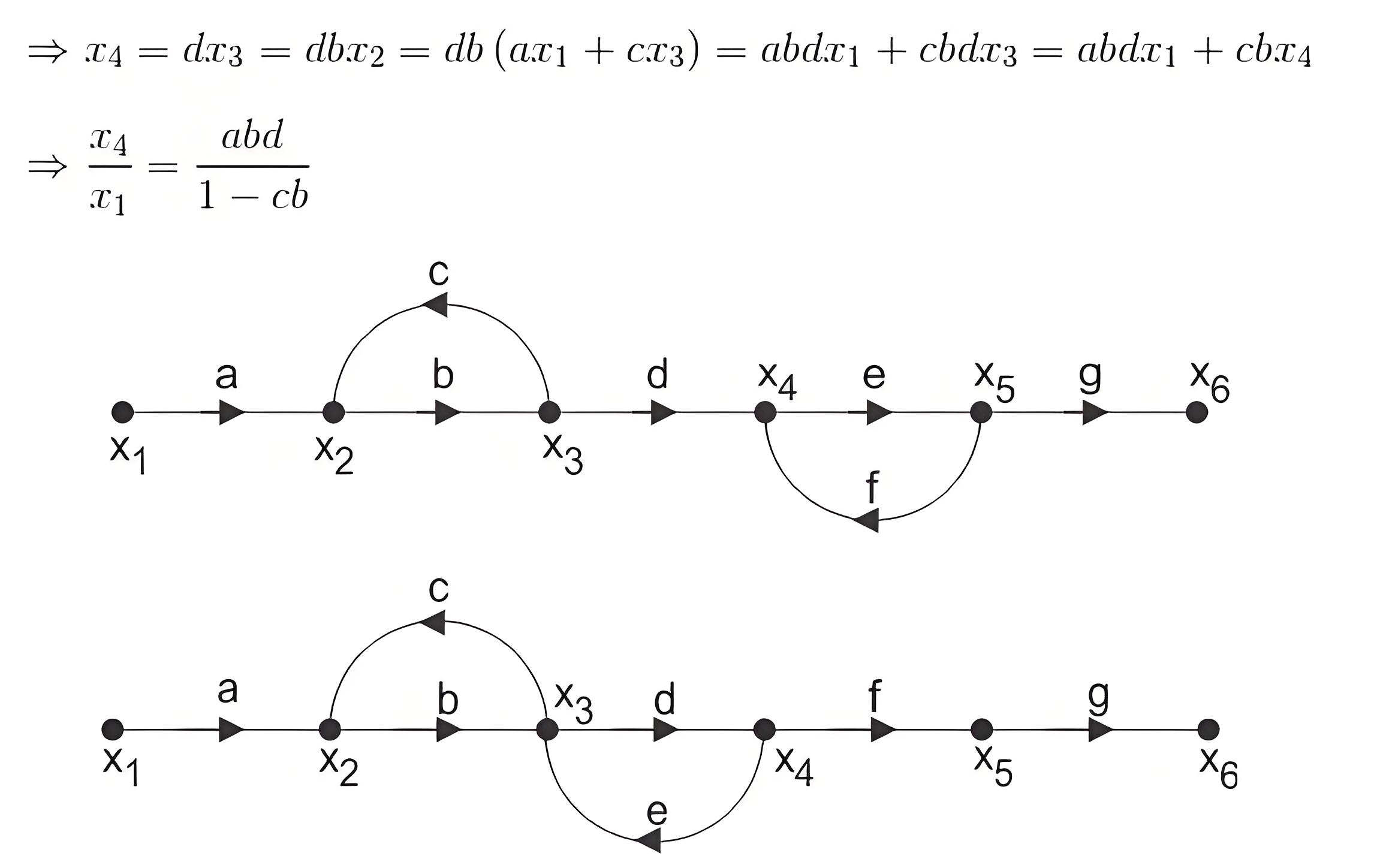
If P is the forward path transmittance between extreme input and output of a signal flow graph. L1, L2…………………. loop transmittance of first, second,.….. loop of the graph. Then for first signal flow graph of control system, the overall transmittance between extreme input and output is
For the second signal flow graph of a control system, the overall transmittance between the input and output is calculated similarly.
Here in the figure above, there are two parallel forward paths. Hence, overall transmittance of that signal flow graph of control system will be simple arithmetic sum of forward transmittance of these two parallel paths.
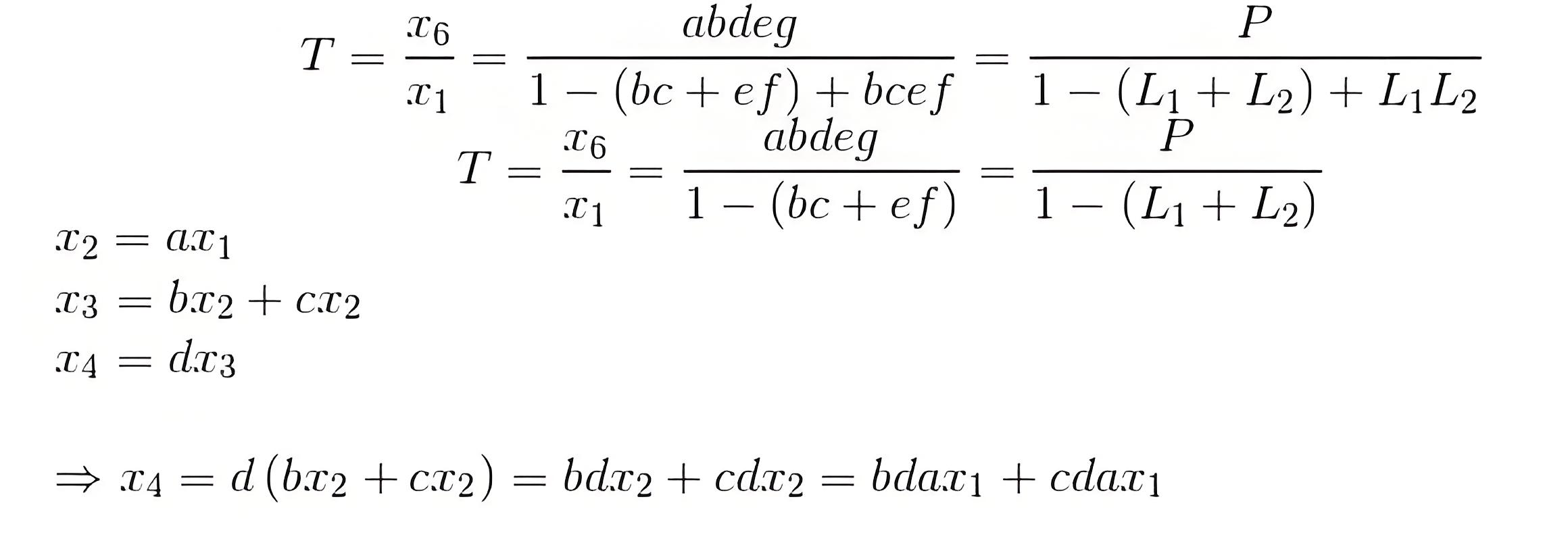

As the each of the parallel paths having one loop associated with it, the forward transmittances of these parallel paths are
Therefore overall transmittance of the signal flow graph is
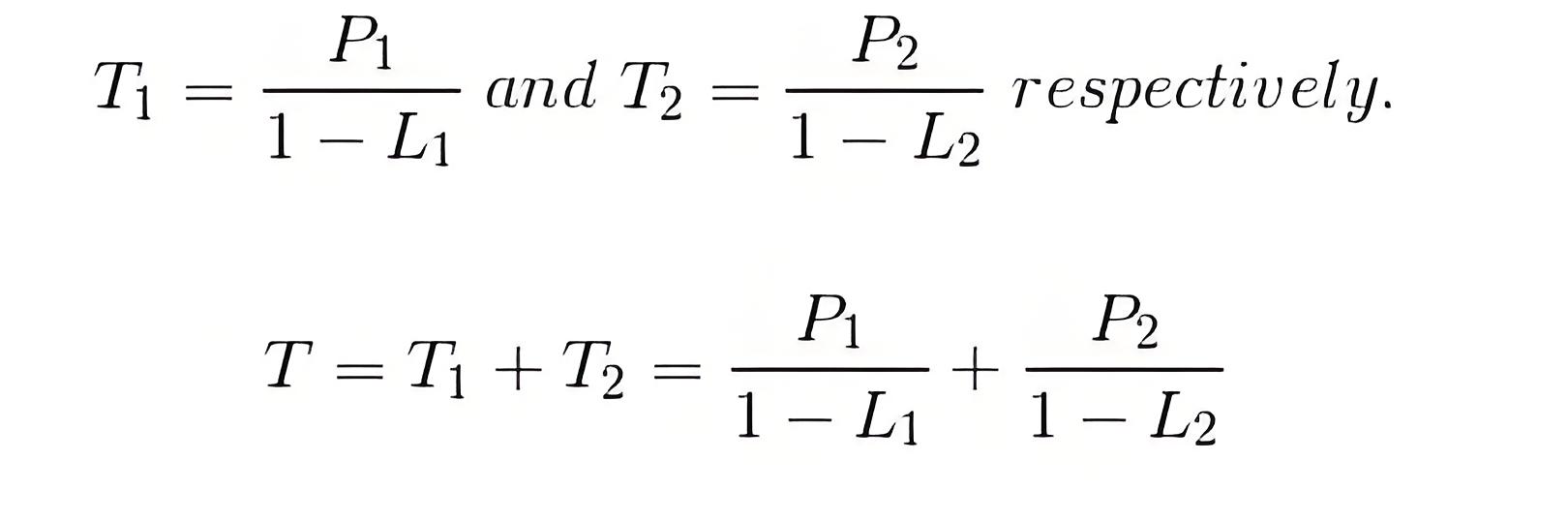
Mason’s Gain Formula
The overall transmittance or gain of a signal flow graph in a control system is given by Mason’s Gain Formula.
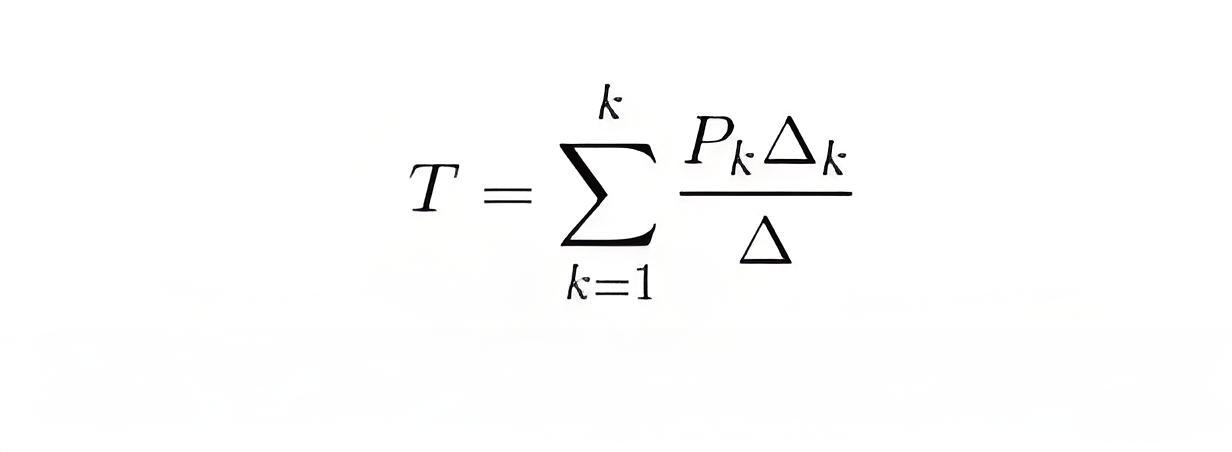
Where, P k is the forward path transmittance of kth in path from a specified input is known to an output node. In arresting Pk no node should be encountered more than once.
Δ is the graph determinant which involves closed loop transmittance and mutual interactions between non-touching loops.
Δ = 1 – (sum of all individual loop transmittances) + (sum of loop transmittance products of all possible pair of non-touching loops) – (sum of loop transmittance products of all possible triplets of non-touching loops) + (……) – (……)
Δ k is the factor associated with the concerned path and involves all closed loop in the graph which are isolated from the forward path under consideration.
The path factor Δk for the kth path is equal to the value of grab determinant of its signal flow graph which exist after erasing the Kth path from the graph.
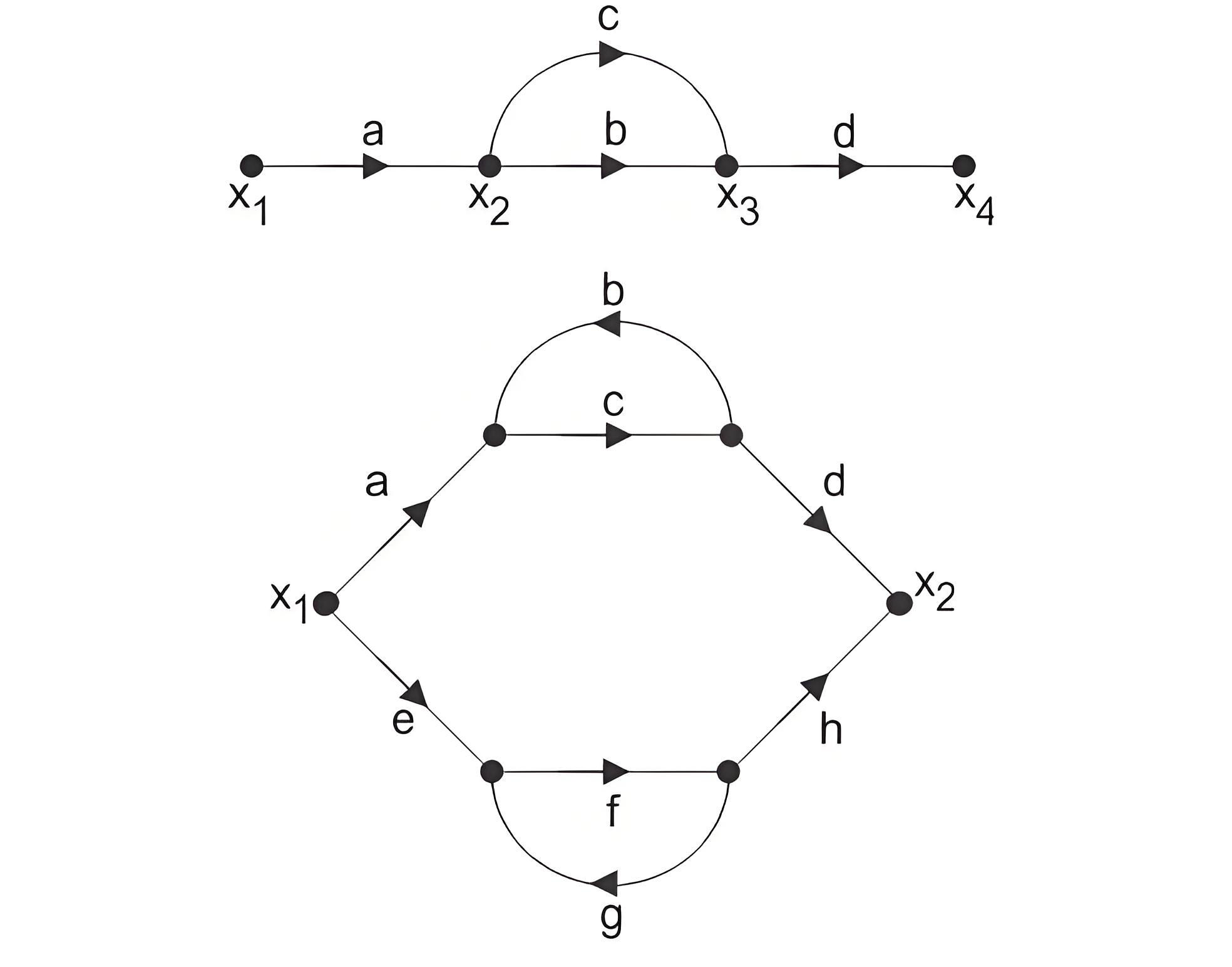
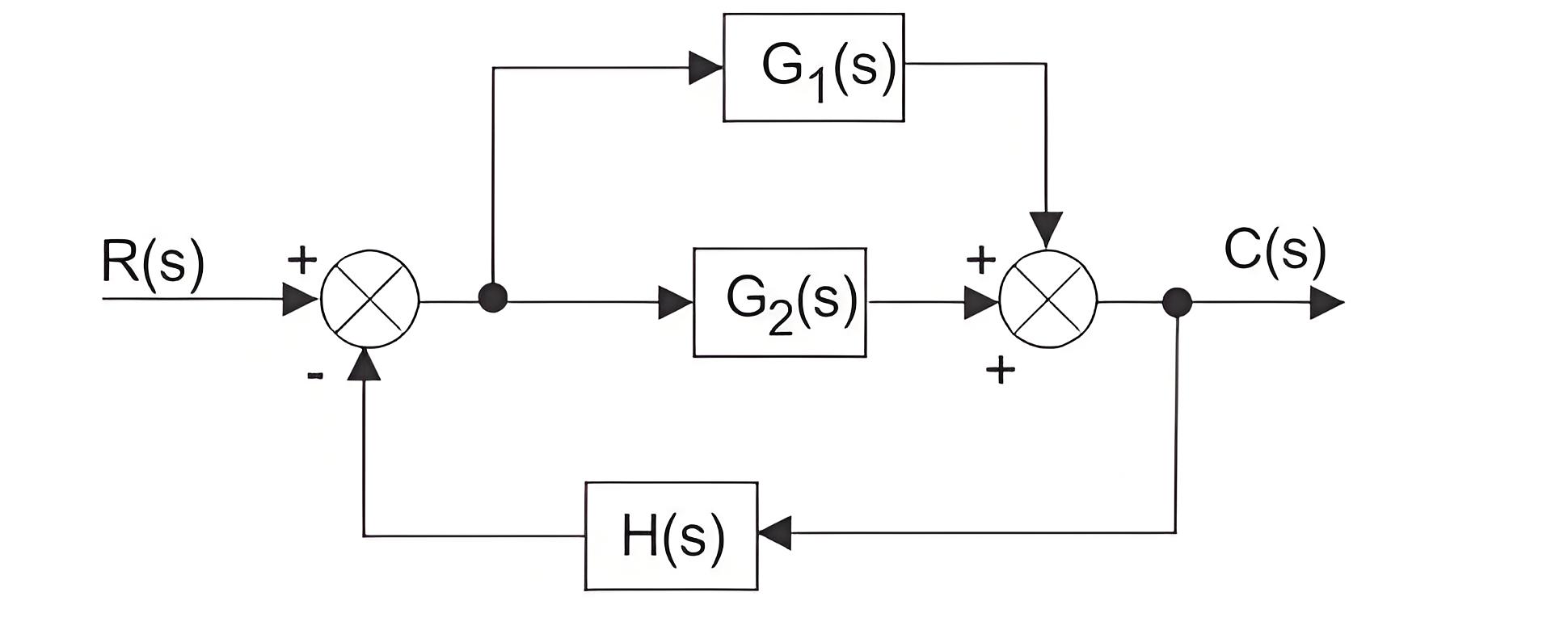
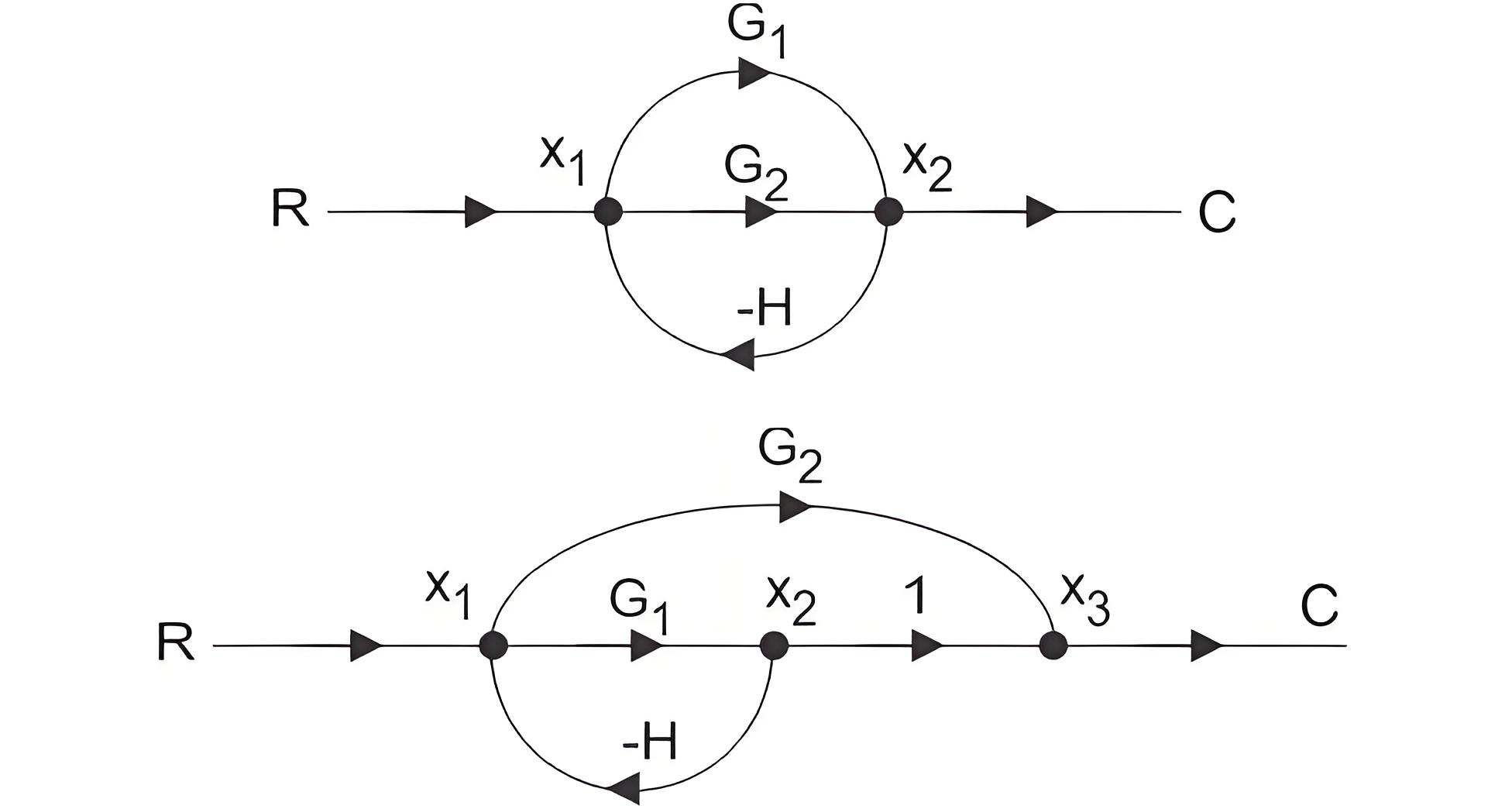
By using this formula one can easily determine the overall transfer function of control system by converting a block diagram of control system (if given in that form) to its equivalent signal flow graph. Let us illustrate the below given block diagram.
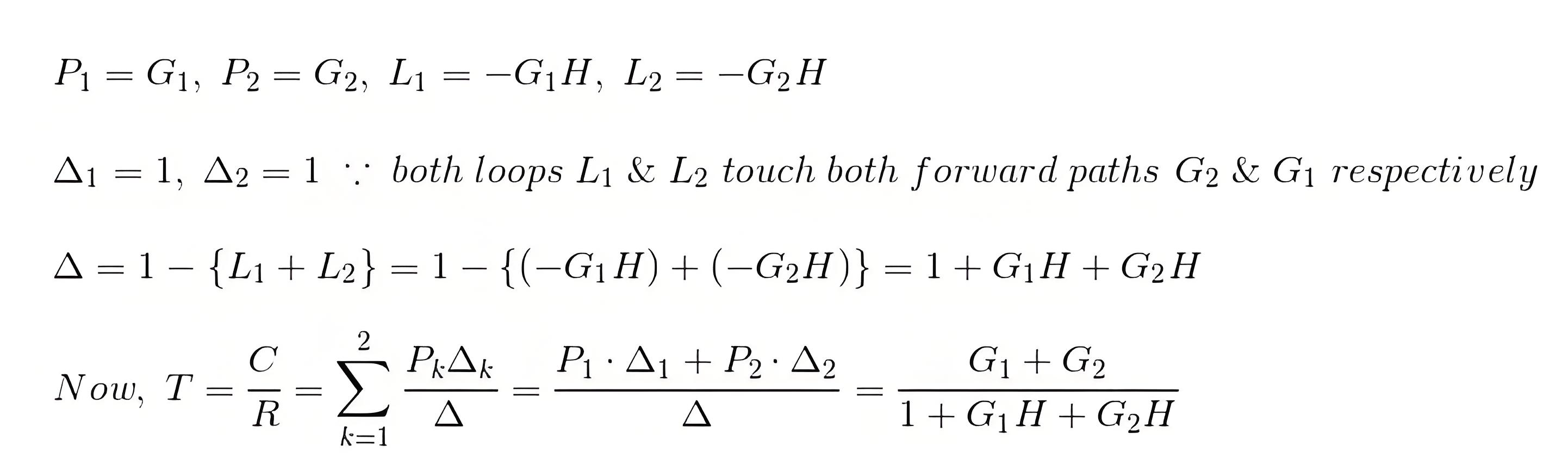
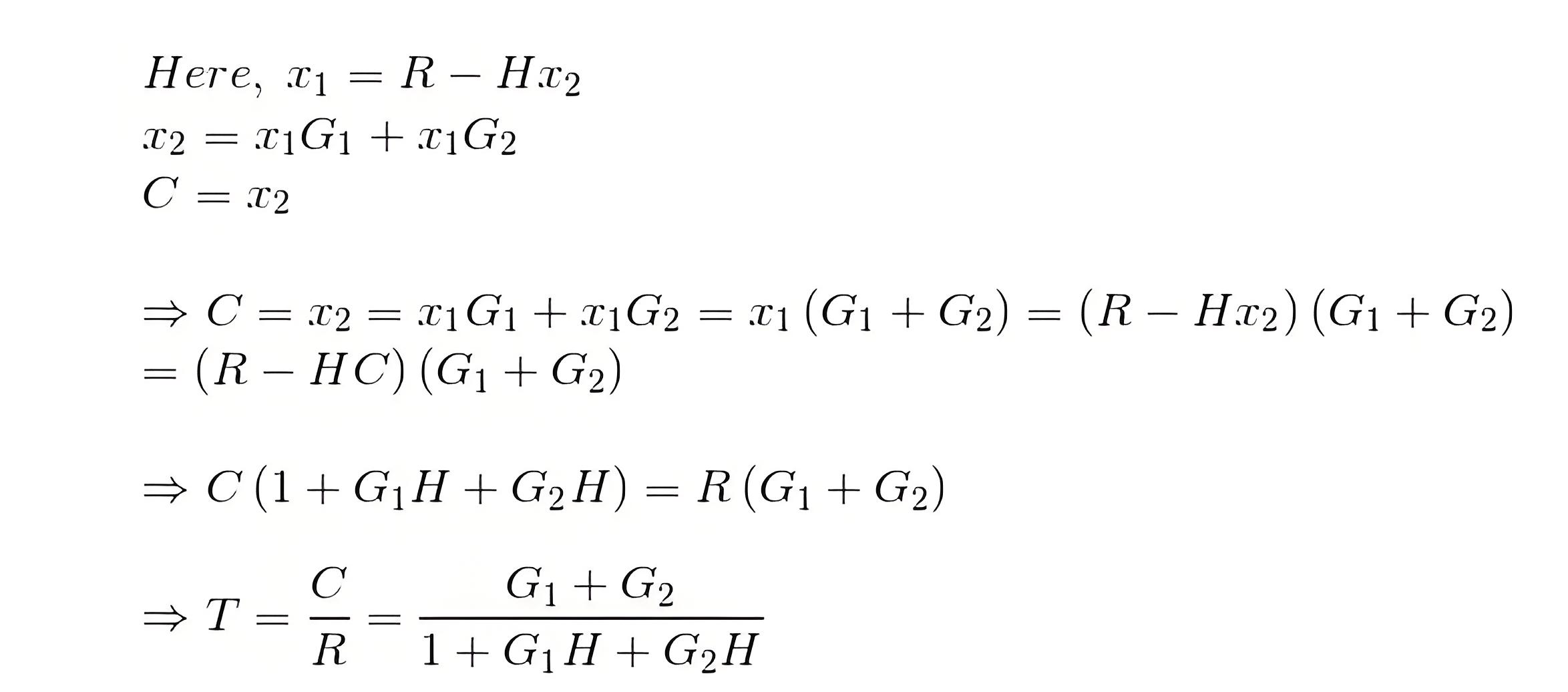
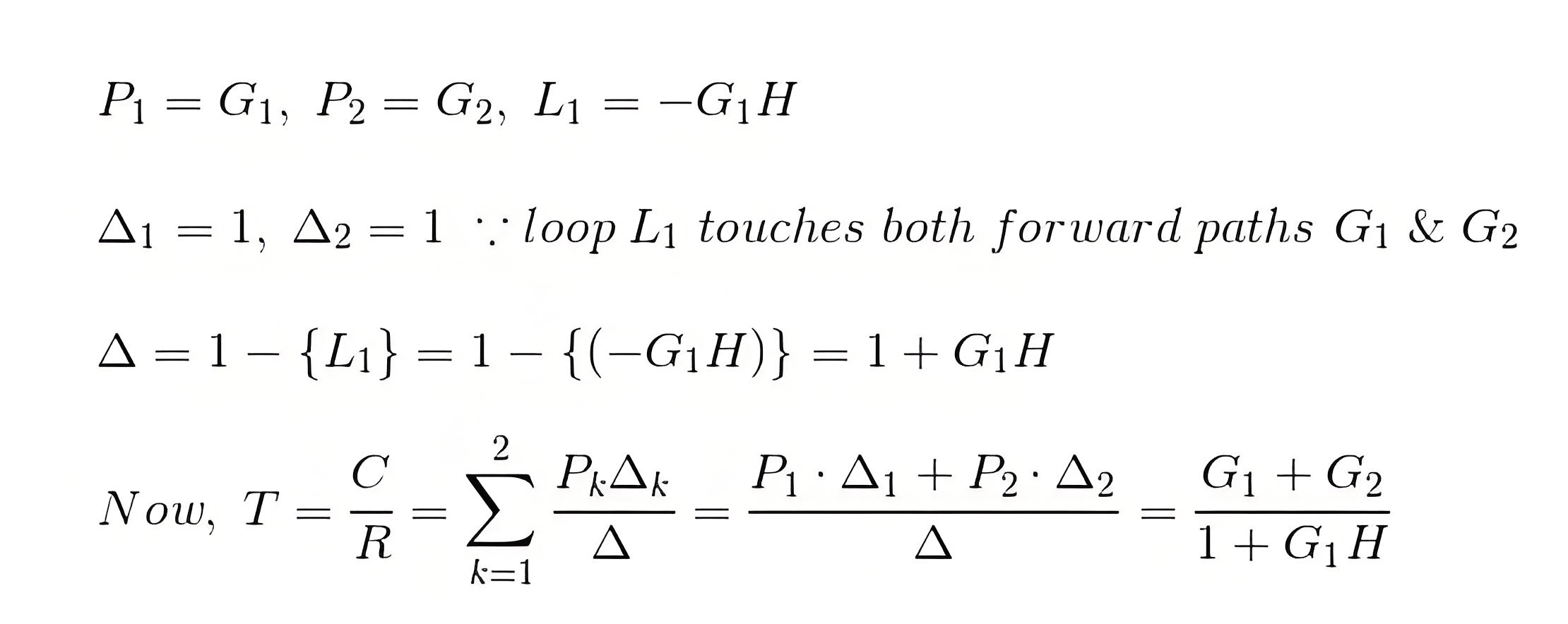
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.