Insulation Dielectric Test of Transformer
Dielectric Test Definition
The dielectric test of a transformer checks the insulation’s ability to handle voltage without breaking down.
Separate Source Voltage Withstand Test of Transformer
This dielectric test checks the main insulation’s ability to withstand voltage between the winding and the earth.
Procedure
All three line terminals of the winding to be tested are connected together.
Other winding terminals not under test and the transformer tank should be connected to the earth.
Then a single-phase power frequency voltage of shape approximately sinusoidal is applied for 60 seconds to the terminals of the winding under test.
The test shall be performed on all the windings one by one.
The test is successful if the insulation does not break down during the test.
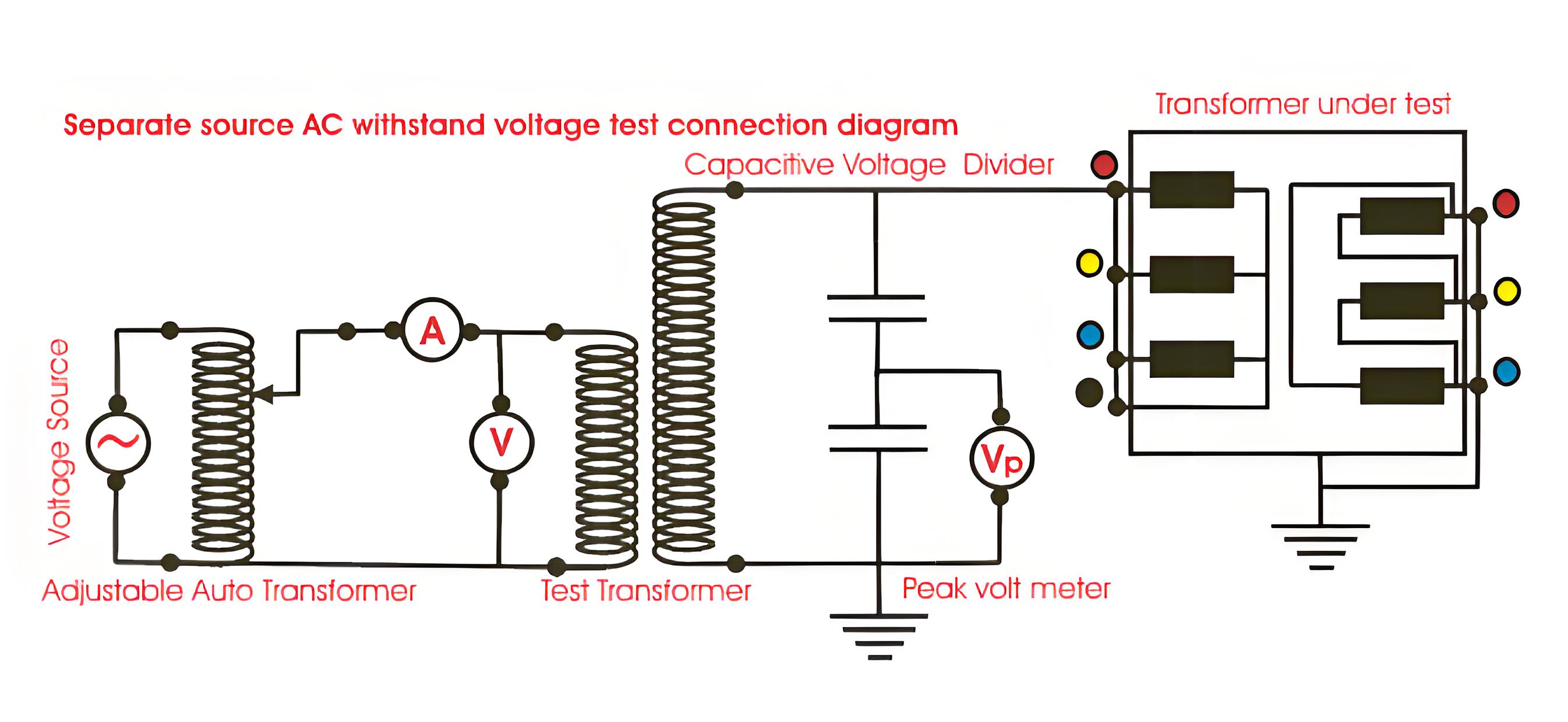
In this transformer testing, the peak value of voltage is measured, that is why the capacitor voltage divider with digital peak voltmeter is employed as shown in the diagram above. The peal value multiplied by 0.707 (1/√2) is the test voltage.
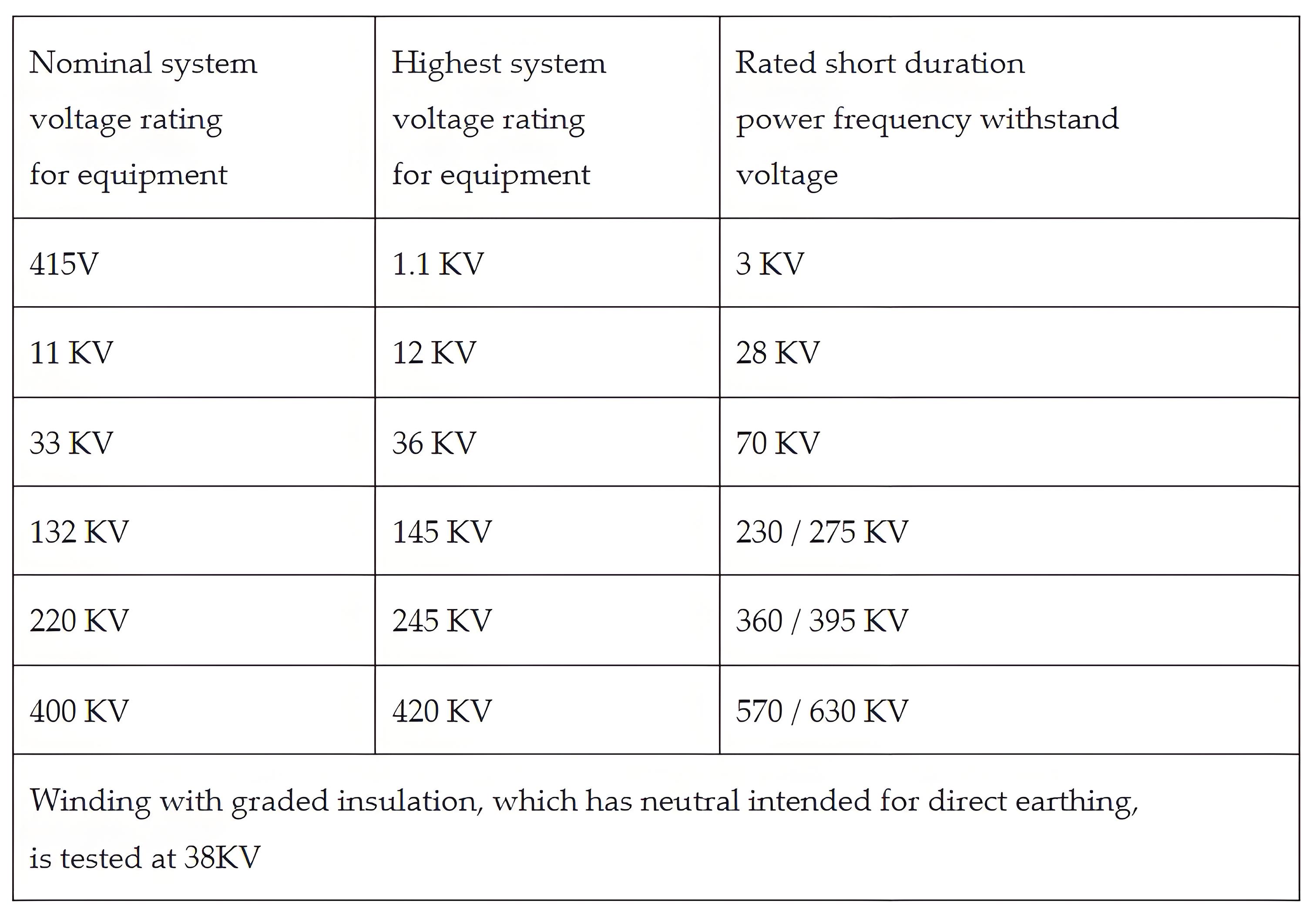
The values of test voltage for different fully insulated winding are furnished below in the table.
Induced Voltage Test of Transformer
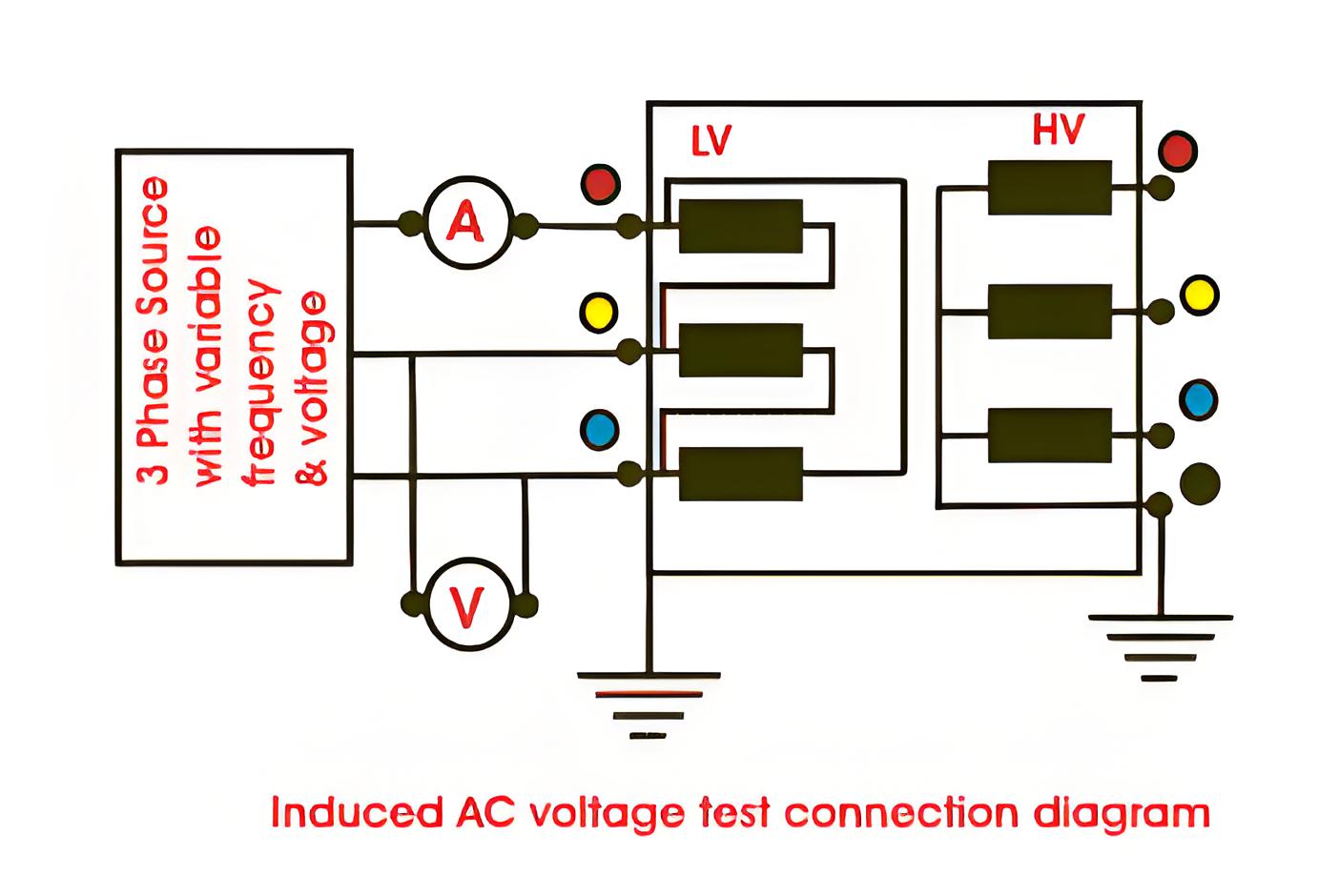
The induced voltage test of transformer is intended to check the inter turn and line end insulation as well as main insulation to earth and between windings-
Keep the primary winding of transformer open circuited.
Apply three phase voltage to the secondary winding. The applied voltage should be twice of rated voltage of secondary winding in magnitude and frequency.
The test should last for 60 seconds.
The test shall start with a voltage lower than 1/3 the full test voltage, and it shall be quickly increased up to desired value.
The test is successful if no break down occurs at full test voltage during test.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.