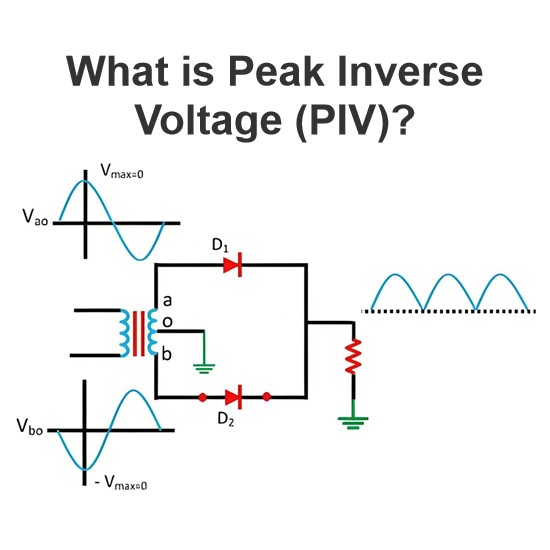
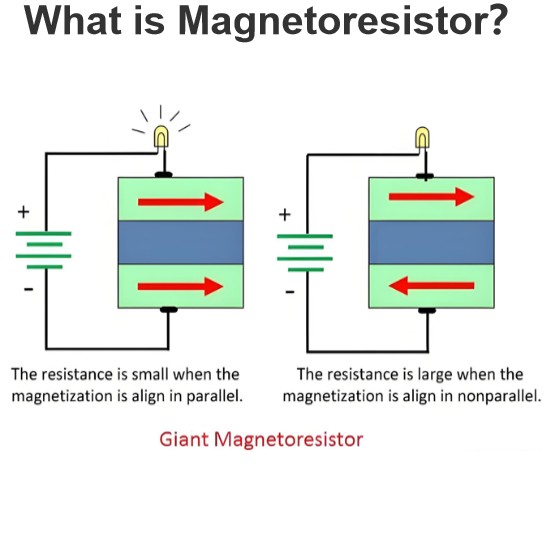
Reasons for using AC for long-distance power transmission
Historical development factor
Early power systems were dominated by alternating current: In the early days of power system development, alternator and transformer technology was relatively mature and easy to manufacture.
Ac system can easily change the voltage level through the transformer to achieve high-voltage transmission to reduce line losses, so AC transmission has been widely used in the early days and formed a huge power grid system.
Technical considerations
Advantages of transformers in AC systems
Ac transmission can be easily raised and lowered using transformers. At the power generation end, the output voltage of the generator is increased to reduce the current and reduce the power loss on the line. At the power end, the voltage is reduced to a level suitable for the user through a transformer. The current DC transformer technology is relatively complex and costly, and it is difficult to adjust voltage as flexibly as AC transformers in long-distance transmission.
Reactive power compensation
Reactive power compensation can be carried out conveniently in AC system. Reactive power is the energy necessary to maintain electric and magnetic fields in a power system, but it does no work externally. In long-distance transmission, a large amount of reactive power is generated due to the inductance and capacitance effects of the line.
By installing reactive power compensation devices in substations, the power factor of the system can be improved, and the line loss and voltage fluctuation can be reduced. In contrast, reactive power control in HVDC systems is relatively complex and requires specialized equipment to compensate.
Grid interconnection
Most of the existing power systems are AC power grids, and the interconnection between AC systems is relatively easy. Through transformers and switchgear, it can realize the connection and power exchange of AC power grids in different regions and different voltage levels, and improve the reliability and stability of power grids.
The interconnection between the DC transmission system and the AC system needs to be converted through the converter station, which is difficult and costly. In large-scale power grids, the interconnection of AC systems makes power allocation and resource sharing more flexible.
Economic cost aspect
Equipment cost
At present, AC transmission equipment such as transformers, switches, circuit breakers and other technologies are mature, and the production cost is relatively low. The equipment of converter station in DC transmission system is complex, including converter valve, DC filter, flat wave reactor, etc., and the cost is expensive.
For example, the cost of building a HVDC converter station can be several times or more than that of an equivalent AC substation.
Maintenance cost
After long-term development and application of AC transmission equipment, the maintenance technology is relatively mature and the maintenance cost is low. The equipment maintenance requirements of DC transmission system are high, requiring professional technicians and special testing equipment, and the maintenance cost is high.
Apply
Long-distance large-capacity transmission: For long-distance (more than a few hundred kilometers), large-capacity transmission needs, HVDC transmission line loss is relatively low. Because DC transmission does not have the inductance and capacitance effects of AC transmission, there is no reactive power problem.
Submarine cable transmission: In submarine cable transmission, because the capacitive current of the AC cable will cause a lot of loss and voltage rise, and the DC cable does not have this problem, so the high-voltage DC submarine cable transmission has a great advantage.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.