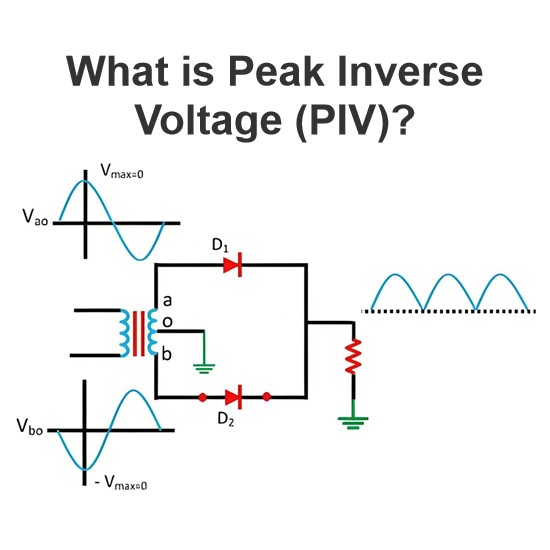
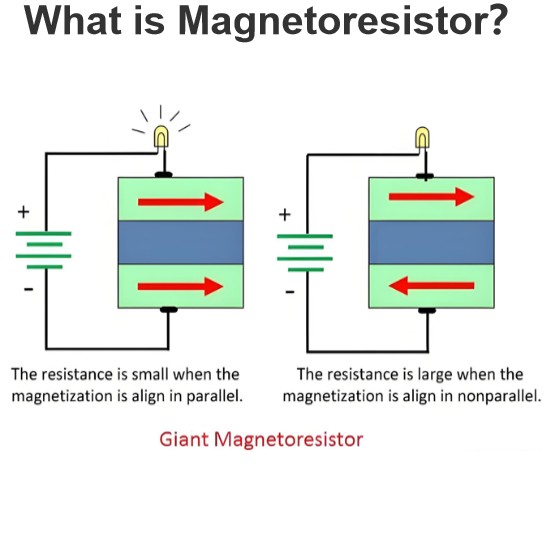
How does current affect a resistor compared to capacitors and inductors (reactive components)?
Comparison of Current Effects on Resistors vs. Capacitors and Inductors (Reactive Elements)
When comparing the effects of current on resistors to those on capacitors and inductors (reactive elements), we need to understand how each component behaves differently under the influence of current.
Impact of Current on Resistors
Basic Properties of Resistors
A resistor is a purely resistive element whose primary function is to impede the flow of current and convert electrical energy into heat. The resistance value R of a resistor is generally constant and does not depend on the current flowing through it. According to Ohm's Law:
V=I⋅R
V is the voltage,
I is the current,
R is the resistance value.
Effects of Current on Resistors
When current flows through a resistor, the resistor converts electrical energy into heat. The amount of heat generated is proportional to the square of the current, according to Joule's Law:
P=I 2⋅R
P is the power,
I is the current,
R is the resistance value.
This means:
Power Dissipation: The greater the current, the more power the resistor dissipates, resulting in more heat generation.
Temperature Rise: The greater the current, the higher the temperature of the resistor, which can lead to performance degradation or damage.
Effects of Current on Capacitors and Inductors
Capacitors (Capacitor)
A capacitor is a storage element primarily used to store electrical field energy. When current flows through a capacitor, the capacitor charges or discharges, and the voltage across its terminals changes over time.
Charging Process: As current flows through the capacitor, it gradually charges, increasing the voltage across it.
Discharging Process: When the voltage across the capacitor exceeds the supply voltage, the capacitor begins to discharge, decreasing the voltage across it.
The impact of current on capacitors includes:
Reactance: In AC circuits, capacitors produce capacitive reactance XC= 1/2πfC ,f is the frequency.
Reactive Power: Capacitors do not consume real power but generate reactive power.
Inductors (Inductor)
An inductor is a storage element primarily used to store magnetic field energy. When current flows through an inductor, it establishes a magnetic field and generates a counter-electromotive force (counter EMF) when the current changes.
Energy Storage Process: As current flows through the inductor, it builds up a magnetic field and stores energy.
Counter EMF: When the current changes, the inductor produces a counter EMF, opposing the change in current.
The impact of current on inductors includes:
Reactance: In AC circuits, inductors produce inductive reactanceXL=2πfL, f is the frequency.
Reactive Power: Inductors do not consume real power but generate reactive power.
Differences Between Reactive Elements and Resistors
Compared to capacitors and inductors (reactive elements), resistors (real elements) differ in the following ways:
Energy Conversion: Resistors convert electrical energy into heat, whereas capacitors and inductors primarily store energy.
Power Consumption: Resistors consume real power, whereas capacitors and inductors consume reactive power.
Temperature Influence: Current through resistors generates heat, leading to temperature increases, whereas capacitors and inductors mainly affect the reactive components of the circuit.
Considerations in Practical Applications
In practical applications, choosing the appropriate element depends on the specific requirements of the circuit:
Current Limiting: For applications requiring current limiting, resistors are useful.
Filtering: For filtering applications, combinations of capacitors and inductors can create various filters.
Energy Storage: For applications requiring energy storage, capacitors and inductors can be used to store electrical and magnetic field energy.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.