What is Diffusion Capacitance?
Diffusion capacitance definition
Diffused capacitance is a kind of differential capacitance effect of p-n junction when it is positively biased. It is caused by the diffusion process of different types of materials in semiconductor devices such as PN junction or MOSFET, that is, a few carriers in the doped region diffuse to the undoped region to form a space charge region, and finally appear as a capacitance effect.
Basic principle
When the PN junction is forward-biased, carriers (electrons and holes) will diffuse from the P and N regions to each other, respectively. In the process of diffusion, P area has accumulated a certain amount of non-equilibrium Jane (electronic), N area accumulated a certain amount of non-equilibrium Jane (hole). These accumulated non-equilibrium minority particles form a certain charge store, like a capacitor, with the ability to store chargThe size of diffusion capacitance is related to the forward bias voltage, temperature and the properties of semiconductor materials. The larger the forward bias voltage, the larger the diffusion capacitance.
The formation of the diffusion capacitance
When an AC voltage is applied to a semiconductor junction, the concentration of the minority varies with the voltage. These minority particles move randomly in the semiconductor and accumulate near the semiconductor junction. This accumulation is equivalent to a capacitance effect, namely the diffusion capacitance.
The expression for diffusion capacitance can usually be written as:
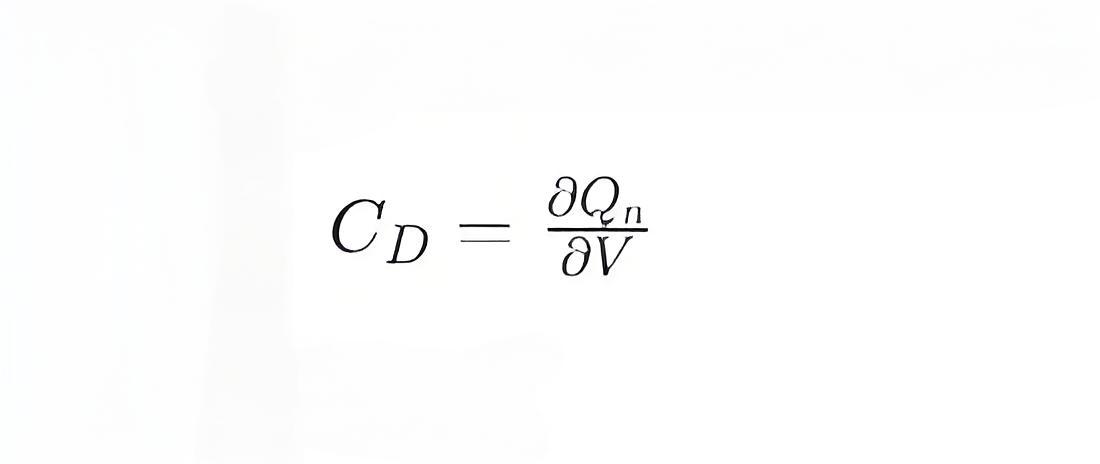
CD is the diffusion capacitance.
Qn is the minority charge.
V is the applied voltage.
Diffusion capacitance in a diode
In diodes, diffused capacitors mainly appear in the forward bias state. When the diode is forward-biased, minority particles (such as holes in N-type semiconductors) are injected into the P-region, resulting in a change in minority concentration. The change of concentration of Jane formed a capacitance effect, namely the diffusion capacitance.
Diffusion capacitance in a transistor
In transistors (such as BJT, MOSFETs, etc.), the diffusion capacitance also exists between the base and the emitter. When the transistor work in high frequency or high speed condition, the influence of the diffusion capacitance more apparent, because it affects the gain of the transistor and frequency response.
Effect of diffusion capacitance
The influence of diffusion capacitance in semiconductor devices is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
High frequency performance: In high frequency applications, diffusion capacitors limit the bandwidth of the device and affect its high frequency performance.
Switching speed: in switching applications, the diffusion capacitance can affect the speed of switching devices, increase switching loss.
Signal distortion: In amplifiers, diffused capacitors may introduce additional phase delay, resulting in signal distortion.
Calculation formula
The calculation of diffusion capacitance is usually based on models in semiconductor physics. For a diode, the diffusion capacitance can be approximated as:
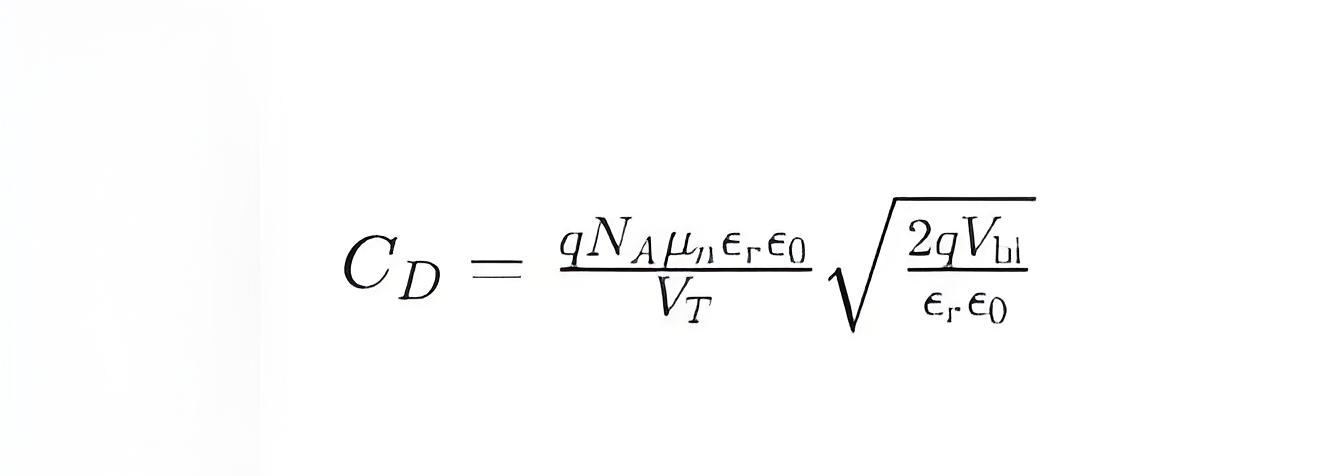
Q is the electronic charge.
NA is doping concentration
μn is electron mobility.
ϵr is the relative dielectric constant.
ϵ0 is the dielectric constant of vacuum.
VT is thermal voltage, n = kT/q, k is the boltzmann constant, T is the absolute temperature.
Vbi is the built-in potential.
Apply
High frequency circuits: In radio frequency (RF) and microwave circuits, the effect of diffusion capacitance cannot be ignored.
High-speed digital circuit: in high-speed digital circuit, the diffusion capacitance can affect the signal rise time and fall time.
Power management: In a power management circuit, diffusion capacitance affects the efficiency of the switching power supply.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.