What is Norton’s Theorem And How to Find The Norton Equivalent Circuit
What is Norton Theorem? (Norton’s Equivalent Circuit)
Norton’s Theorem (also known as the Mayer–Norton theorem) states that it is possible to simplify any linear circuit to an equivalent circuit with a single current source and equivalent parallel resistance connected to a load. The simplified circuit is known as the Norton Equivalent Circuit.
More formally, Norton’s theorem can be stated as:
“A circuit having any linear bilateral elements and active sources can be replaced by a simple two-terminal network consisting of an impedance and a current source, regardless of the complexity of the network.”
Norton theorem is a parallel to Thevenin’s theorem. And it is widely used in circuit analysis to simplify complex networks and to study the circuit’s initial condition and steady-state response.

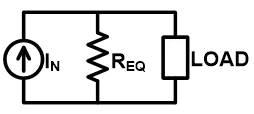
Norton Theorem
As shown in the above figure, any complex bilateral network simplifies into a simple Norton equivalent circuit.
Norton equivalent circuit consists of an equivalent impedance connected parallel with a current source and load resistance.
The constant current source used in Norton equivalent circuit is known as Norton current IN or short circuit current ISC.
Norton theorem was derived by Hans Ferdinand Mayer and Edward Lawry Norton in 1926.
Norton Equivalent Formula
As shown in the Norton equivalent circuit, the Norton current is divided into two paths. One path passes through the equivalent resistance and the second path passes through the load resistance.
Therefore, the current passing through the load resistance can be derived by the current divider rule. And the formula for the Norton theorem is;
How to Find Norton Equivalent Circuit
Any complex bilateral network is replaced by a simple Norton equivalent circuit. And it consists of;
Norton equivalent resistance
Norton equivalent current
Load resistance
Norton Equivalent Resistance
Norton equivalent resistance is similar to the Thevenin equivalent resistance. To calculate the Norton equivalent resistance, we need to remove all active sources of the network.
But the condition is; all sources must be independent sources. If the network consists of dependent source/s, you need to use other methods to find Norton equivalent resistance.
In case, the network consists of only of independent sources, all sources are removed from the network by short-circuiting the voltage source and open-circuit the current source.
While calculating the Norton equivalent resistance, the load resistance is open-circuited. And find the open-circuit voltage between load terminals.
Sometimes, the Norton resistance is also known as Thevenin equivalent resistance or open-circuit resistance.
Let’s understand with an example.
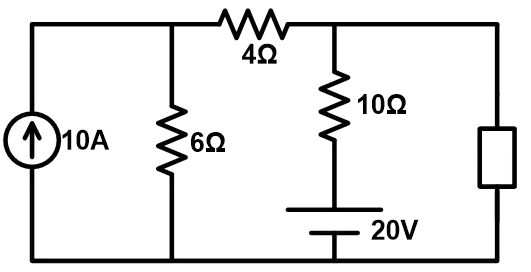
First, check the network having any dependent sources? In this case, all sources are independent sources; 20V voltage source and 10A current source.
Now, remove both sources by the short-circuiting voltage source and open-circuit current source. And open load terminals.
Now, find the open-circuit voltage by making series and parallel connections of resistances.
Resistances 6Ω and 4Ω are in series. So, the total resistance is 10Ω.
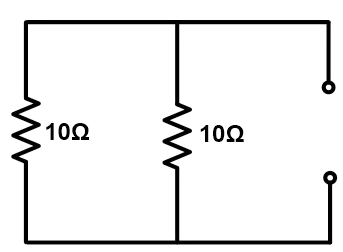
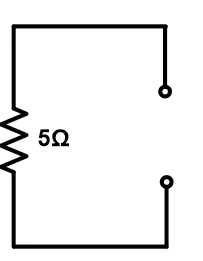
Both 10Ω resistances are in parallel. So, equivalent resistance REQ = 5Ω.
Norton Equivalent Current
To calculate the Norton equivalent current, the load resistance is short-circuited. And find current passing through the short-circuited branch.
So, Norton current or Norton equivalent current is also known as short-circuit current.
In the above example, remove load resistance and make short-circuit the load branch.
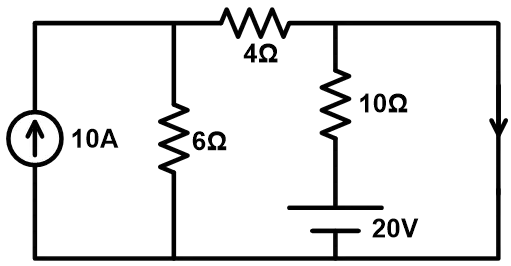
In the above network, the branch containing the voltage source is neglected as it is a redundant branch. It means it is a parallel branch of a short-circuited branch.
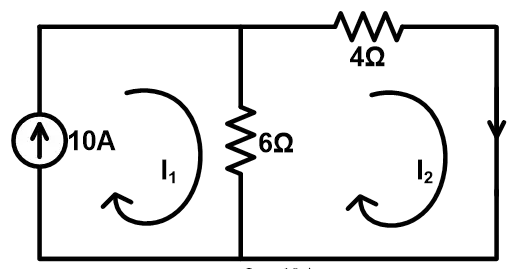
Apply KVL in loop-2;![]()
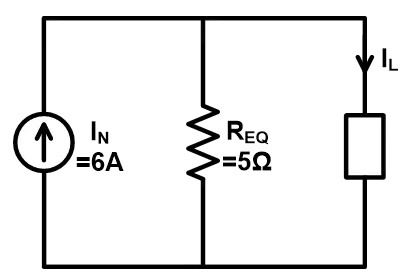
Current passing through the load is IL. According to the current divider rule;
Norton Equivalent Resistance with Dependent Source
To calculate the Norton equivalent resistance for a circuit having a dependent source, we need to calculate the open-circuit voltage (VOC) across the load terminals.
Open-circuit voltage is similar to the Thevenin equivalent voltage.
After finding the Thevenin equivalent voltage and Norton current; put this value in the below equation.
Norton Equivalent Circuit Examples
Example-1 Find the Norton Equivalent Circuit Across Terminals AB.
Find Norton equivalent circuit across terminals AB in given active linear network shown in below figure.
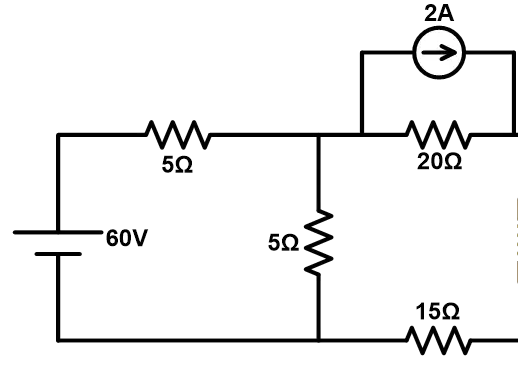
Step-1 Find Norton equivalent current (IN). To calculate IN, we need to short-circuit the terminals AB.
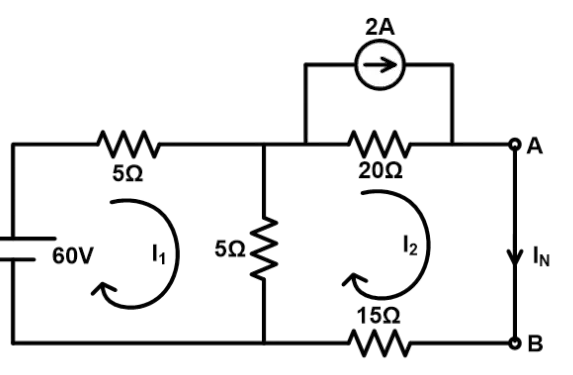
Apply KVL in loop-1;
Apply KVL in loop-2;
From the current source;
Hence;
By solving equation-1 and 2; we can find the value of current I2 which is same as Norton current (IN).
Step-2 Find equivalent resistance (REQ). For that, current source open circuited and voltage source short-circuited.
Step-3 Put the value of Norton current and equivalent resistance in the Norton equivalent circuit.
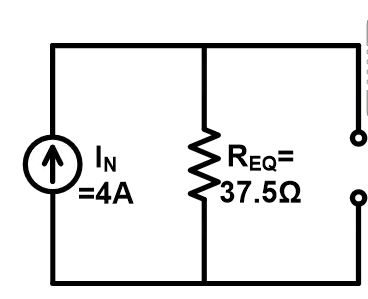
Example-2 Find Norton and Thevenin equivalent circuit for given network
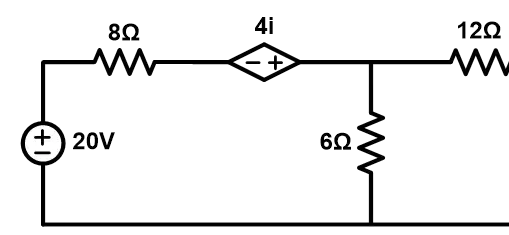
Step-1 Find the Norton current (IN). For that short terminals AB.
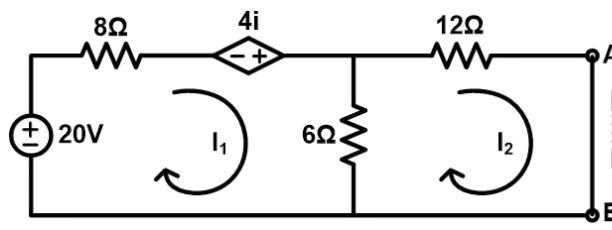
Apply KVL to the loop-1;
Now, apply KVL at loop-2
Put this value in equation-3;
Step-2 The network consists of a dependent voltage source. Therefore, equivalent resistance cannot find directly.
To find the equivalent resistance, we need to find an open-circuit voltage (Thevenin voltage). For that open terminals AB. And due to the open circuit, the current flowing through the 12Ω resister is zero.
So, we can neglect the 12Ω resister.
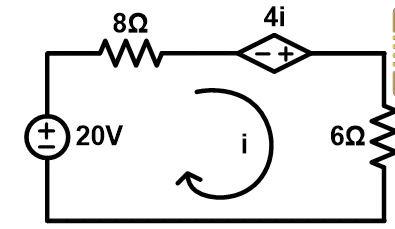
Voltage across 6Ω resistance is same the voltage across terminals AB.
Step-3 Find equivalent resistance;
Step-4 Put the value of Norton current and equivalent resistance in the Norton equivalent circuit.
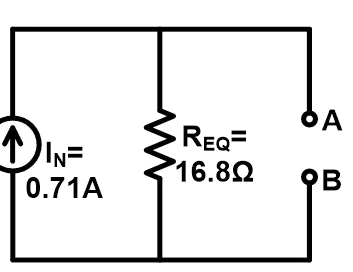
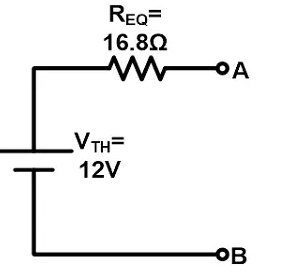
Step-5 Put the value of Thevenin voltage and equivalent resistance in the Thevenin equivalent circuit.

Norton and Thevenin Equivalent Circuits
Norton equivalent circuit is a dual network of the Thevenin equivalent circuit. Norton and Thevenin theorem widely used to solve complex circuits in network analysis.
As we have seen, the Norton equivalent circuit consists of a Norton current source and Thevenin equivalent circuit consists of a Thevenin voltage source.
The equivalent resistance is the same in both cases. To convert Norton to Thevenin equivalent circuit, source transformation is used.
In the above example, the Norton current source and parallel equivalent resistance can be converted into a voltage source and resistance connected in series.
The value of voltage source will be;
And you will get the exact Thevenin equivalent circuit.
Source: Electrical4u.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.