ELI the ICE man: What is it
What is ELI the ICE man?
ELI the ICE man is used to remember the relationship between current and voltage in an inductor and capacitor. ELI the ICE man stands for the fact that voltage [E] leads current [I] in an inductor [L] (that’s the ELI part) and current [I] leads voltage [E] in a capacitor [C] (that’s the ICE part).
ELI the ICE man is a mnemonic. That is to say that it’s a learning technique that aids information retention in human memory.
So ELI the ICE man helps us remember that:
ELI: Voltage [E] leads current [I] in an inductive circuit [L]
ICE: Current [I] leads voltage [E] in a capacitive circuit [C]
Or rephrased in more detail:
In an inductive (L) circuit, the measured voltage (E) sine wave precedes the measured current (I). ELI tells us that the voltage (E) leads or comes before the current (I) in an inductor (L).
In a capacitive circuit, the sine wave of current (I) precedes the measured sine wave of voltage (E). ICE tells us the current (I) leads or comes first before voltage (E) in a capacitor (C).
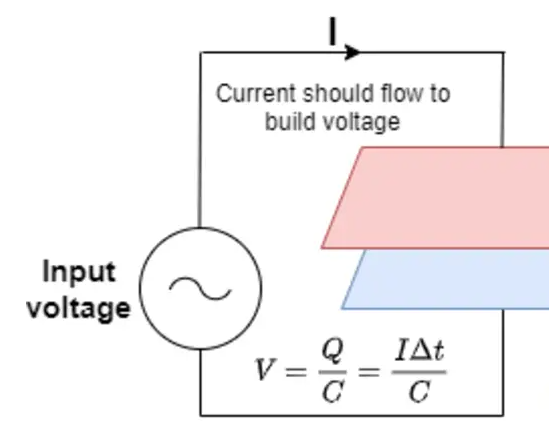
A capacitor is a device which is an electric field store electrical energy. It is a two-terminal passive electronic component. A capacitor’s effect is known as capacitance.
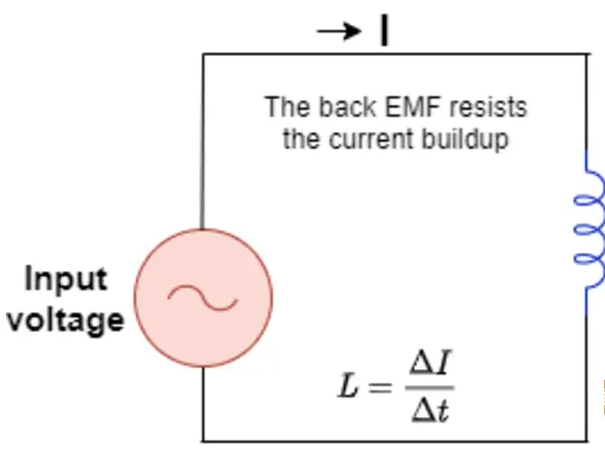
An inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component, also known as a coil, choke, or reactor, that stores energy when electrical current flows through it in a magnetic field.
In a capacitor, the voltage is directly proportional to the electrical charge on it. So, the current must lead the voltage in time and phase in order to conduct the charge to the capacitor plates. This results in an increase in the voltage.
In an inductor, when a voltage is applied, it resists the current change. This current slowly increases than the voltage, hence it lags in phase and time.
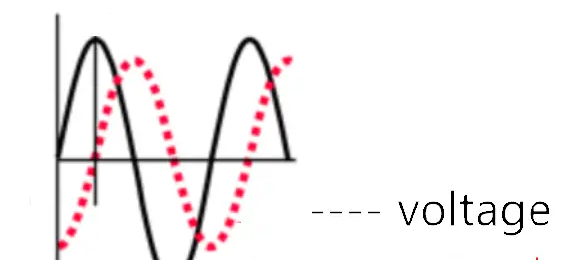
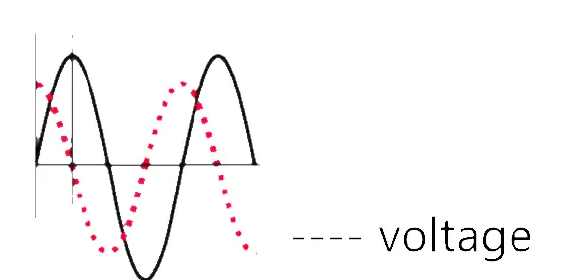
The current and voltage don’t peak at the same time when capacitors or inductors are involved in an AC circuit. The phase difference is said to be the fraction of a cycle difference between the peaks expressed in degrees.
The phase difference is lesser than equal to 90 degrees. It is usual to use the angle by which the voltage leads the current.
This leads to a positive phase for inductive circuits since current lags the voltage in an inductive circuit.
The phase is negative for a capacitive circuit since the current leads the voltage. Here the mnemonic ELI the ICE man helps to remember the sign of the phase.
ELI the ICE man Examples
In a circuit with just an inductor and an AC power source, there is a 90-degree phase difference between the current and voltage.
The voltage leads the current by 90 degrees. This is an example where ELI is important and it tells that in an inductor (L), the EMF (E) is ahead of the current (I).
In a circuit with only a capacitor and an AC power source, there is also a 90-degree phase difference between the current and voltage.
The voltage lags the current in this case. This is an example where ICE is important and it tells that in a capacitor (C), the voltage EMF (E) is behind the current (I).
Source: Electrical4u.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.