What is Synchronous Condenser ?
What is Synchronous Condenser ?
Synchronous Condenser Definitio
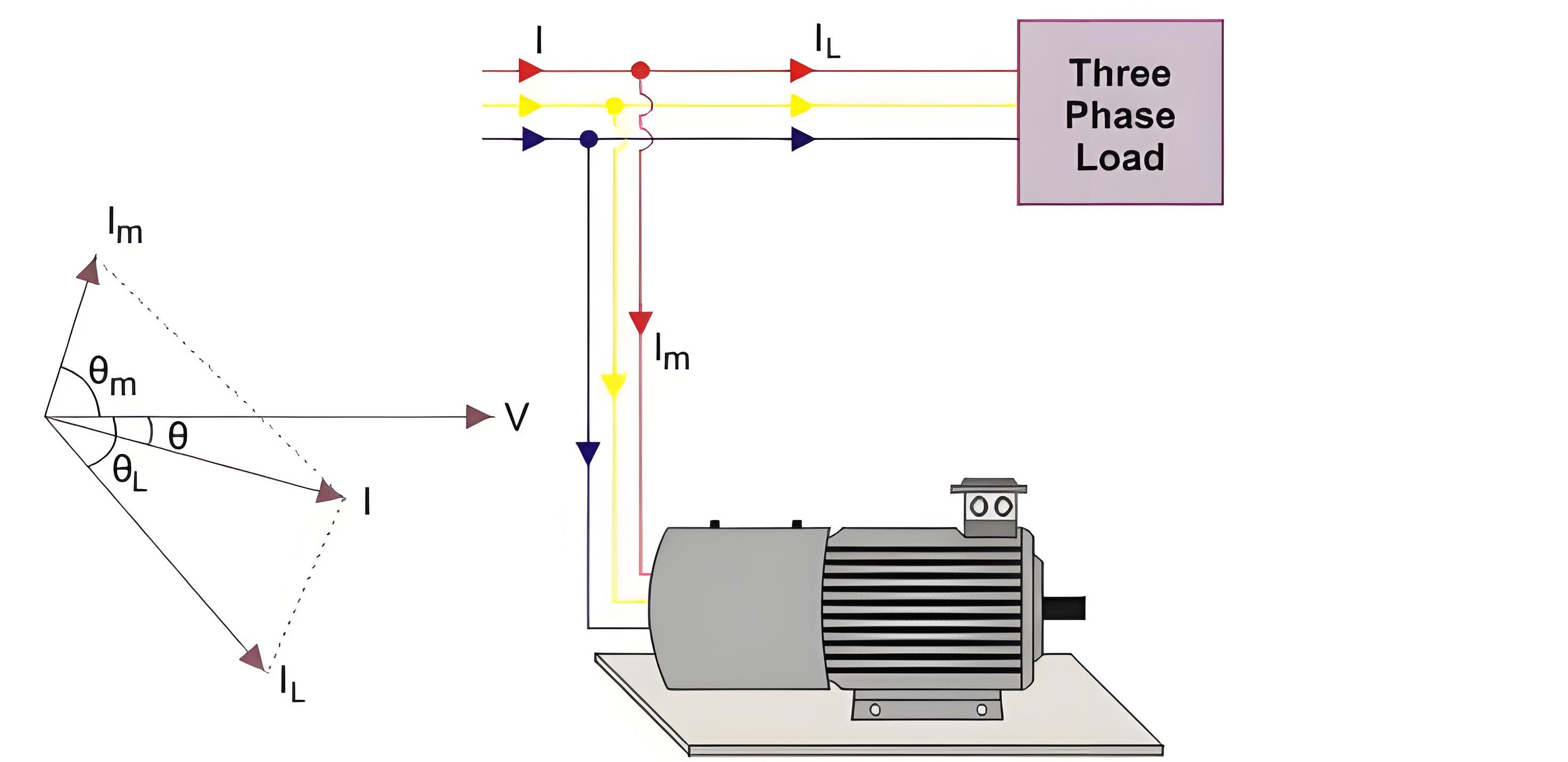
A synchronous condenser is defined as a synchronous motor running without a mechanical load, used to improve the power factor of power systems.
Improving Power Factor
It draws a leading current when over-excited, which helps balance the lagging current from inductive loads.
Three-Phase System Usage
In a three-phase system, the synchronous motor operates at no load to improve the overall power factor by adjusting the current angle.
Synchronous Condenser Advantage
Smooth, continuous control of the power factor
Synchronous Condenser Disadvantage
The system is not silent since the synchronous motor has to rotate continuously.
Economic Considerations
Synchronous condensers are economical for large power networks but less so for systems below 500 kVAR, where capacitor banks are preferred.
Smooth Control
Synchronous condensers provide smooth, continuous power factor adjustment, unlike capacitor banks, which adjust in steps.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













