What is an SWR Meter?
What is an SWR Meter?
SWR Meter definition
A standing wave meter, also known as a standing wave meter, is used to measure the mismatch between a transmission line and its load (usually an antenna), helping technicians with impedance matching.

SWR definition
The standing wave ratio measures the ratio of maximum to minimum voltage or current along a transmission line, reflecting the efficiency of impedance matching and indicating the presence of standing waves.
SWR formula and calculation
VSWR can be calculated from various parameters. By definition, VSWR is the ratio of the maximum voltage to the minimum voltage on a line.
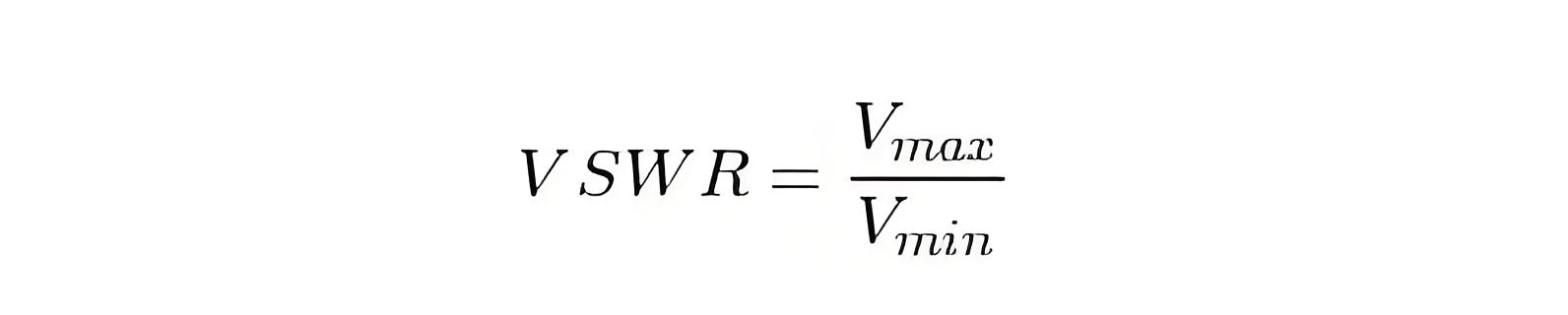
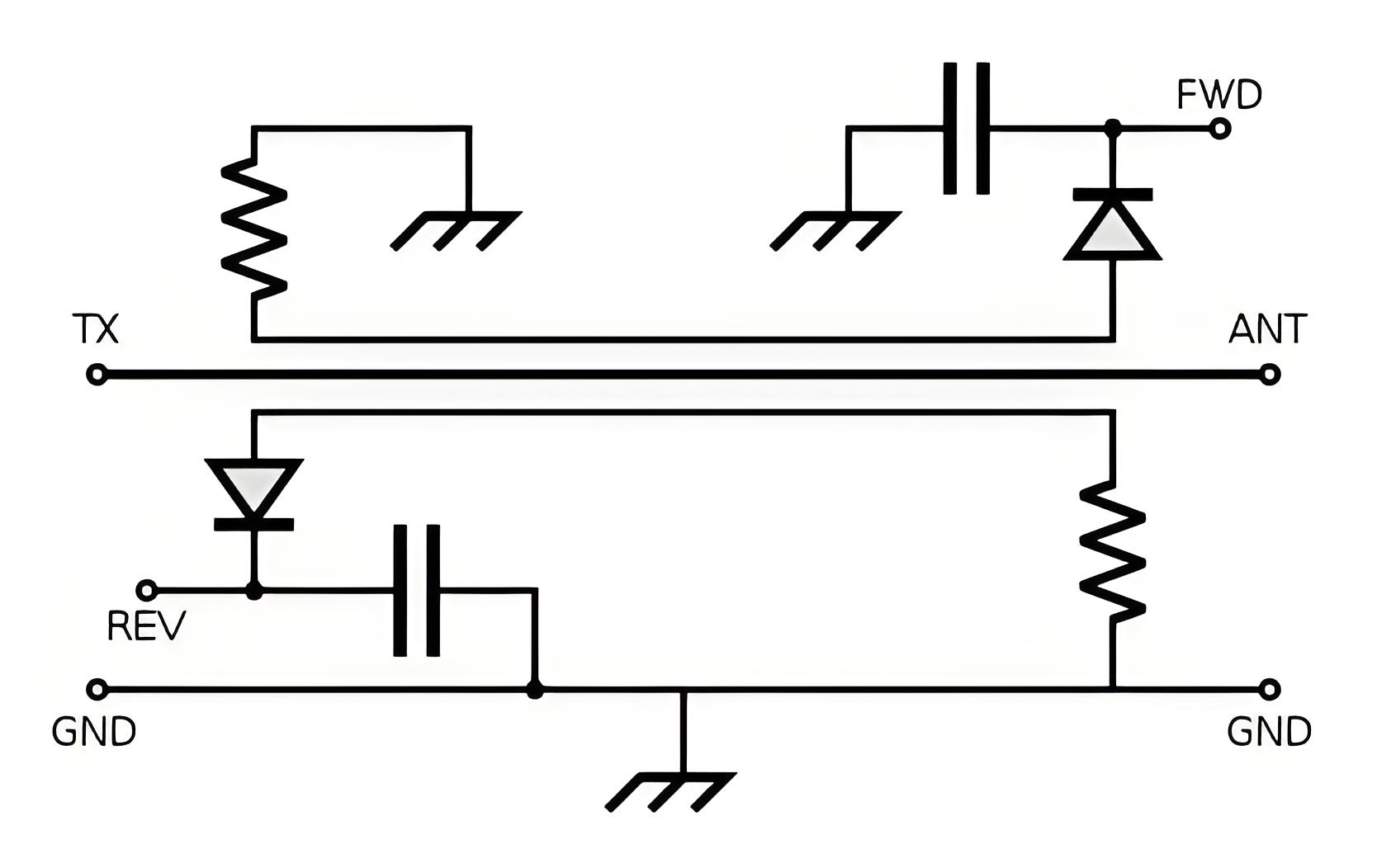
The working principle of directional standing wave ratio meter SWR
Directional VSWR meters use directional couplers and diode Bridges to measure the amplitude of forward and reverse waves and help determine impedance mismatches.
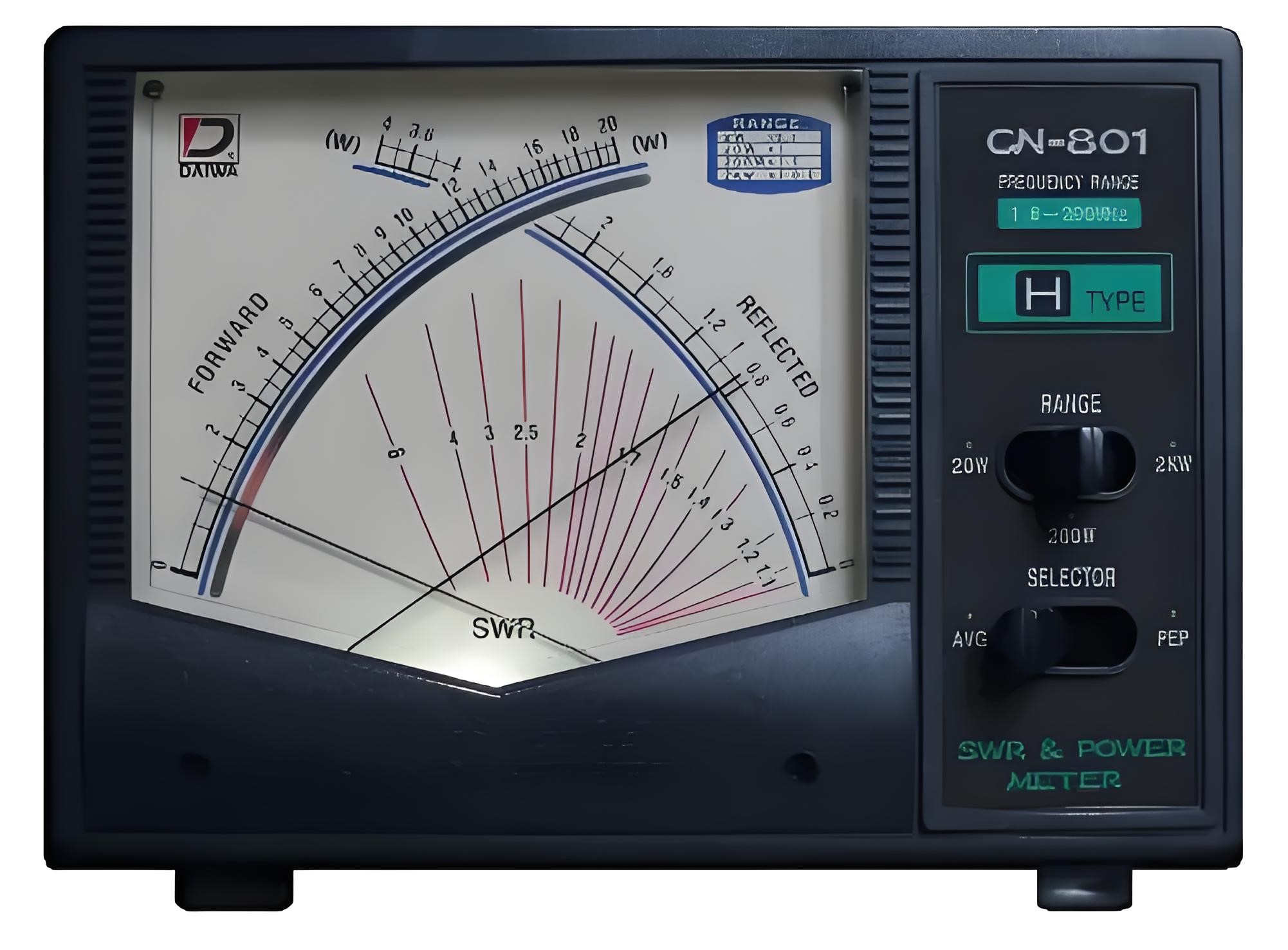
Methods of measuring SWR
SWR can be measured using techniques such as slotted lines or directional SWR meters, which assess transmitted and reflected wave amplitude to determine SWR values.
How to use a SWR meter
Look for clear channels or frequencies
Reduce power consumption
Set mode switch
Set the standing wave ratio meter
Adjust forward reading
Switch the meter to reverse
Stop transmission
Check other frequencies
Application of SWR
The most common use of SWR meters is during the installation and tuning of transmitting antennas.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













