What is Superconductivity?
What is Superconductivity?
Superconductivity Definition
Superconductivity is defined as the property of certain materials to have zero electrical resistance at very low temperatures.
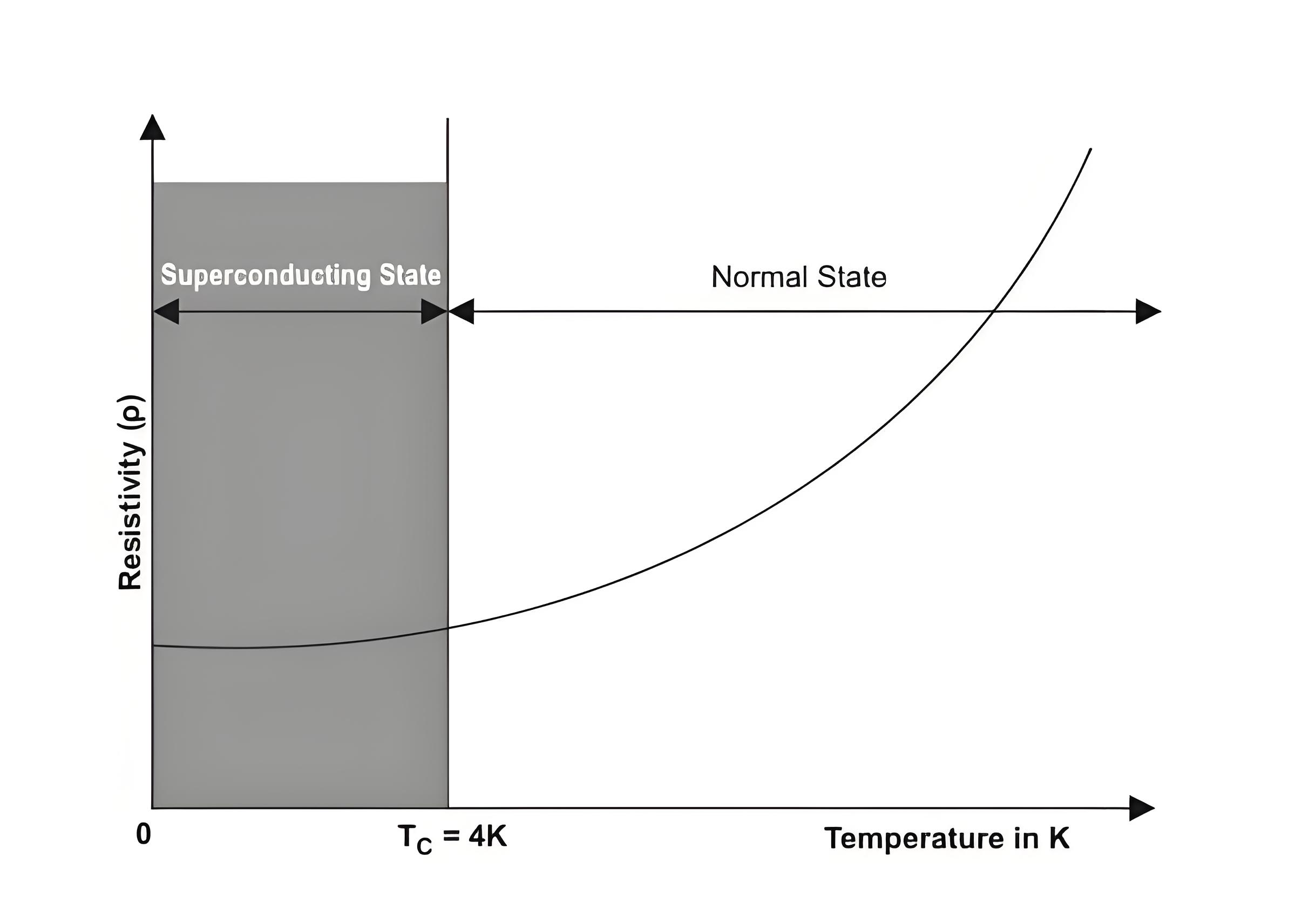
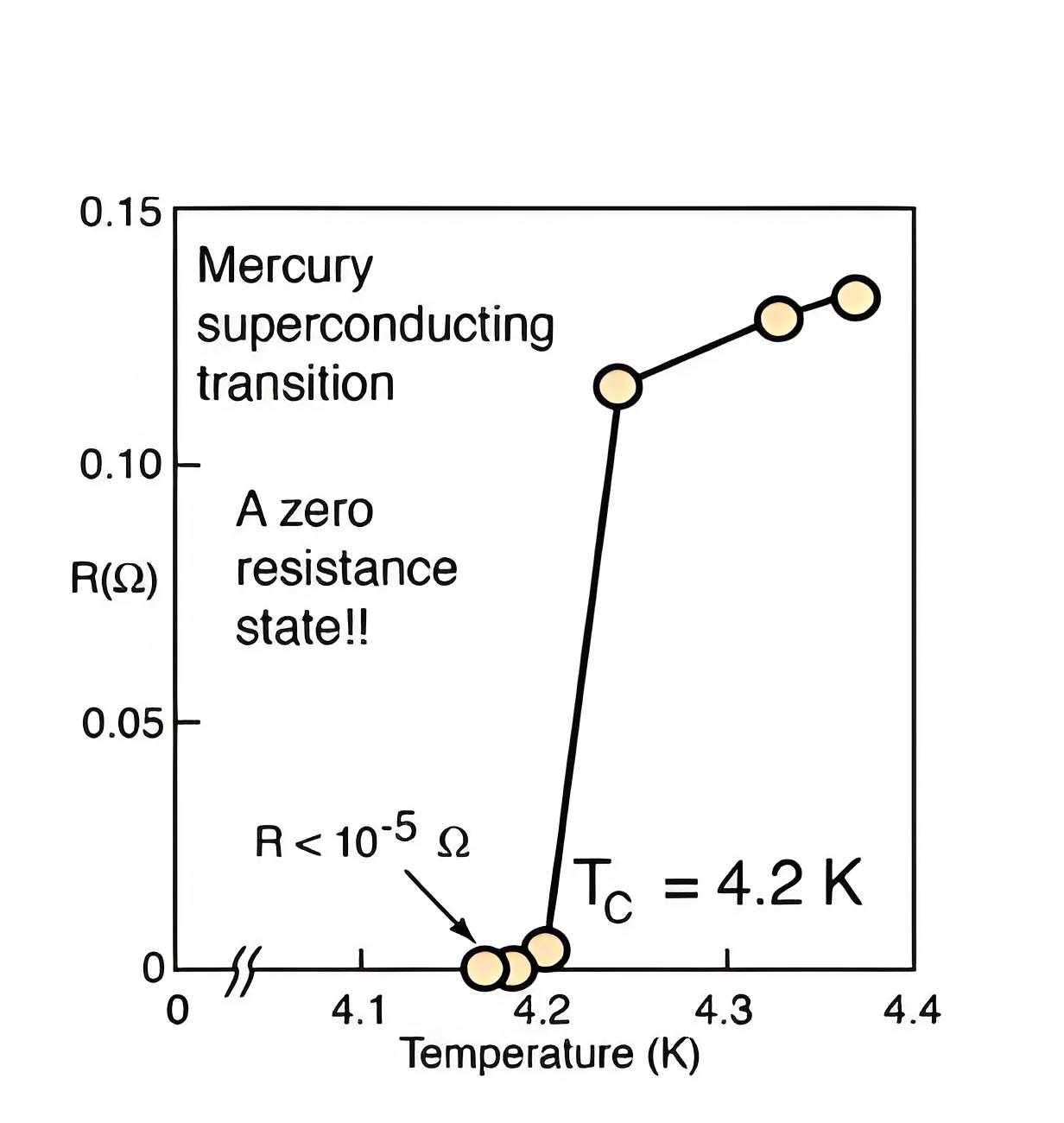
Critical Temperature
The critical temperature is the specific temperature below which a material becomes superconducting.
Properties of Superconductors
Zero electric resistance (infinite conductivity)
Meissner Effect: Expulsion of magnetic field
Critical Temperature/transition temperature
Critical Magnetic field
Persistent currents
Josephson Currents
Critical current
Meissner Effect
Superconductors exhibit the Meissner effect, where they expel magnetic fields when cooled below their critical temperature.
Critical Current and Magnetic Field
Superconductivity is lost if the current through the material exceeds the critical current or if an external magnetic field exceeds the critical magnetic field.
Applications of Superconductivity
Superconductivity is used in medical imaging, quantum computing, maglev trains, and particle accelerators.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













