What is the Seebeck Effect ?
What is the Seebeck Effect ?
Seebeck Effect Definition
The Seebeck effect is defined as the conversion of temperature differences into electric voltage, enabling various practical applications.
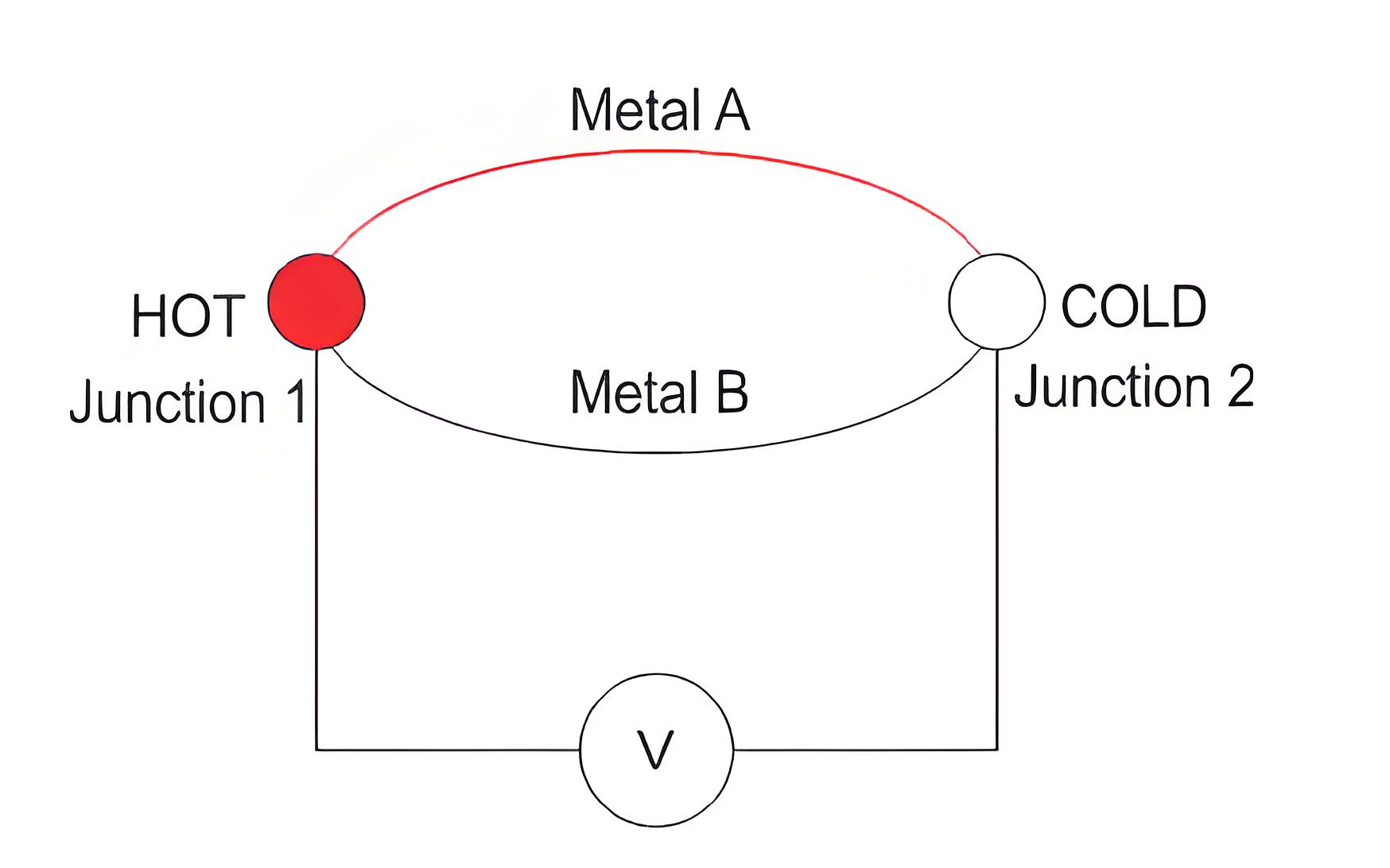
Temperature to Electricity
This effect generates electricity when there is a temperature difference across the junctions of two different materials.
Key Applications
Thermocouples
Thermoelectric generators
Spin caloritronics
Material Requirements
Effective materials for the Seebeck effect include metals with low Seebeck coefficients and semiconductors with higher coefficients for better performance.
Advantages
Simple
Reliable
Versatile
Limitations
Availability
Compatibility of materials
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













