What is a Pull-up Resistor?
What is a Pull-up Resistor?
Pull-up resistance definition
A resistor used in an electronic circuit to ensure the known voltage state of a signal.
Basic structure of pull-up resistor
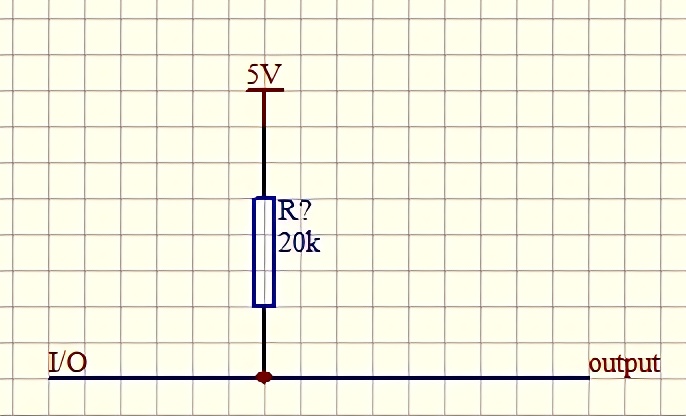
Working principle
On the wire to which the pull-up resistor is connected, if the external component is not enabled, the pull-up resistor "weakly" pulls up the input voltage signal. When the external component is not connected, the external "looks" high impedance to the input. At this time, the voltage at the input port can be pulled up to a high level by pulling up the resistor. If the external component is enabled, it will cancel the high level set by the pull-up resistor. In this way, the pull-up resistor allows the pin to maintain a certain logic level even when external components are not connected.
Pull-up resistor function
Pull-up resistors prevent ambiguous voltage states in digital circuits by maintaining voltage control when the switch is disconnected.
Calculation formula of pull-up resistance
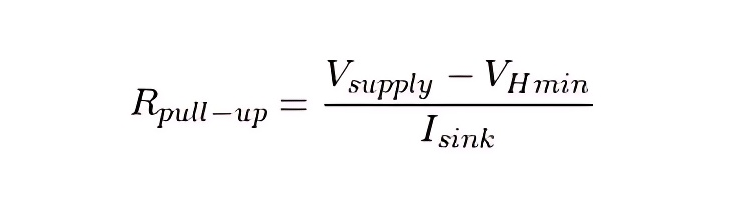
Application of pull-up resistance
Pull-up resistors are used as interface devices between switches and digital circuits.
Used in the I2C protocol bus to make a single pin act as an input or output.
In resistive sensors, it is used to control the current before analog-to-digital conversion.
Shortcoming
The disadvantage of pull-up resistors is that they consume additional energy when the current flows through them and may cause a delay in the output level. Some logic chips are sensitive to the transient state of the power supply introduced by the pull-up resistor, which forces an independent, filtered voltage source to be configured for the pull-up resistor.
We aim to gather electrical knowledge and share it with others.













