What is a Schottky Diode?
What is a Schottky Diode?
Schottky Diode definition
The reverse recovery time is extremely short (can be as small as a few nanoseconds), the positive pilot voltage drop is only about 0.4V, and the rectification current can reach thousands of amps, which can be used as a switching diode and a low-voltage high-current rectifier diode.
Schottky Diode structure
It is formed by connecting doped semiconductor regions (usually N-type) with metals such as gold, platinum, titanium, etc. The formation is not a PN junction, but a metal-semiconductor junction.
Schottky Diode equivalent circuit
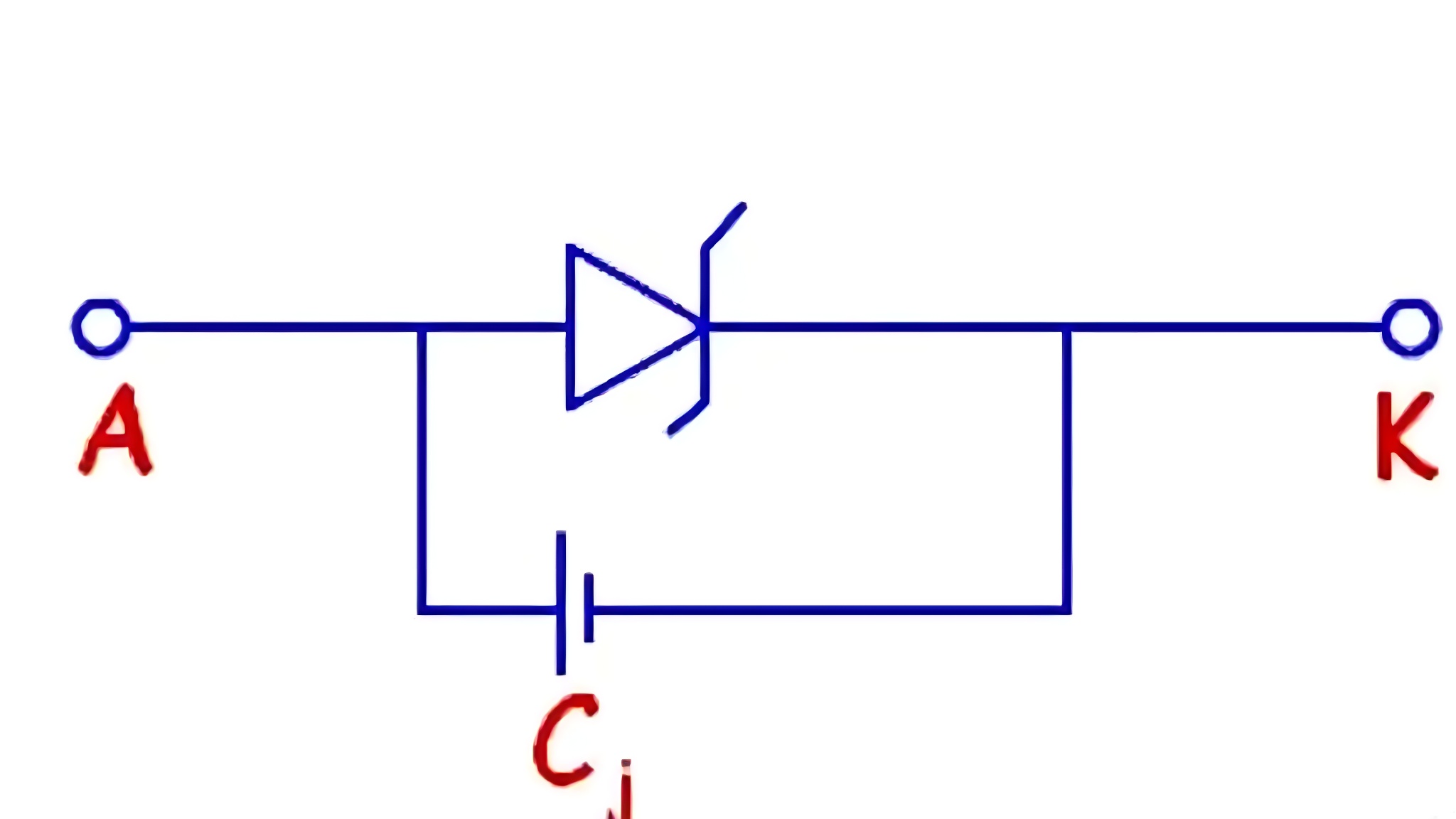
Schottky Diode main parameters
Reverse voltage
Forward current
Forward voltage
Leakage current
Junction capacitance
Recovery time
Schottky Diode advantages and disadvantages
Advantage
Low forward voltage, high speed switching, low noise, low power consumption
Shortcoming
The leakage current is large and the reverse voltage is low
Schottky diode selection
The type of Schottky diode to be selected should be determined according to the voltage VO, current IO, heat dissipation, load, installation requirements, and temperature rise required by the switching power supply.
Schottky diode applications
Used to protect the voltage regulator circuit against the accidental application of reverse polarity at the input
Provides a return path when the switch is off
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













