What is Permeance?
What is Permeance?
Permeability definition
Permeability is defined as a measure of the ease with which magnetic flux passes through a material or magnetic circuit.
The Permeability formula
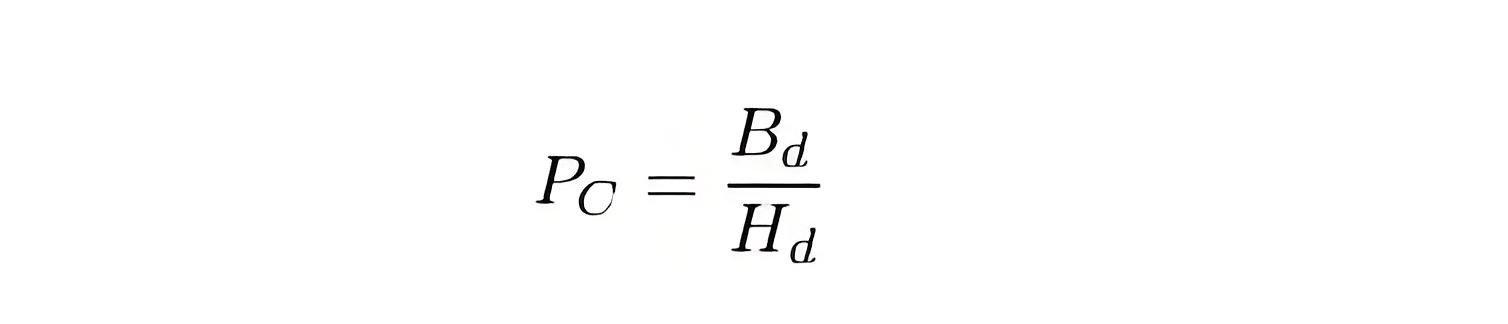
The Magnetic Permeability is calculated by dividing the magnetic flux by the product of the number of ampere-turns and the magnetic path length to show its dependence on the magnetic flux and path.
Analogy with conductance
The Permeability in a magnetic circuit is similar to the conductivity in an electrical circuit and measures the degree to which a material allows magnetic flux to flow.
A unit of Permeability
The unit of Permeability is Weber per ampere-turns (Wb/AT) or Henry.
Permeability
The Permeability coefficient is the ratio of the flux density to the strength of the magnetic field and represents the operating point of the magnet on the B-H curve.
Magnetic Permeability calculation formula
Interpolation formula
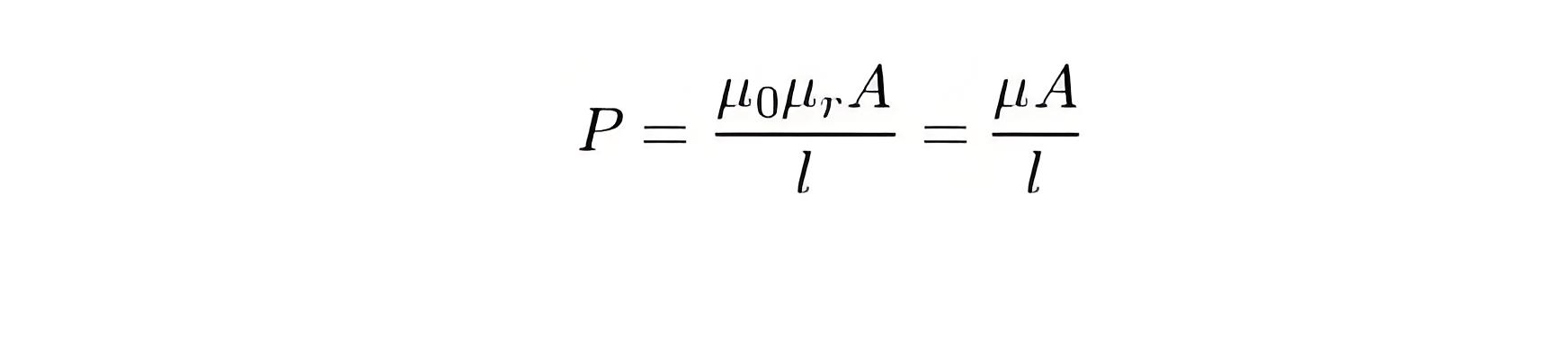
u0= Free space permeability (vacuum)
ur= relative permeability of a magnetic material
l= Length of magnetic circuit (in meters)
A= cross-sectional area (square meters)
Magnetic Leakage Coefficient
The ratio of magnetic flux density to magnetic field strength at the working slope of the B-H curve.
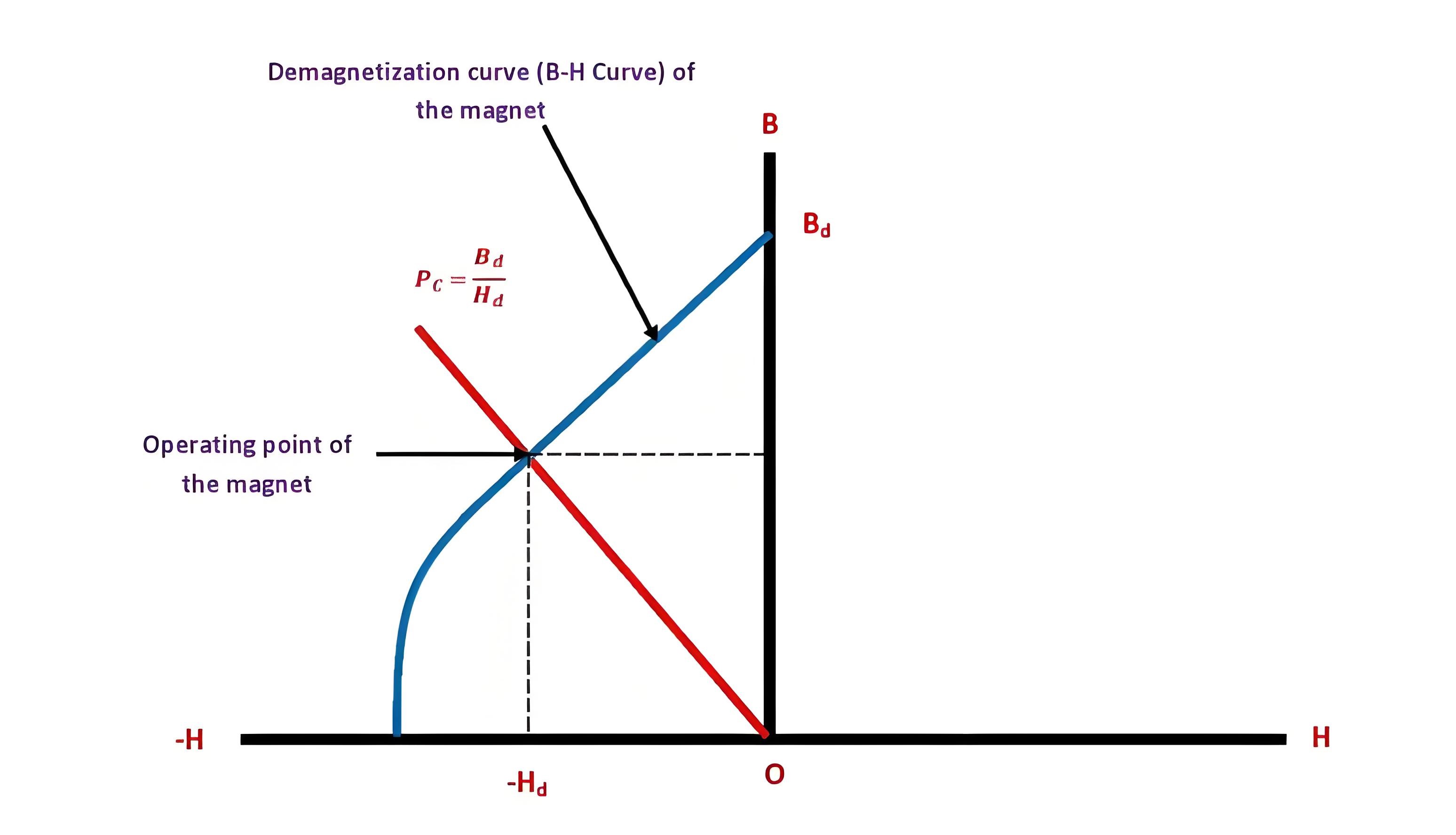
The relationship between permeability and magnetic leakage coefficient
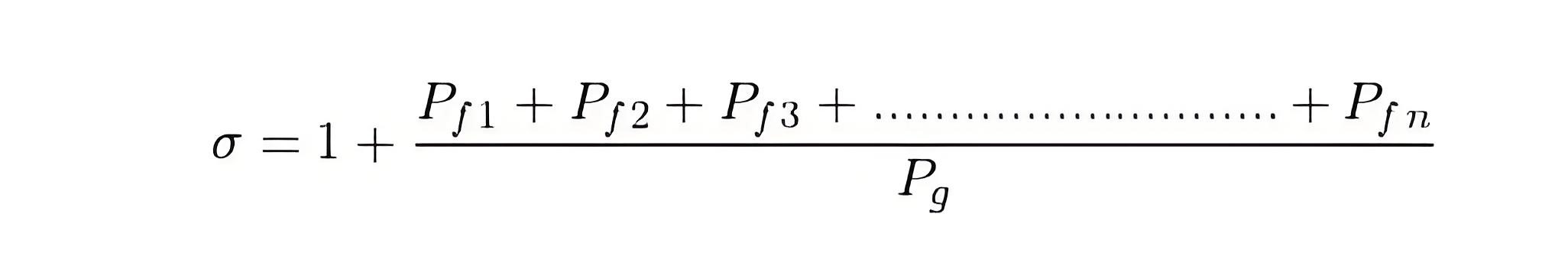
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













