What is the Meissner Effect ?
What is the Meissner Effect ?
Meissner Effect Definition
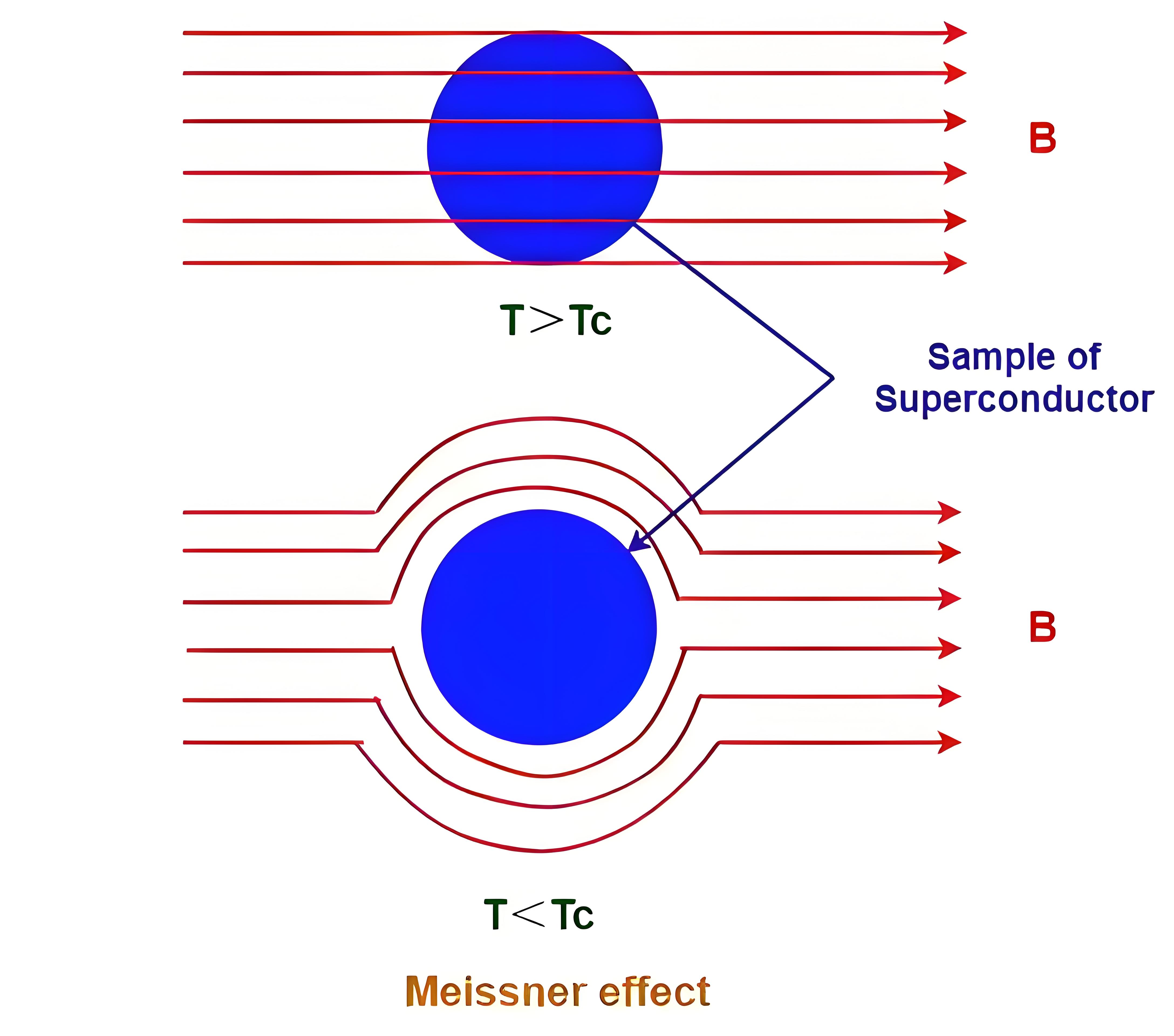
The Meissner effect is defined as the expulsion of magnetic fields from a superconductor when it is cooled below its critical temperature.
Discovery and Experiment
German physicists Walther Meissner and Robert Ochsenfeld discovered the Meissner effect in 1933 through experiments with tin and lead samples.
Meissner State
The Meissner state occurs when a superconductor expels external magnetic fields, creating a state with zero magnetic field inside.
Critical Magnetic Field
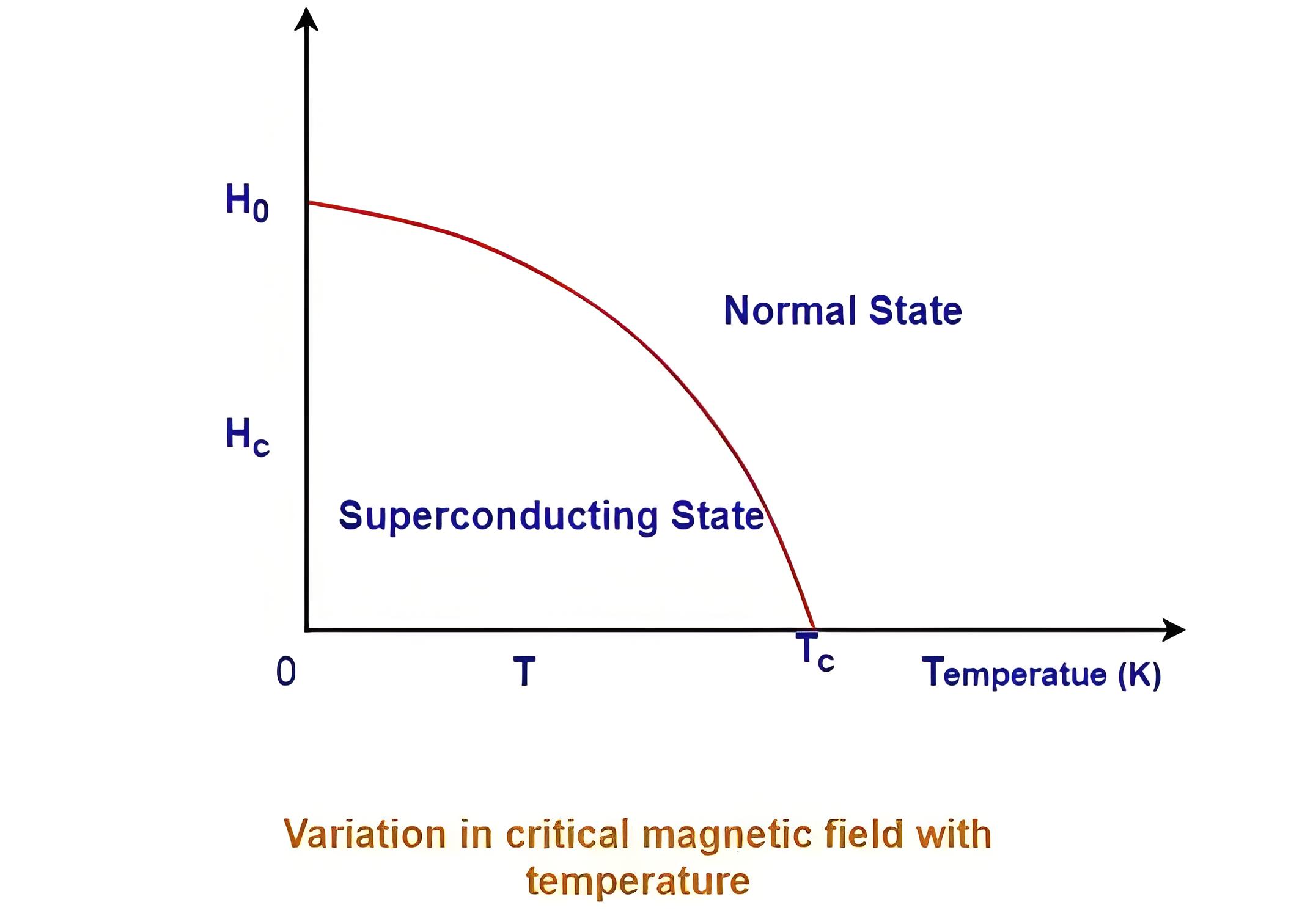
A superconductor returns to its normal state if the magnetic field exceeds the critical magnetic field, which varies with temperature.
Application of Meissner Effect
The application of the Meissner effect in magnetic levitation is crucial for high-speed bullet trains, allowing them to float above tracks and reduce friction.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













