What is an IGBT?
What is an IGBT?
IGBT Definition
An Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) is defined as a semiconductor device that combines the advantages of Power MOSFETs and Power BJTs.
Structure
The IGBT structure includes an additional p+ injection layer, which enhances its performance compared to PMOSFETs.
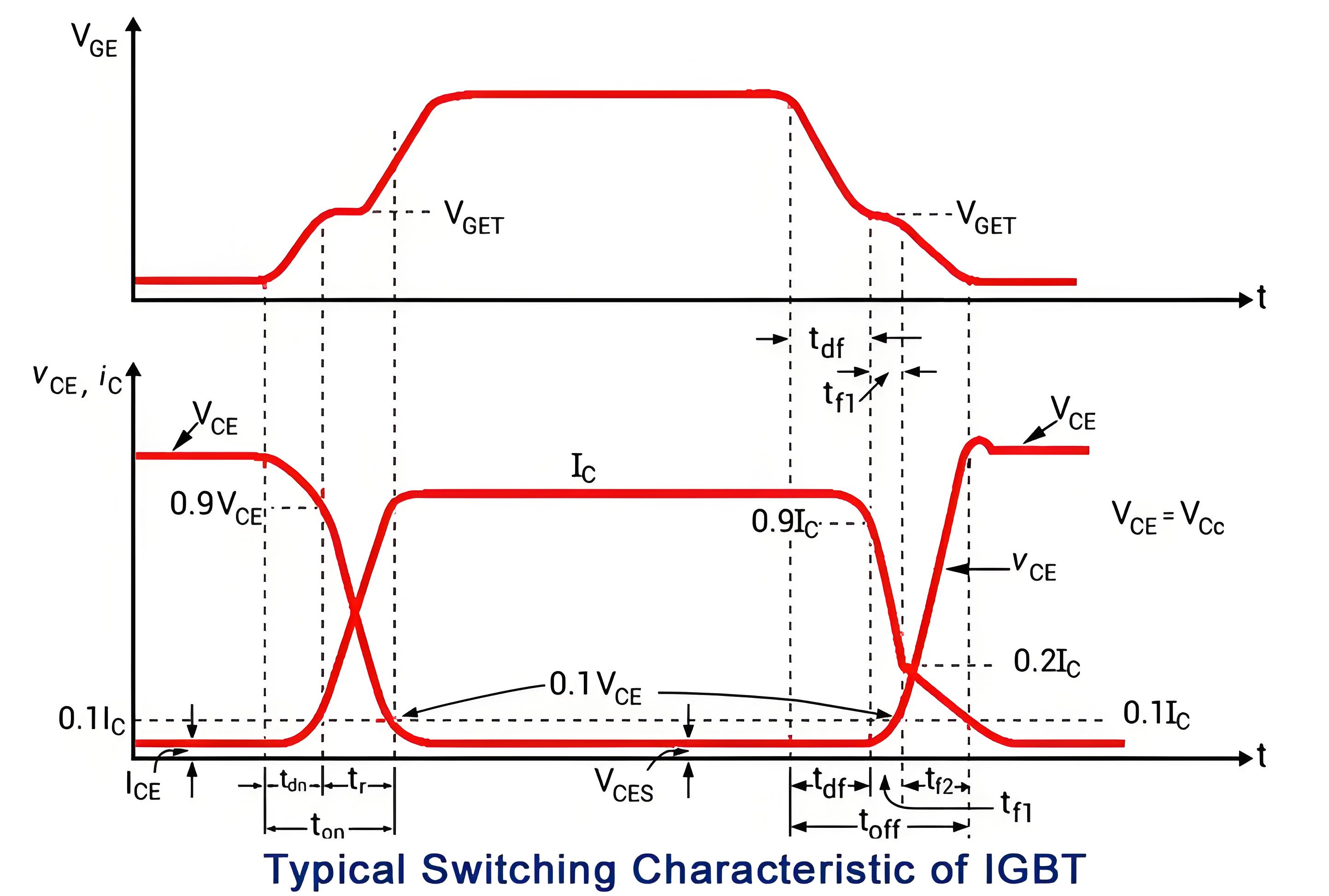
Switching Characteristics of IGBT
IGBT switching involves distinct turn-on and turn-off times, with specific delay and rise/fall times affecting performance.
Latching Up
Latching up occurs when the IGBT stays on even after the gate voltage is reduced, requiring special commutation circuits to turn it off.
Advantages
Lower gate drive requirements
Low switching losses
Small snubber circuitry requirements
High input impedance
Voltage controlled device
Temperature coefficient of ON state resistance is positive and less than PMOSFET, hence less On-state voltage drop and power loss.
Enhanced conduction due to bipolar nature
Better Safe Operating Area
Disadvantages
Cost
Latching-up problem
High turn off time compared to PMOSFET
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













