What is Moore’s Law ?
What is Moore's Law ?
Moore’s Law Definition
Moore’s Law is defined as the observation that the number of transistors in an integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years.
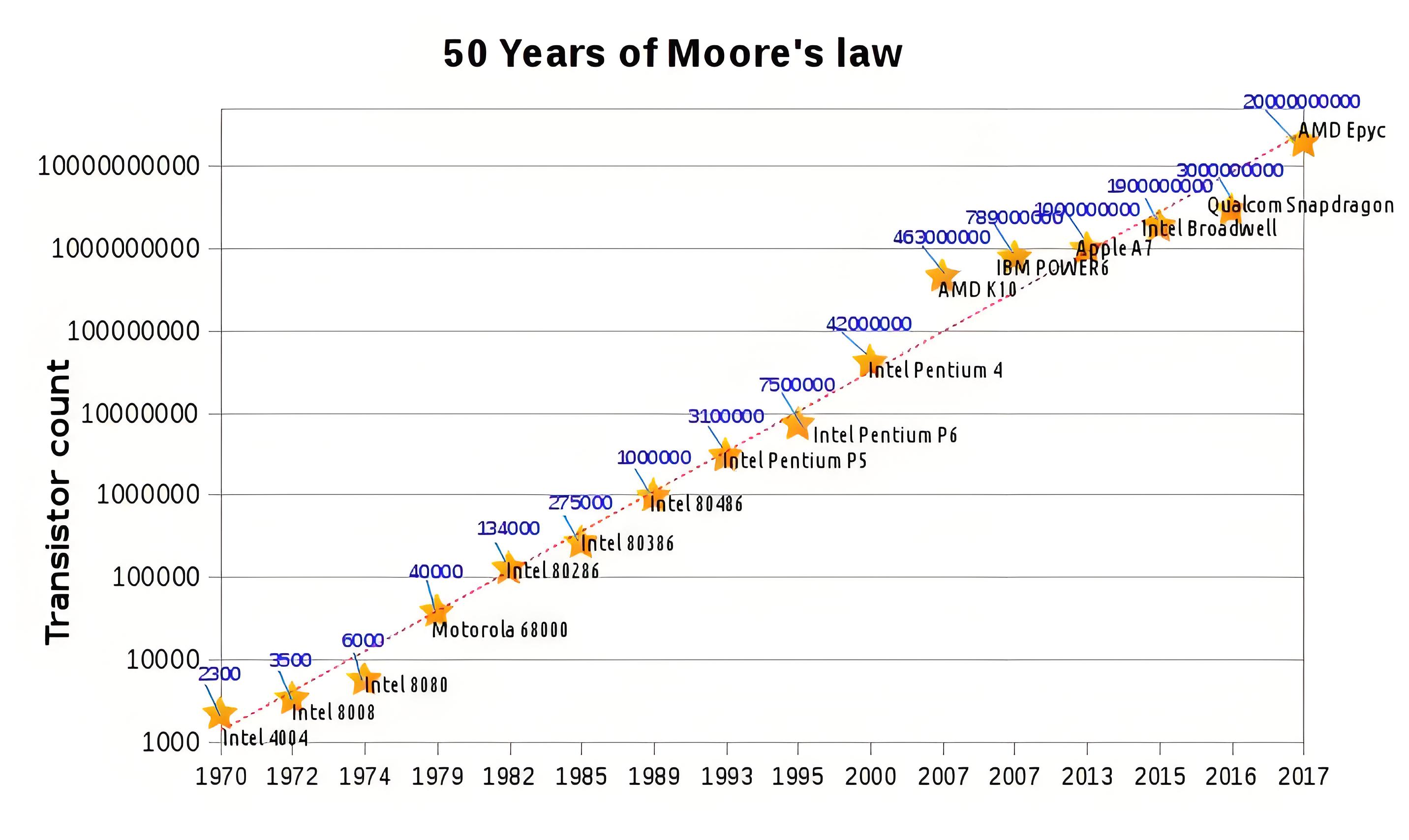
Historical Impact
Moore’s Law has significantly driven the advancement of technology, affecting various devices and industries.
Technological Contributions
Innovations like the transistor, integrated circuits, CMOS, and DRAM have enabled Moore’s Law.
Current State
The industry has shifted focus from Moore’s Law to developing chips based on needs and applications rather than just size scaling.
Economic Perspective
Moore’s Second Law highlights the rising costs of semiconductor fabrication, doubling every four years.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













